Folic AcidFolic Acid or pteroylmonoglutamic acid is an organic compound. It is made of one pteridine nucleus, one molecule of para-aminobenzoic acid and one glutamic acid moiety. Some microorganisms need para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) for the synthesis of folic acid. Folic acid is a synthetic form of folate or vitamin B9 that is found in certain foods. So, it is a complex B vitamin which is also known as folate or vitamin B9. Folic acid gets its name from the Latin word folium which means "leaf", as it is commonly found in leafy plants. Folic Acid Formula and Structure:The chemical formula or molecular formula of folic acid is C19H19N7O6. Its molar mass is 441.40 gmol-1. The molecule of folic acid is formed by a chain of 6 members and it also has one aryl ring joined to a dihydropteridine ring. 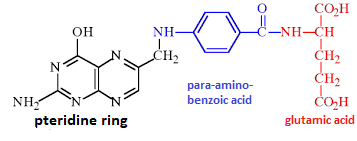
It consists of three large sub-components: pteridine ring, para-aminobenzoic acid, and glutamic acid. The pteridine ring is conjugated to para-aminobenzoic acid by a methylene bridge which is further joined to glutamic acid by a peptide bond. HistoryIn 1931, Lucy Wills discovered the nutritional benefits of folic acid for the first time when she was doing research on anemia in pregnant workers in Bombay, India. She treated patients with yeast and liver extracts. Later, in 1941, folic acid was first isolated from spinach and synthesized in pure crystalline form by Bob Stokstad in 1943. Physical properties of folic acid
Chemical properties of folic acid
Uses of folic acidFolic acid is naturally found in citrus fruits and dark green vegetables such as spinach, mustard leaves, etc. Folic acid plays a vital role in human health. Here are the following four important uses of folic acid: Pregnancy: Folic acid is very beneficial for expecting mothers. It promotes fetus growth and helps prevent birth defects. Its intake during pregnancy reduces the chances of neural tube defect, miscarriage, low birth weight, and premature baby or poor growth in the womb. For men: Folic acid is also beneficial for men. It helps in stabilizing the sperm count in men and thus increases the chances of conception. Skin benefits: Folic acid is also needed to maintain the health and beauty of the skin. It plays the role of an anti-ageing agent, antioxidant and moisturizer. It also helps in treating acne and dead skin cells. For hair: It is also good for the health and growth of hair. It improves blood circulation in the scalp. Its deficiency may lead to grey hair and hair loss. The other benefits of folic acid include improved digestion and heart health, reduces depression, and helps prevent diabetes, cancer, memory loss. Further, it helps in the treatment of various infections such as gum infections. Folic Acid Natural Sources
Difference between Folic Acid and FolateFolate is the natural form of vitamin B9 in food, whereas, the synthetic form of folate is called folic acid. So, the basic difference between them is that folic acid is the synthetic or artificial form of vitamin B9, whereas, folate is naturally found vitamin B9. Folic Acid Side EffectsNo serious side effects of taking too much folic acid have been found. However, in some cases, an upset stomach was seen as a side effect of folic acid. Folic acid is water soluble, so if someone takes more folate, it will be passed out through urine. Folic Acid Deficiency SymptomsThe deficiency of folic acid may cause a type of anemia called megaloblastic anemia. Further, its deficiency during pregnancy may increase the chances of congenital irregularities. Some common symptoms of folic acid deficiency are as follows:
The following groups are generally at higher risk of folic acid deficiency
Next TopicAcid Rain
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










