Fundamental of the Data StructureA data structure is a specialized format of data for arranging and storing data so that any user can easily access and worked within an appropriate data to run a program efficiently. Computer memory data can be organized logically or mathematically, and this process is known as a data structure. In general, selecting a particular format of data depends on two factors. The data must be rich enough to satisfy the real relationships of the data in the real world. And on the other hand, the data structure should be so simple that one can easily process the data when it needs to be used. Characteristics of data structuresFollowing are the characteristics of the data structures as follows:
Basic Operations of Data StructuresSome basic functions are chosen based on all types of data that occur in a data structure.
Needs of the data structuresData is a basic fact or entity information that is used to calculate or manipulate. Two types of data are used in a data structure, such as numerical data and alphanumeric data. These data structures specify the nature of the data item undergoing some function. Integers and floating points are types of numeric data types. The data can be single or a set of values that are organized in a particular fashion. The data organization leads to memory that creates a logical relationship between data items and makes it necessary to use data structures. Advantages of Data StructuresThere are some advantages of data structure:
Disadvantages of data structures
Following are the data structures and their uses are as follows: Array: An array data structure is a collection of elements of the same data type used to store data in contiguous memory locations. It has a fixed size collection of data elements that cannot be changed at runtime of a program. It is mostly used in a computer program to organize the data so that related items or values can be easily searched or sorted in a system. 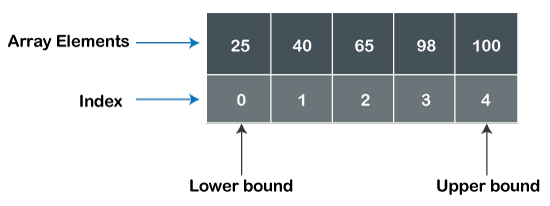
Linked List: It is a collection of data links called nodes where each node contains a data value and the address of the next link. All elements of the linked list are not stored in neighbouring memory locations. In simple words, it is a sequence of data nodes that connect through links. Each node of a list is consists of two items: the basic idea behind the uses of a linked list in a data structure is that each node within the structure includes a data part where we store values, and a pointer indicates the next node can be found. The linked list's starting point denotes the head of the list, and the endpoints represent the node's tail. 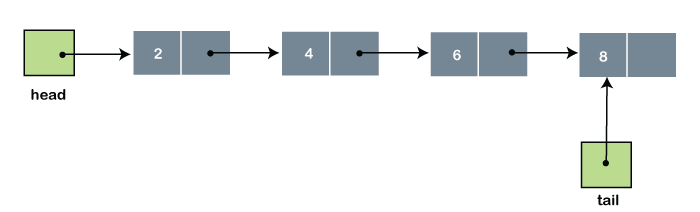
Stack: It is a linear data structure that enables the elements to be inserted and deleted from one end, called the Top of Stack (TOS). A stack data structure follows the last in first out (LIFO) operation to insert and remove an element from the stack list. It is an abstract data type with two possible operations to insert and delete elements in the stack: push and pop. A push operation is used in the stack to insert elements at the top of the list, hide those elements that already available in the list, or initialize the stack if it is empty. The pop operation is used in the stack data structure to delete a data item from the top of the list. 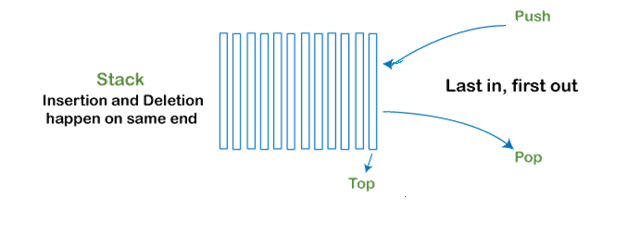
