Elasticsearch Query DSLQuery DSL stands for Domain Specific Language. In elasticsearch, searching is performed using the search query, which is based on JSON. Elasticsearch provides full query DSL that helps to define queries. There are two clauses in elasticsearch that make a query, which are - 1. Leaf Query Clauses - Leaf query clauses are those clauses that search for a specific value in a specific field like term, match, or range queries. These queries are used by themselves. 2. Compound Query Clauses - Compound Query is a wrapper clause created by combining leaf query clauses and other compound queries. It helps to extract the desired information. A query begins with a query keyword. It contains conditions and filters inside it in the form of JSON objects. A list of several queries with examples are described below - Match All QueryIt is a basic query that returns all the documents present in the specified index. It returns all data of the document with a max_score 1.0 for every object. See the example given below - Copy Code Response The above query will fetch all the documents presents in the book index and return back to the user. See the response below - Screenshot Look at the screenshot below in browser - 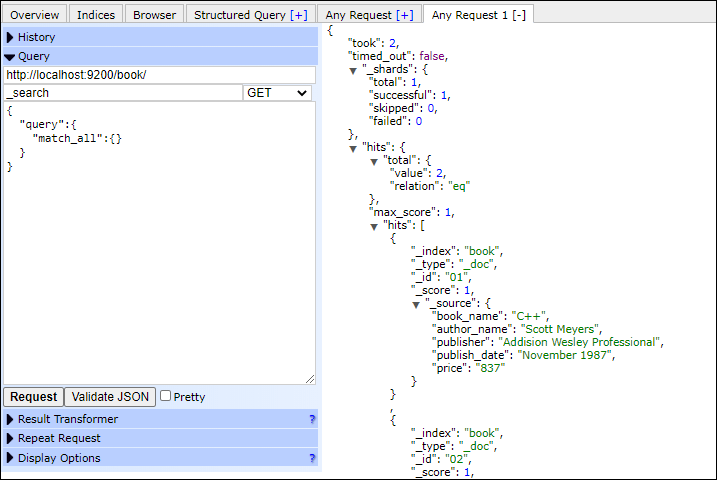
Full Text QueryFull text queries are high-level queries. These are responsible for running full text queries on full text fields and understanding how a field being queried is analyzed. Full text query work according to the analyzer associated with the specific document or index. We will discuss a different number of full text queries.
Let's discuss each full text query one by one - Match QueryThis query helps to fetch the documents by matching a text with the value of one or more fields. In the below example, we will execute a query to fetch the documents that contain Hauston state in state field. Note that it will search these documents in all those indexes that contain student word at the end of index name. For example - student, student1, student2, etc. Copy Code Response By executing the above query, two documents have returned from index student and student1. See the output given below - Screenshot 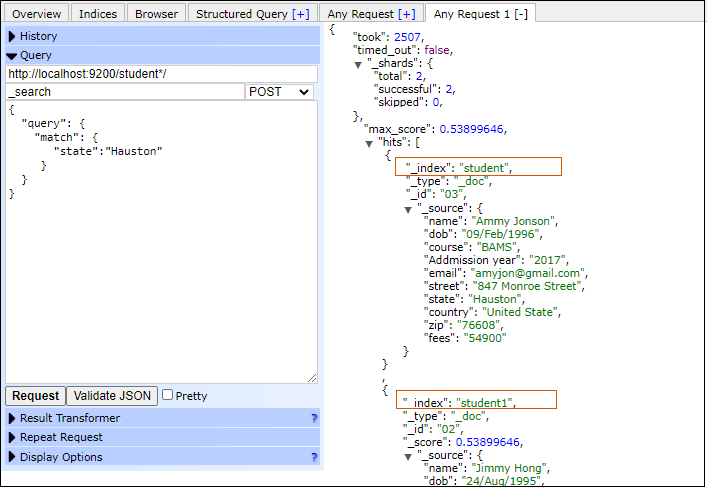
