English SentenceA sentence is a group of words that collectively have a meaning. A sentence is the fundamental unit of language that expresses a whole notion. It accomplishes this by adhering to the fundamental grammatical principles of syntax. "Ali is walking," for instance, is a simple English sentence. 
Also, to state (declare) a coherent thought, a complete sentence must include at least a subject and a major verb. A brief example: He dances. She walks. The subject is the noun that performs the primary verb. The primary verb is the verb used by the subject. The initial word of a written sentence in English and many other languages is capitalized. Based on the fact that the sentence is a statement, request, inquiry, exclamation, or a command, there is a punctuation mark at the conclusion. In general, a sentence is a word or collection of words that represents a complete notion by making a statement/order, posing a question, or proclaiming. Example:
A sentence should have at minimum one subject and one verb. The subject of a sentence can be buried at times, but the verb should always be apparent and present in the sentence. The verb is referred to as the sentence's core. Example: Do this. (The subject 'you' is concealed in this statement, but the verb 'do' is viewable.) Definition of Sentence"[A sentence] is a sequence of words, usually beginning with a capital letter, that conveys a notion in the shape of a statement, inquiry, direction, or exclamation." Characteristics of A SentenceIn other terms, a complete English sentence must contain three elements:
Sentence structure is the arrangement of all the portions of a sentence. To create more sophisticated and fascinating sentences, you must first learn how sentence structure functions. The guidelines for all sorts of sentence structures are explained below so that you can communicate properly, precisely, and confidently. But, before we get into the specifics, let's go through the fundamentals again. 
Sentence Structure Fundamentals in EnglishThe following statements concerning sentences in English are correct :
Basic Parts of A SentenceA verb and a subject are required in every phrase; a verb is an action, and a subject is a noun that performs the action. I'm sitting . The verb, in this case, is 'am sitting.' 'Sit' is the main verb, but in the present continual, we use the -ing form and affix the auxiliary verb am. So the subject is I, the person who sits. Imperative sentences (commands) are an exception to the rule because they only require a verb. We can presume that the subject is the individual to whom the speaker is speaking. Start ! Stop ! This one word constitutes an entire sentence. The verb is 'start,' and there is no need for a subject since it is a command. Some sentences may include objects, which are nouns that take part in the activity. Assume you misplaced your chart and ask a buddy to give you one. My friend provides me with his chart . In this instance, provides is the verb, and my friend is the subject because they are the one who provides. A word chart is a direct object, which is the noun that obtains the action. The immediate object in this situation is the item being provided-a chart. The noun that obtains the direct object is known as the indirect object. In the preceding example, the indirect object is 'myself' because I am the one who gets the chart. Indirect objects are those that come in between the verb as well as the direct object. Have you ever noticed how the subject employs the pronoun I while the objects utilize the pronoun me? There are differences between subject and object pronouns, so make absolutely sure you are using the correct one. Only a subset of verbs known as transitive verbs can employ direct and indirect objects. However, because transitive verbs are so prevalent, you'll be utilizing them a lot. Consider another example. Carr throws Neymar the football . Can you name the verb, subject, and direct and indirect object ? The verb is 'throws' since it is the action in the statement . Carr is the subject since he is the one who throws . The football is the direct object since it is the thing being thrown . Neymar is the indirect object since he obtains the football . There Are Four Types Of Sentence StructureYou can generate four various forms of sentence structure based on how you join clauses:
Sentences are also classified according to their functionality, which can be declarative, interrogative, exclamatory, or imperative. These are distinct from sentence structure kinds (complex, compound, etc.), and the two can be combined and matched. Let's look more closely at each kind of sentence structure and how to create it. Sentences that are simple Simple sentences consist of a single independent clause, not more or not less. Subjects and verbs are included, but objects might also be included . Childhood is the most fantastic fairy tale . True splendor is born of the silent conquering of oneself . 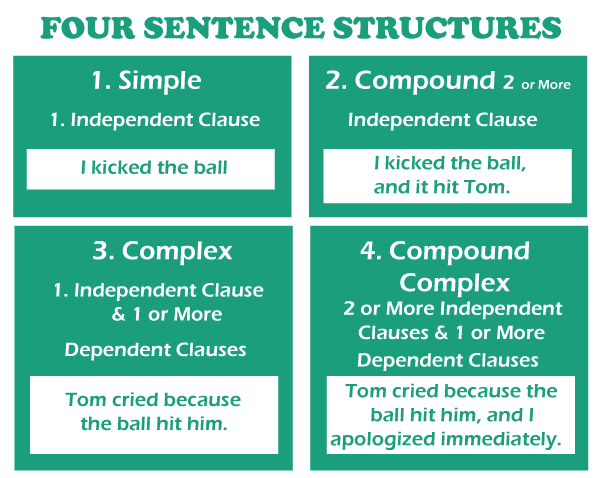
Compound SentencesA compound sentence is a sentence that combines two or more separate clauses into a single sentence. There are two ways to join the separate clauses: Between the sentences, are using a comma and a coordinating conjunction (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, and so, abbreviated as FANBOYS) . A semicolon is used between the clauses . At first, it may appear challenging, but everything is hard . Be oneself; everybody else has stolen you . Complex SentencesA complex sentence contains one major independent clause and one or more subordinate clauses. Whereas compound sentences employ coordinating conjunctions to connect clauses, complex sentences utilize subordinating conjunctions, as stated previously. Use a comma well before the independent clause if the subordinating clause appears before. If the independent clause appears first, there is no need for a comma. Every narrative will laud the hunters until the tiger learns to write. Whenever a person is unable to find a deep feeling of meaning, they turn to pleasure. Sentences with compound-complexity Compound-Complex SentencesAs the name implies, integrate compound sentences with complicated sentences. They must have at least two separate clauses and one subordinating clause. To unite them, obey the grammar rules for each; make sure you're utilizing your coordinating and subordinating conjunctions correctly. "If you are going to be insane, you must be compensated for it, or you'll be put in jail." "If you desire success, don't seek for it; simply do what you like and trust in, and it will happen easily." Sentences serve various functions: The most common sort of sentence is a declarative statement, sometimes known as a declaration. It conveys a message. It concludes with a complete stop. (The kitty is cute.) An interrogative statement, often known as a query, asks something. It concludes with a question mark '?' (Are you satisfied?) An exclamatory statement, or exclamation, says something unusual. It concludes with an exclamation point! (That is the most joyful dog I have seen in a while!) An imperative statement, often known as a command, instructs someone to perform a task. (Pass the fish to the cat.) Grammar Rules for Sentence PartsYou're probably aware that a proper sentence, also referred to as an independent clause, can stand alone. But what makes a sentence comprehensive, and how do sentence components interact? You'll rarely mix up sentences again after you've figured out the rules. Subjects Are CriticalEvery sentence should comprise a subject: the person, location, animal, thing, or idea doing the activity described in the sentence. As an example:
Predicates Manifest ActionThe remaining sentence is known as the predicate . It conveys the subject's action or gives further information about the subject. For instance;
Subjects and Predicates Must Be In AgreementSome of the most fundamental and crucial English grammar rules concern subject-verb agreement, which states that a singular subject requires a singular predicate (and a plural subject should include a plural predicate). For instance: This novel is filled with mystery and suspense. (The single subject of this sentence is 'novel', and the singular verb is 'is'. ) Seal and Beth appear ecstatic to embark on this new adventure. (The plural subjects Seal and Beth, as well as the plural verb, is 'appear' .) Use the Proper Sentence TypeWe utilize punctuation to develop what a sentence is attempting to accomplish, but verbs must also contribute. Make sure you're using the proper sentence type; there are 4 to pick from.
