How Many States in India | Largest State in IndiaIndia is a democratic republic with a Parliamentary system of Government. It is the seventh-largest country in the world. Managing such a big country from one location is not easy, so the Indian Constitution gives the power to the central government to form states with their state governments headed by the Chief Ministers. As of now (2020) after the Jammu and Kashmir became a union territory on 6 August 2019, there are 28 states and 8 union territories in India. List of States in India by area starting with the largest state in India: 1) RajasthanRajasthan is the largest state of India in terms of the area situated in the north-western part of India. The capital of Rajasthan is Jaipur and its geographical area is 342,239 sq. km. and the Literacy rate is 66.1 percent. 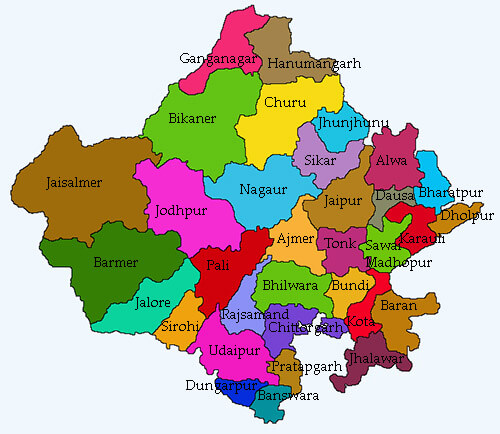
Neighbouring states of Rajasthan: The state is bordered on the north and north-east by Punjab, and Haryana; on the east and south-east by Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, and on the south-west by Gujarat, and on the west and northwest, it shares borders with Pakistan. Rajasthan was formed on 30 March 1949. The current chief minister of Rajasthan as of June 2020 is Ashok Gehlot and its governor is Kalraj Mishra and it has 33 districts. The state is home to the Indus Valley Civilization, which is one of the world's first and oldest civilizations. The Thar Desert, which is located at western Rajasthan and is known as the Great Indian Desert or the ocean of sands, is the seventh-largest desert in the world. The state is also one of the leading tourist destinations in India. 2. Madhya PradeshMadhya Pradesh is the second-largest state of India in terms of area. It is often called the "Heart of India." As the name (Madhya Pradesh) suggests, it is located in Central India. Its capital is Bhopal, the geographical area is 308,000 sq. km. and the literacy rate is 70.6 percent and the population of Madhya Pradesh is 7.25 crores (72597565) based on 2011 census. 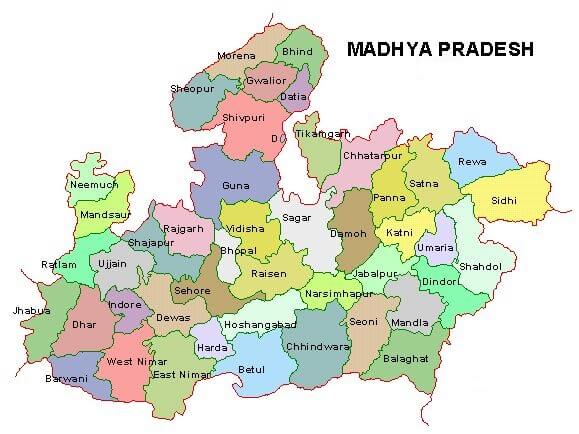