Multi Match QueryThis query allows us to search the documents by matching a text or phrase in more than one field. In the below example, we will search for the documents that contain Rodney either in street, state or in both. Copy Code Response By executing the above query, we get three documents, two from student index and another one from the student1 index. See the output given below - Screenshot 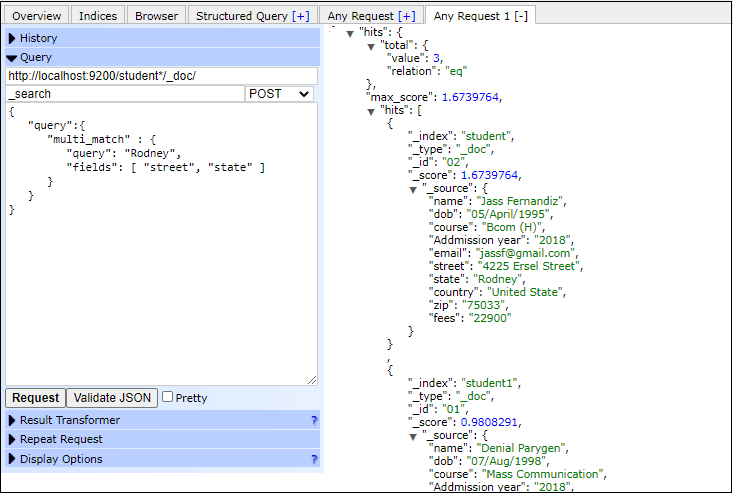
Query String QueryThis query allows us to fetch the documents whose any of the field contains the text passed to query string. In the below example, we will pass a string "Horse riding" to search the documents in the student* indexes and display all the documents matched. Copy Code Response By executing the above query, we get two documents, one from student index and another from the student1 index. See the output given below - Screenshot Look in the below screenshot, two documents are fetched from the database that contains Horse Riding string in the Hobbies field. 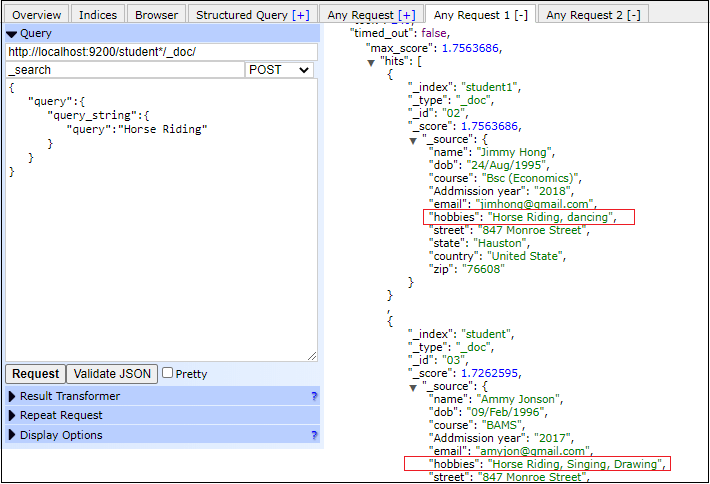
Term Level QueryThe term level query deals with structured data rather than full text field search. Structure data like number, dates, and enums, etc. See the given example of term level query - Copy Code Response By executing the above query, we will get all the documents that have zip code 76011. Screenshot 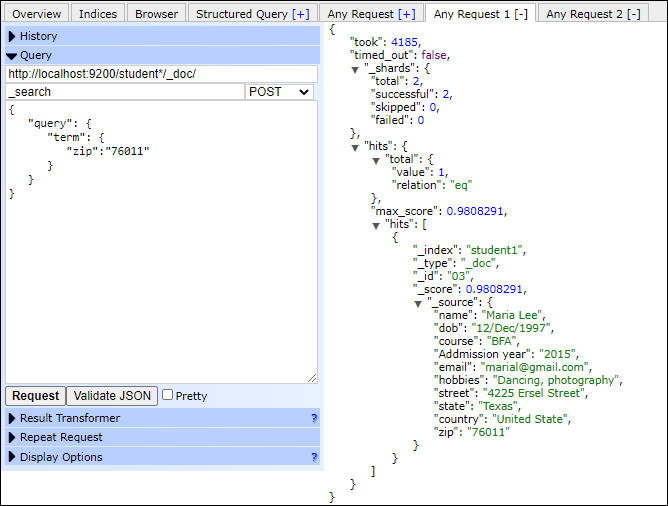
Range QueryThe range query allows us to search the documents that have values between the specified range. To perform the range query, we need to use some operators, such as -
By putting any of this condition, we can classify the data for the given range in that condition. See the example given below - Copy Code Response By executing the above query, two documents are fetched from the student index where fees is greater than 50000 as we used gt condition. See the response given below - Similarly, we can use other conditions gte, lt, or lte as needed to classify document and fetch them. Screenshot 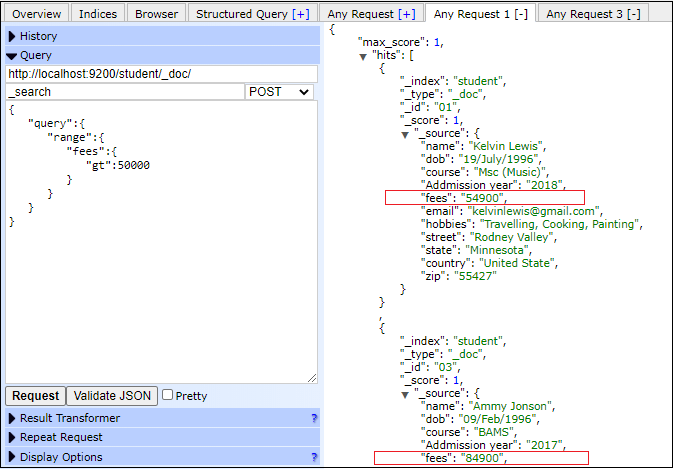
Other types of term level queriesBelow some term level queries are as follows -
Type QueryThe type query us allows to find the document of a specific type (default is _doc) specified by the user in the query. In elasticsearch, the default document type is _doc, but document type can also be user-defined. If the documents are present of the particular type specified in query, it returns those documents list, otherwise it will return a null value. For example - Copy Code Response By executing the above query, several documents of _docs type from the multiple indexes such as - book, student, new_student, and student1 (which we have created) have returned. See the output below - Screenshot In the below screenshot, you can see that the documents returned from the book and student indexes are _doc type, as mentioned in query for search. 