Capitalization and Punctuation GuidelinesThe punctuation that segregates one complete sentence from the next complete sentence determines the quality of the sentence. Understanding capitalization and punctuation rules help to make your writing simpler to read - whereas there are very few who remember, they're fairly simple. Capitalization Is CriticalEvery sentence must begin with a capital letter. Proper nouns (such as names of individuals, names of location, the majority of words in a title, organizations, days each week, holidays, the first word of a statement within quotation marks, etc.) are also typically capitalized. As an example:
Direct Objects Disseminate InformationWhenever direct objects are used, the reader gains a better understanding of the sentence. As an example:
Objects That Are Indirect Obtain Direct Object ActionThe action that direct objects obtain from verbs is passed on to indirect objects. As an example:
Every Sentence Necessitates The Use Of Terminal Punctuation.Put a terminal punctuation mark at the conclusion of your sentence. A period, exclamation mark, or question mark are examples of these. As an example: Give me your funds . I told her to flee ! Can you think of that woman's boldness ? Colons And Semicolons Cannot Be Used InterchangeablyIt appears that colons and semicolons work in a similar way - but they don't. When composing a list of items, trying to introduce a long, direct quote, or trying to separate two clauses whenever the second one explains the first, use a colon. As an example: In my backpack, I have: Shirts, chino pants, leather shoes, and body wash. According to the poet: "Miracle does exist. Who could doubt it when there are unicorns and flowers, wind music and starry silence? " She had all she needed: buddies who wouldn't fail her . A semicolon is only required when linking two independent clauses (rather than coordinating conjunction) or while separating items in a list that already contains commas. As an example:
Commas Serve Specific FunctionsIt can be challenging to retain all the comma rules. Commas are used to differentiate parts of a sentence, whether these are items in a series or clauses and phrases in a statement. As an example:
Parentheses Provide Additional InformationTo encircle words that clearly define other parts of a sentence, use parentheses. They include details that aren't necessary to the main point, so they're full of supplementary (but intriguing) information. As an example:
Only Apostrophes Denote Missing Letters And Ownership.People adore apostrophes, although they have just two functions: indicating when letters are absent in contractions and indicating a noun's possession. As an example:
You're a magnificent banner . Common Sentence ErrorsBelow are some of the most popular sentence problems and expert tips on how to fix them to assist you in improving your sentences. 1. Run-onsRun-on sentences, also referred to as "fusion sentences," arise when clauses are smashed together without the required connecting words. To correct a run-on sentence, simply use the appropriate conjunctions. If the sentence remains difficult or overly long, consider dividing it into two or more statements. 2. Sentence FragmentsSentence fragments exist when a statement is incomplete, such as when it has a missing subject or verb or is a subjugating or subordinate phrase on its own. To repair a sentence fragment, simply determine what is absent and replace it. Check that your statement has a subject and a verb (until it's an imperative sentence), and if it's a subordinate clause, try connecting it to a relevant independent clause. 3. Verb-Subject AgreementIf the subject is single in English, the verb must always be singular as well; if the subject is plural, the verb should likewise be plural. In most circumstances, simply adding or removing the plural s will correct this and result in subject-verb agreement. The issue is that this inaccuracy can be difficult to detect at times. Using plural words to describe one subject is a common instance of this. Example: A combination of effort, passion, and tears culminates in success. The subject is mixing, and the verb is culminating, both of which are single. Don't be deceived by "additional" words like effort, passion, and tears-while they are plural; they do not render the subject plural. 4. Prepositions At The EndPeople frequently tell you that ending a sentence with a preposition is incorrect, although this is not totally true. It's discouraged in formal writing, such as school notes, but it's normally entirely acceptable-and sometimes even desirable. For beginners, prepositions always require an object; ending a phrase with an objectless preposition risks appearing ambiguous. If you wrote, "The crow flew beyond," your readers might question, "Beyond what?" It's also important to note that phrasal verbs frequently include prepositions . For example, Five enthusiastic puppies are nearly too many to bear. This sentence is acceptable since the phrase still includes an object, despite the fact that the object comes initially. Phrasal verbs are likewise disapproved upon in formal writing, so don't use them at the end-or start-of a formal statement. 5. The Passive VoiceAlthough not precisely a grammatical mistake, passive voice indicates weak writing. The subject of a clause obtains the action in a passive voice. The main verb is represented by a participle and a form of "to be." Example: A football was thrown by the player . Consider the following sentiment written in the active voice . For instance, The player threw the football . It's not only shorter but also more direct and simpler to understand. Active voice also sounds better, resulting in more dynamic and vivid text. In most circumstances, switching from passive to active voice improves the clarity of your writing. 6. Subordinate Clauses Should Be Used Sparingly.Subordinate clauses start with words like "because" or "although" and offer the audience useful (but not required) information. Sentences with excessive subordination can feel sluggish and include more detail than the reader can handle. To correct this, divide the statement into 2-3 smaller, clear and comprehensive sentences. 7. Use A Conjunction To Correct A Comma SpliceTo correct comma splices, utilize conjunction between sentences. A comma splice happens when two independent clauses are connected by a comma. Replace the comma with periods (or other ending punctuation) to split the sentences that were previously connected by a comma splice. Fix a comma splice by inserting conjunction between the two phrases.
Next TopicTypes of Sentences
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