Neighbouring states of Madhya Pradesh: On the north, it is bounded by Uttar Pradesh; on the east by Chhattisgarh, on the south by Maharashtra, and on the west by Rajasthan and Gujarat. Madhya Pradesh was formed on 01 November 1956. The current chief minister of Madhya Pradesh as of June 2020 is Shivraj Singh Chouhan and its governor is Anandiben Patel and the state has 52 districts. The state is rich in natural resources and biodiversity. It is the only state of India that produces diamond and is one of the major cotton-producing states in India. The major railway route that connects the north and south regions of India passes through the Madhya Pradesh. 3) MaharashtraMaharashtra is located in the western region of the country. The capital of Maharashtra is Mumbai, the geographical area is 3.08 lakh sq. km. the literacy rate is 82.3 per cent and the number of districts in Maharashtra are 36 and is population is around 11.2 crores (112,372,972) as found in 2011 census. 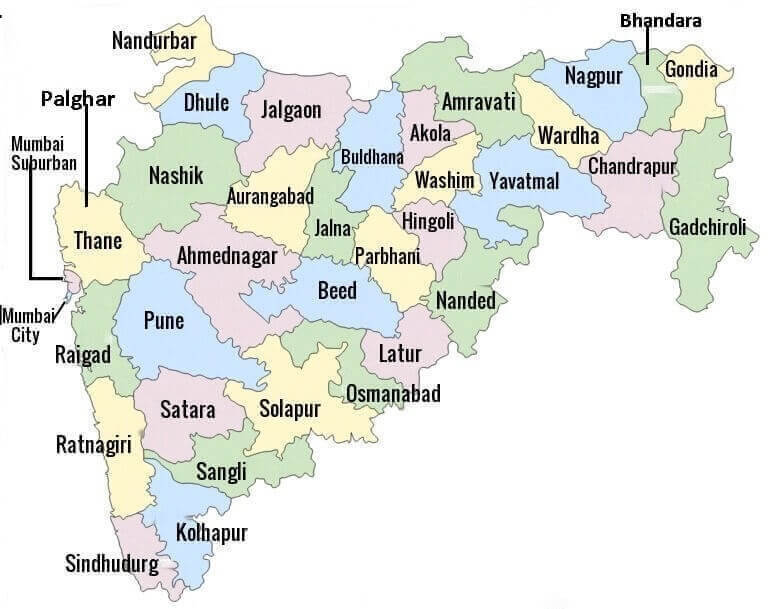
Neighbouring states of Maharashtra: On the west it is bordered by the Arabian Sea, on the north, it shares its border with Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, on the east it is bordered by Chhattisgarh and on the south, it is bordered by Andhra Pradesh. Maharashtra became a state on 01 May 1960. As of March 2020, Uddhav Thackeray is the chief minister and Bhagat Singh Koshyari is the governor of Maharashtra and the state is divided into 36 districts. It is one of the major sugarcane, cotton and pomegranate producers in the country. Besides this, jowar, bajra, whear, mung, urad, tur are the major crops grown in Maharashtra. The stock exchanges of India (BSE & NSE), and commodity exchanges including the capital market are located in Mumbai. The Jalgoan district of Maharashtra is famous for the production of bananas. 4) Uttar PradeshUttar Pradesh is the most populous Indian state located in the western part of the country. The capital of Uttar Pradesh is Lucknow, its geographical area is 240,928 sq. km. and its literacy rate 67.68 per cent and as per the census of 2011, the population of Uttar Pradesh is around 20 crore (199,812,341). 
