Excel FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY functionWant to forecast your future data parameters quickly and perfectly? Kudos to Excel for introducing powerful inbuilt advanced functions and saving 80% time for you. One such function is Excel FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function. In this tutorial, you will discover the definition of FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function, its syntax, parameter, error type and reasons, and real-time examples to understand how this formula calculates the length of a recurring pattern in the specified timeline. What is FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function?"The FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function is an inbuilt function that calculates the length of a recurring pattern in a given timeline. This function is mostly used with FORECAST.ETS because both functions use the same algorithm to detect seasonality." In simple terms, the FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function is used to calculate the season length for numeric data such as sales, inventory, expenses, etc., displaying a seasonal pattern. If Excel cannot detect any pattern, the FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function returns zero. SyntaxParametersValues (required) - This argument signifies a range or array of historical data for which you want to predict future values. Timeline (required) - This parameter represents an array of dates/times or independent numeric values with a constant step between them. Data completion (optional) - This parameter accounts for missing points.
Aggregation (optional)- This parameter specifies how the algorithm should aggregate values that have the same timestamp. Since it is an optional parameter, it could be omitted as well. But if supplied, this parameter argument can be any integer between 1 and 7 indicating the following:
Note: It is better to perform aggregation before using FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY to make results as accurate as possible.ReturnThe Excel FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function returns the length in time of a seasonal pattern based on existing values and a timeline. Excel FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY not workingThe FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function will return errors as shown below:
ExamplesExample 1: Using the FORECAST.ETS. SEASONALITY function calculate the length of the seasonal trend.As you can see in the below table, we are given a monthly sales table for 2020, and based on the previous value. 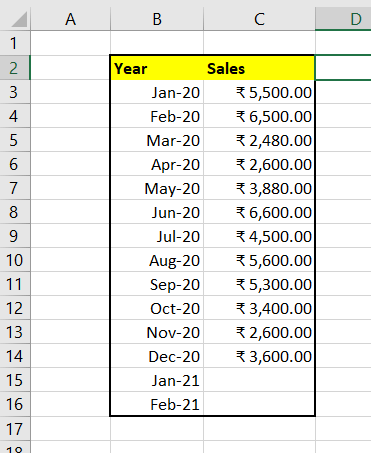
To compute the seasonal length of the predicted sales value using the Excel FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY () function follow the below-given steps: Step 1: Predict the sales using FORECAST.ETS The function FORECAST.ETS is tied with FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function because both the function use the same algorithm and it helps to predict the forecast accuracy. Therefore, we will predict the sales revenue for the 2 months and later using FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function will calculate the length of the seasonal trend. Use the below given formula to calculate the future values for the given data set. =FORECAST.ETS(B15,$C$3:$C$14,$B$3:$B$14,1,1,1) 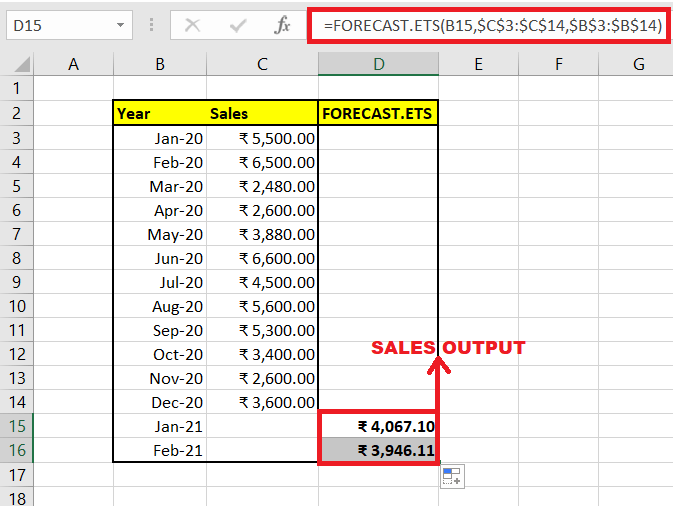
STEP 3: Select a cell Once we have predicted the sales output, next we will select a cell to compute the seasonal length for the given data. STEP 2: Type the FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function To compute the length of a recurring pattern in a given timeline, we will use the inbuilt FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY() function. Therefore, start typing the function with the equal to (=) symbol followed by the pre-defined FORECAST.ETS. SEASONALITY function. Our formula will become: =FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY( 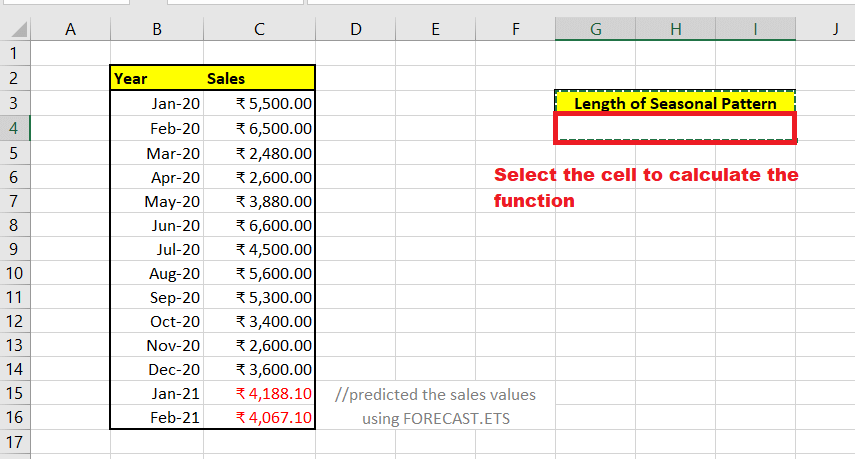
STEP 3: Supply the Parameters
Therefore, the overall formula becomes: =FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY($C$3:$C$16,$B$3:$B$16,1,1) 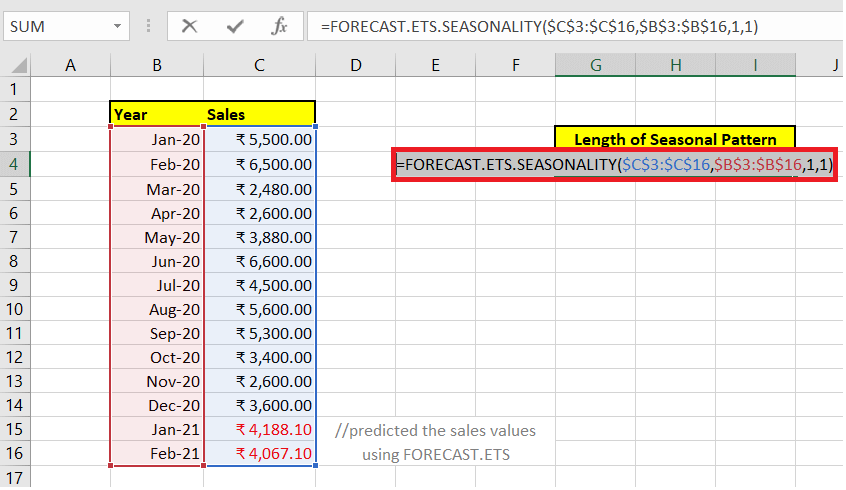
Step 4: The FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function will return the output As a result, the FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function will calculate the season length for numeric sales data. Since this function is not able to detect any pattern so it has returned zero. 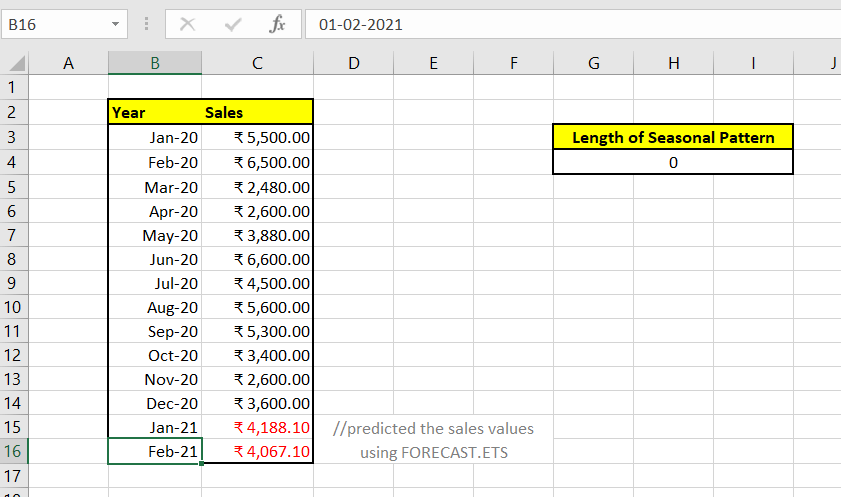
Next, we have predicted some more data values using the FORECAST.ETS function. Now, this function has returned a seasonal value of 7, since now it can detect the pattern of the predicted sales data. Refer to the below image: 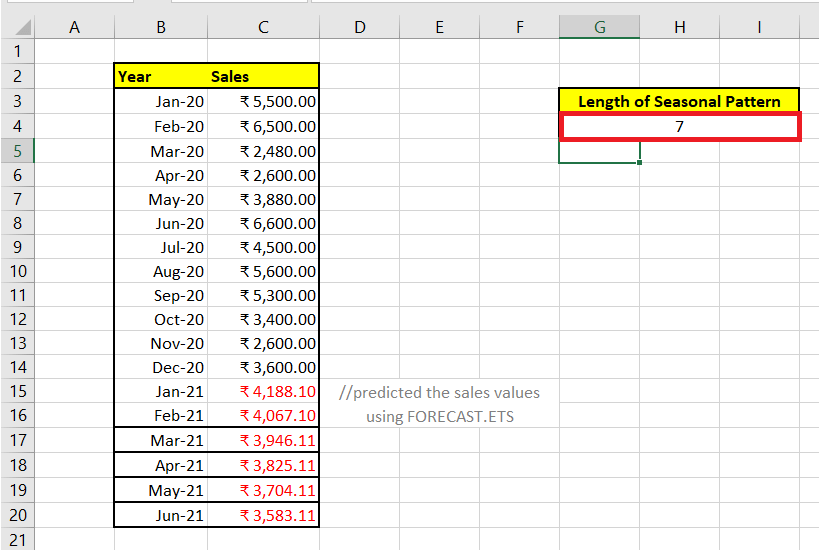
Next TopicGrowth Function in Excel
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










