What is the full form of the EUEU: European UnionEU stands for European Union. The European Union is a set of political and economic cooperation of 27 countries. Many consideration factors make these countries look like a union in the world. 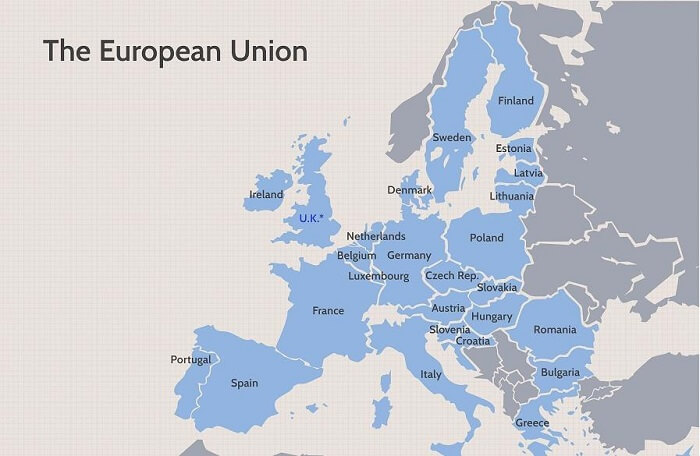
What are the objectives of the EU or European Union?The European Union is an international organization which was started with a motto. The following are the objectives of the European Union:
What are the reasons for the formulation of the EU or European Union?It was seen that after the Second World War, the coming together of the many European countries was the remedy to the nationalism which had destructed the continent. It was at the University of Zurich in 1946 that the former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom backed the creation of the United States of Europe. Further moving on, the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) was created in 1952 under the Treaty of Paris. It had six countries that made coal and steel production units as a common market. The countries included the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Italy, Germany, France and Belgium. In the same year, the European Court of Justice got established under the same treaty. Till 2009, it was known as the Court of Justice of the European Communities. 
Further, in 1957, through the Euratom Treaty, an organization named European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC) was established to create a particular market for nuclear power in Europe. At present, it has the same members as the European Union. Then, it was in 1957, the Treaty of Rome led to the formation of the European Economic Community (EEC). The sole purpose of this community was to bring about economic integration with a common market and customs union among its six founding members. Its existence ceased in 2007 with the Lisbon Treaty and included its activities in the European Union. The major turning point occurred in 1965 in Brussels, where the merger agreement was reached. It was finalized to merge the three other organizations of the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC), and European Economic Community (EEC) into one institute named the European Communities (ECs). It was when the Schengen Agreement got effective in 1995, ten years of its formation in 1985, that it led the way toward open borders. Through this agreement, there was no control over the passport to travel in most member states. Then the Single European Act of 1986 by the European Community led to an economic merger and formation of a common European currency, foreign policy and domestic policies. Later, there came the turning point that led to the establishment of the European Union as it is now. The Maastricht Treaty was signed in the year 1992. This treaty was also known as the Treaty of the European Union and was given a forward jerk by the end of the Cold War. The following are the effects of this treaty -
Organizations within the European UnionSeveral institutions are used to carry out the governance of the European Union. These organisations include the European Central Bank, the European Commission, the European Parliament, the Council of the European Union, the European Council, and the European Court of Justice. The EU's executive branch is known as the European Commission. It is in charge of drafting and executing EU legislation, overseeing the EU budget, and speaking on behalf of the EU abroad. One commissioner represents every participant state on the European Commission, which is presided over by its president. The EU is governed by the European Parliament. It is responsible for approving the EU budget, adopting laws, and controlling the European Commission. The 705 members of the European Parliament are chosen by the citizens of the EU member states. The primary EU body responsible for making decisions is the Council. It is in charge of establishing EU legislation, coordinating EU policies, and negotiating foreign agreements on behalf of the EU. This body is made up of ministers from the national governments of the EU's member states. The heads of state or government of the EU member states are present in the European Council, along with the presidents of the European Council and the European Commission. The European Council establishes the overall course and priorities for the EU. The management of the euro and preservation of the eurozone's price stability is within the purview of the European Central Bank. It establishes the monetary policy for the eurozone and undertakes financial market transactions to carry out that policy. The Court of Justice of the European Union is the legal arm of the EU. It offers legal guidance and ensures that EU legislation is administered uniformly throughout all member states. One judge from each member state makes up the Court of Justice, which is presided over by the Court of Justice President. European Union policiesThe policies of the European Union are extensive and address a variety of topics, including commerce, agriculture, energy, the environment, and social concerns. Among the most important EU policies are the following: Common Agricultural Strategy (CAP): The CAP is an EU strategy that supports farmers financially and encourages environmentally friendly farming practices. It guarantees inexpensive access to wholesome food for EU residents while safeguarding rural areas and the environment. A system of regulations known as the Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) controls fishing activities in EU waters and ensures the sustainability of fisheries. It encourages ethical fishing methods and helps coastal communities maintain their way of life. Energy Policy: The EU's energy strategy strives to provide its population with a safe, cheap, and sustainable energy supply. In addition to guaranteeing the competitiveness of the EU's energy industry, it encourages the adoption of renewable energy sources and energy-saving techniques. Environment: The EU's environmental policy seeks to preserve the natural world and advance sustainable growth. It covers laws governing biodiversity, waste management, air and water quality, and climate change. Social Policy: The goal of the EU's social policy is to protect citizens' rights and promote social cohesion. It consists of social welfare, employment, education, and healthcare initiatives. The Future of the European UnionA number of obstacles that the European Union must overcome will determine its destiny. These difficulties include: Brexit: Since the UK decided to leave the EU, there have been doubts regarding the EU's future and its ties to the UK. The result of the trade discussions between the EU and the UK will have enormous repercussions for the future of the EU. Migration: With numerous refugees and migrants coming to Europe from Africa and the Middle East, the EU is currently experiencing a migration crisis. As a result, there is increased pressure on EU member states to agree on a strategy for handling migration and refugees. Economic Challenges: The EU is dealing with financial difficulties, such as high debt levels in some of its members and slow economic development. The EU is taking steps to address these issues, including structural reforms and investments in education and innovation. Increasing Populism: Concerns about the future of the EU and its democratic and human rights principles have been expressed as a result of the emergence of populist groups in various EU member states. By encouraging communication and collaboration among its member nations, the EU is attempting to allay these worries. ConclusionA distinctive political and economic union, the European Union has aided in fostering peace, stability, and prosperity throughout Europe. Throughout its history, it has had several difficulties, but it has always been able to get through them and go forward. The EU is now dealing with a lot of difficulties that will determine its future, but it has the resources and fortitude necessary to overcome these difficulties and come out on top. The EU's position as a global player will become more significant as the globe becomes more linked, and its ideals of democracy, human rights, and the rule of law will be more vital than ever.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