Neighbouring states of Uttar Pradesh: On the north, it shares borders with Nepal; on the northwest, it shares with Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand; on the west with Delhi, Haryana and Rajasthan; on the south with Madhya Pradesh; on the southeast with Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand, and on the east with Bihar. It became a state on 24 January 1950. As of now, there are 75 districts in Uttar Pradesh and as of June 2020, its chief minister is Yogi Adityanath and its Governor is Ram Naik. The famous tourist destination Taj Mahal, which is one of the Seven Wonders of the World, is also located in Agra, Uttar Pradesh. Besides this, it is the largest producer of food grains in the country. There are 42 national highways and 83 state highways in the state. 5) GujaratGujarat is located on the western coastline of India, which is around 1600 km long. The capital of Gujarat is Gandhinagar, its geographical area is 196,063 sq. km. The literacy rate is 78.03 per cent and the population of Gujarat is around 6.04 crore based on the 2011 census. 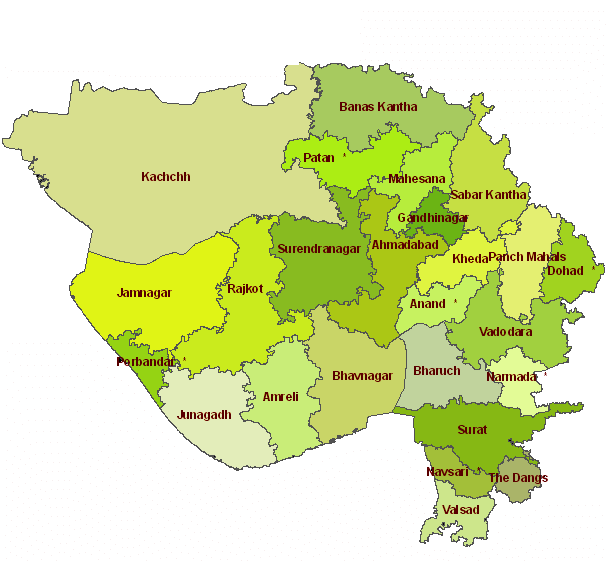
Neighbouring states of Gujarat: It is bounded by Madhya Pradesh in the east; the Arabian Sea in the west; Rajasthan in the north and northeast and on the south and south-east by Maharashtra. Gujarat was formed on 01 May 1960. It has a total of 33 districts and the chief minister of Gujarat as of 2020 is Vijay Rupani and its governor is Acharya Devvrat. It is known as the petroleum capital of India as it has many oil refining companies. It is also the largest producer of processed diamonds. The major crops produced in Gujarat are cotton, groundnut and tobacco. There are 13 national highways and 300 state highways in Gujarat. 6) KarnatakaKarnataka is located in the southern part of India. The capital of Karnataka is Bengaluru and its geographical area is 191,791 sq. km., the literacy rate is 75.6 per cent and its population is around 6.42 crores. 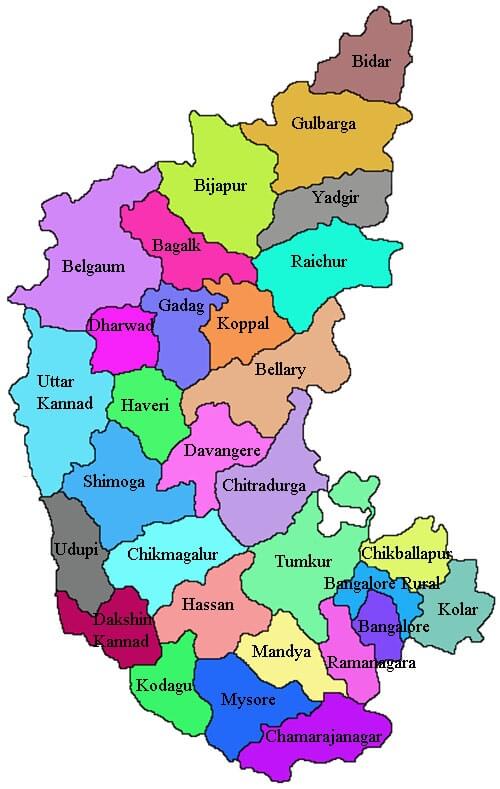
Neighbouring states of Karnataka: On the north, it shares boundaries with Maharashtra; on the east with Andhra Pradesh, on the southwest with Kerala, on the southeast with Tamil Nadu, and on the west, it is bordered by the Arabian Sea. Karnataka was formed on 01 November 1956. Formerly, its name was Mysore, later in 1973, it was renamed Karnataka. It has 30 districts and 28 Lok Sabha seats. As of June 2020, the chief minister of Karnataka is B.S. Yediyurappa and its governor is Vajubhai Vala. It is a major producer of coffee, raw silk, sandalwood goods and milk. Besides this, the major crops grown in Karnataka include rice, maize, jowar, ragi, and major pulses includes gram and tur. The major commercial crop of Karnataka is sugarcane; it is the fourth-largest producer of sugarcane in India. The road network of the state comprises 14 national highways and 115 state highways. 7) Andhra PradeshAndhra Pradesh is located beside the eastern coast in the south of India. The capital of Andhra Pradesh is Hyderabad. Its geographical area is 160,205 sq. km. The literacy rate is 67.4 percent and the population as per 2011 census is 4.8 crores. 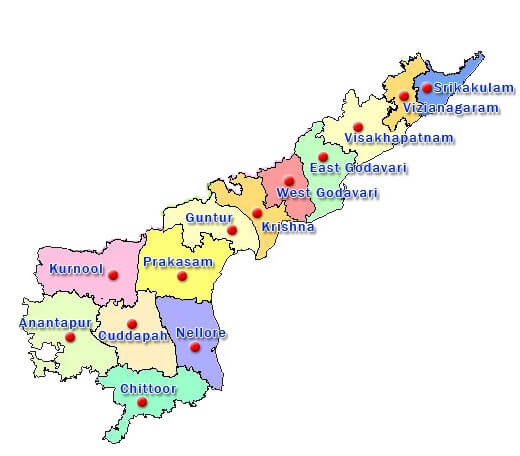