Queue: It is a linear data structure that enables the insertion at one end of the list, known as the rear, and the deletion of the elements occurred at another end of the list, called the front. It is a sequential collection of data elements based on the First in First out (FIFO) data structure, which means the first inserted elements in a queue will be removed first from the queue list. These queue operations are described below:

Graphs: A graph is a non- linear data structure consisting of finite sets of vertices (nodes) and edges to create an illustrated representation of a set of objects. These edges and nodes are connecting through any two nodes in the graph. The connected node can be represented as a directed or undirected graph. In a directed graph, each node is directly connected with edges in only one direction. In an undirected graph, each node is connected with edges in all directions. Hence it is also known as a bidirectional node. 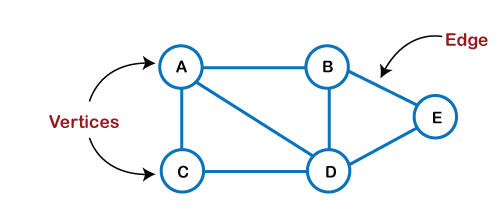
Trees: It is a type of non-linear data structure representing the hierarchical data. It is a finite set of elements where one of these nodes or elements is called a root node, and the remaining elements of a data structure consisting of a value called Subtrees. Every node of the tree maintains the parent-child relationship, where only one parent node and the remaining node in the tree is the child node. A node can have multiple child nodes but has a single parent node. There are some types of trees, such as a binary tree, binary search tree, expression trees, AVL tree and B trees. 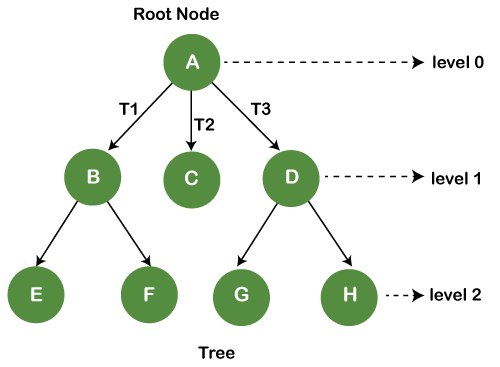
Heap: A heap data structure is a special type of complete binary tree that satisfies the heap property and arranged the elements in a specific order. Max and Min heap are the types of heap data structures. In Max heap, the root node's value is always higher or equal to the value of all existing child nodes in the heap tree. While in Min heap, the value of the root node/element is always shorter than the existing elements of the heap node. Each child node's value in the min-heap is equal to or larger than the parent node's value. 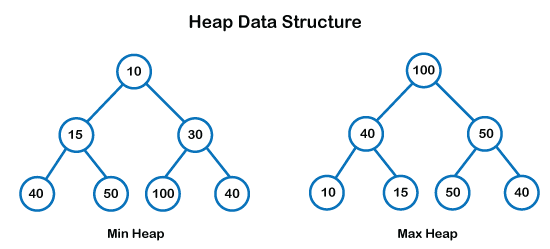
Hash Table: It is a non-linear type of data structure that holds and organizes data in key-value pairs to access the particular keys/data elements. A key is a null value that is mapped or linked to an element. Hashing makes our data structure much simpler and faster when performing insertion and search operations on various data elements, regardless of the data's size. 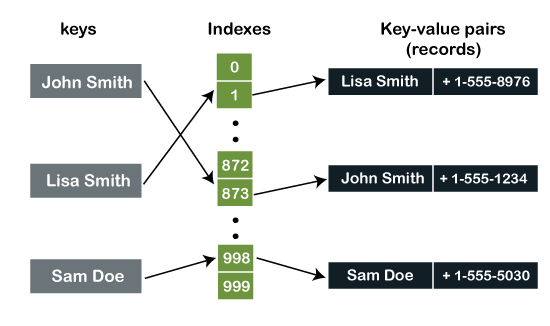
Dictionary: A dictionary is a type of data structure that holds data elements in a group of objects and is similar to a hash table, except that it is an ordered or unordered collection of data elements in key-value pairs. Each key is associated with a single value. When we retrieve a key, the dictionary will return the associated value of a key. For example, students = {'James' = 25, 'Jasmine' = '17', 'Rosy = '19', 'Margret' = '24', 'Price' = '28'}
Next TopicHash Table
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