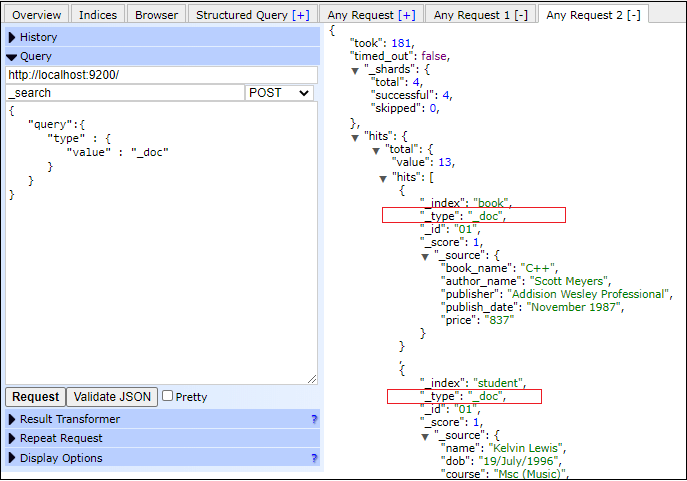
Now, turn to the compound queries, which we discussed in brief earlier. Here, we will elaborate compound queries in detail with example. Compound QueryAs the name defines, compound query is a collection of different queries. These queries are merged together using the Boolean operator such as AND, OR, NOT, or for several indices or having function calls. It is responsible for wrapping leaf queries and other queries together. Basically, these queries are used for either combining their results, changing their behaviors, or switching from query to filter context. Let's take an example to understand the compound query given below - Copy Code Response The above query has returned 0 document and have max_socre null and total value as zero. See the response given below - Screenshot 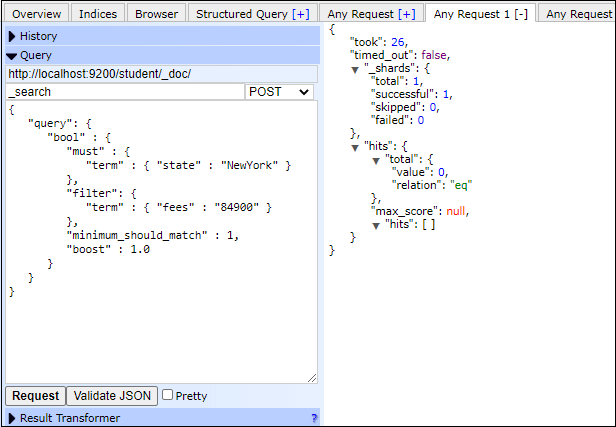
Geo QueryThe Geo queries deal with geo point and geo location. It helps to find the school or any geographical object near to any location. For this, we need to use the geo point data type like the location of a place. Remember that, there are two types of geo data (geo_point and geo_shape) supported by elasticsearch that are - geo_point - geo_points are the field that supports lon/lat pairs. geo_shape - Similar to geo_points, geo_shape are also fields that support points, lines, circles, polygons, and multi-polygons, etc. Look at the example given below - Copy Code Execute the below query to create an index named geo_query_example with mapping and location. Response By executing the above code, an index with a geo_query_example name has created. See the response given below - Screenshot 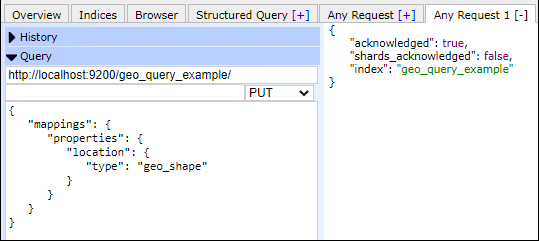
Add data to index Now, add the following data into the geo_query_example index created above. Response By executing the above code, data is added successfully in the geo_query_example index. See the response given below - Screenshot 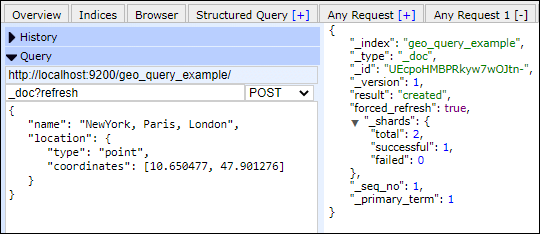
Next TopicElasticsearch Analysis
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