Neighbouring states of Andhra Pradesh: On the north, it is joined with Chhattisgarh; on the northeast with Odisha; on the west with Karnataka and Telangana; on the south with Tamil Nadu and on the east by the Bay of Bengal. The state was formed on 01 Nov 1956. It has 13 districts and as of June 2020, the chief minister of Andhra Pradesh is Y.S. Jagan Mohan Reddy and governor is Biswabhusan Harichandan. The major crops grown in Andhra Pradesh are rice, bajra and jowar. Godavari and Krishna are the two major rivers of India that flow through this state. Andhra Pradesh is known as Kohinoor of India as well as Egg bowl of Asia. It has the second-longest coastline in India (972km). 8) OdishaOdisha is situated in the eastern part of India. The capital of Odisha is Bhubaneswar. Its geographical area is 155,707 sq. km., the literacy rate is 72.87 per cent and population of Odisha is 4.2 crores as per the census of 2011. 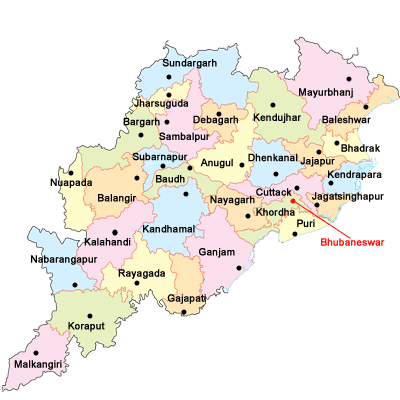
Neighbouring states of Odisha: On the north, it is shares borders with Jharkhand; on the northeast with West Bengal; on the south bordered by Andhra Pradesh; on the west by Chhattisgarh, and on the east by the Bay of Bengal. Odisha was formed on 15 August 1947. It is divided into 30 districts. As of June 2020, its chief minister is Naveen Patnaik and Governor is Ganeshi Lal Mathur. This state was established as a province (Orissa) of British Govt. on 01 April 1936 during the colonial rule in India. On 04 November 2011, it was renamed Odisha. The major crops grown in Odisha are wheat, ragi, maize, and paddy. The major rivers that flow in this state include Mahanadi, Brahmani, Baitarni, Tel, etc., and the major minerals produced are Iron, Manganese, Bauxite, Dolomite, Tin, Coal, etc. 9) ChhattisgarhChhattisgarh is situated in central India. The capital of Chhattisgarh is Raipur. Its geographical area is 137,898 sq. km. the literacy rate is 70.3 per cent and population as per 2011 census is 2.56 crore. 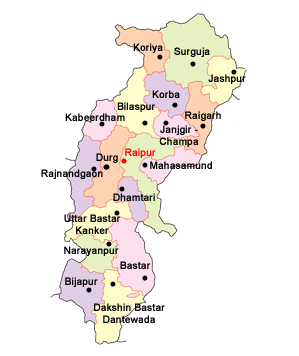
Neighbouring states of Chhattisgarh: On the west of Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh are located; in the north, it shares borders with Uttar Pradesh; in the east with Jharkhand and Odisha and in the south with Andhra Pradesh. Chhattisgarh was formed on 01 November 2000. It was carved out of Madhya Pradesh. It has 27 districts. As of June 2020, its chief minister is Bhupesh Baghel and Governor is Anusuiya Uikey. It is the leading producer of coal, dolomite and iron ore. The major crops of Chhattisgarh are maize, jowar, groundnut, wheat, gram, and paddy. Based on its rice cultivation, it is also known as the rice bowl of India. 10) Tamil NaduTamil Nadu is located in the southernmost region of India. The capital of Tamil Nadu is Chennai, its geographical area is 130,058 sq. km. and as per the census of 2011, its population is 6.24 crore. 
Neighbouring states of Tamil Nadu: On the north, it is surrounded by Andhra Pradesh; on the west by Kerala and Karnataka, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and the Bay of Bengal is on the east of Tamil Nadu. It is formed 26 January 1950. Formerly, its name was Madras but later on 14 January 1969, it was renamed Tamil Nadu. The chief minister of the state as of June 2020 is Edappadi K. Palaniswami and the governor is Banwarilal Purohit. The state is divided into 37 districts. The major crops of Tamil Nadu are rice, ragi, bajra, jowar and maize including tea, coffee, coconut, sugarcane. It is also one of the leading producers of banana and minerals that include molybdenum, vermiculite, garnet, dunite, rutile, etc. 11) TelanganaTelangana is situated on the south-central region of India. The capital of Telangana is Hyderabad. Its geographical area is 114,840 sq. km. the literacy rate is 66.5 per cent and the population as per 2011 census is 35193978 (3.5 crores). 
Neighbouring states of Telangana: On the south and east, it is bordered by Andhra Pradesh; on the west by Karnataka and Maharashtra and on the north by Chhattisgarh and Odisha. Telangana was formed in June 2014. It is carved out of Andhra Pradesh or was formed after the split of Andhra Pradesh state. As of June 2020, its chief minister is K Chandrasekhar Rao; Governor is Tamillisai Soundararajan and the state has 33 districts. The Godavari is the longest river in Telangana; Rice is the major crop as well as widely consumed food of the state. Other important crops of this state include mango, cotton, sugarcane and tobacco. Besides this, Telangana is a leading producer of some minerals such as dolomite, barytes, feldspar, barytes, laterite, limestone, Sand and Quartz. 12) BiharBihar is located in the eastern region of India. The capital of Bihar is Patna, its geographical area is 94,163 sq. km. the literacy rate is 61.8 per cent and the population as per the census of 2011 is 10.4 crore. 
Neighbouring states of Bihar: On the north, it is surrounded by Nepal; on the east by West Bengal, on the west by Uttar Pradesh, and on the south by Jharkhand. Bihar was formed on 01 April 1936 after it was separated from Bengal during the British rule in India. As of June 2020, the chief minister of Bihar is Nitish Kumar and its governor is Phagu Chauhan and it has 38 districts. The Ganges is the longest river in Bihar. The major cereal crops of the state include wheat, rice and maize. It is the largest producer of some vegetables such as potato, eggplant, onion and cauliflower. 13) West BengalWest Bengal is situated in eastern India. Its capital is Kolkata, the geographical area is 88,572 sq. km. the literacy rate is 77.1 per cent and the population is 9.13 crores as per the census of 2011. 
Neighbouring states of West Bengal: It has Bhutan and Nepal to the north; Assam to the northeast; Bangladesh to the east; Odisha to the southwest and Bihar to the west. West Bengal was formed on 26 January 1950. The current chief minister of West Bengal as of June 2020 is Mamata Banerjee and the Governor is Keshari Nath Tripathi. It has 23 districts. Its main rivers include Hooghly, Jaldhaka, Teesta, Rupnarayan. Wheat, jute and sugarcane are major crops of the state. Besides this, it is the second-largest fish producing state in India. It mostly produces coal and some other minerals such as copper, iron, fireclay, china clay, limestone, etc. 14) Arunachal PradeshArunachal Pradesh is located in the northeast of India. The capital of Arunachal Pradesh is Itanagar. Its geographical area is 83,743 sq. km. the literacy rate is 65.38 per cent. As per 2011 census, the population of Arunachal Pradesh is 13.2 Lakhs (1382611). 
Neighbouring states of Arunachal Pradesh: on the west, it shares borders with Bhutan; in north and northeast with Tibet; in the east and southeast with Myanmar and in the south with Assam and Nagaland. Formerly, Arunachal Pradesh was North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA). It became a Union Territory on 20 January 1972. Later, on 20 February 1987, it became a full-fledged state. As of June 2020, the chief minister of Arunachal Pradesh is Pema Khandu and its governor is B. D. Mishra. It has 25 districts. The major crops grown in Arunachal Pradesh are rice, wheat, maize, millet, sugarcane, including ginger, and oilseeds. The Brahmaputra is the longest river that flows through this state. The major minerals found in this state include iron-core, limestone, granite and sillimanite. 15) JharkhandJharkhand is situated in the eastern part of India. The capital of Jharkhand is Ranchi. Its geographical area is 79,714 sq. km. the literacy rate is 66.4 per cent and the population is 3.3 crores as per the census of 2011. 
Neighbouring states of Jharkhand: On the east, it is bounded by West Bengal; on the west, it shares borders with Chhattisgarh and Uttar Pradesh; on the north with Bihar and on the south with Odisha. Jharkhand was formed on 15 November 2000. As of June 2020, its chief minister is Hemant Soren and its governor is Draupadi Murmu. It has 24 Districts. The main river of Jharkhand is the Damodar that is also known as the 'Dev' river in this state. Rice, wheat and maize are the main crops grown in Jharkhand. The minerals found in this state include Coal, Bauxite, Uranium, Iron ore, Limestone, Pyroxenite, Quartz, Quartzite, etc. 16) AssamAssam is situated in the northeast region of India. The capital of Assam is Dispur. Its geographical area is 78,438 sq. km. and the literacy rate is 72.2 per cent. As per the 2011 census, the population of the state is 3.1 crores. 
Neighbouring states of Assam: On the north, it is surrounded by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh; on the east by Nagaland, Manipur and Arunachal Pradesh and on the south, it shares borders with Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram and to the west with West Bengal. Assam became a part of India on 15 August 1947. As of June 2020, the chief minister of Assam is Sarbananda Sonowal and its governor is Jagdish Mukhi and it has 33 districts. The Brahmaputra is the longest river in Assam. The other major rivers are the Barak and the Manas. The principal crops grown in Assam include rice, maize, wheat and potato and pulses, whereas, the major cash crops are jute, tea, sugarcane, cotton, oilseeds, and tobacco. The major mineral reserves of this state include iron-ore, limestone, granite, and sillimanite. 17) Himachal PradeshHimachal Pradesh is situated in the northern part of India. Shimla is the capital city of Himachal Pradesh. The geographical area of the state is 55673 sq. km. the literacy rate is 83.8 per cent and the population is 68.65 lakhs according to the 2011 census. 
Neighbouring states of Himachal Pradesh: On the north, the state is surrounded by Jammu &Kashmir; on the west and the South-West by Punjab; on the south by Haryana; on the South-East by Uttar Pradesh and on the east by China. Himachal Pradesh came into existence as a political entity on 15 April 1948 by integrating different smaller states. Later it became a union territory and after a few years, it became a state on 25 January 1971. As of June 2020, its chief minister is Jai Ram Thakur and its governor is Bandaru Dattatreya and it has 12 districts. In terms of volume, the Chenab or Chandrabhaga is the largest river of Himachal Pradesh. The main crops grown in the state are wheat, maize, rice and barley. Its mineral resources include salt, mica, gypsum, clays, limestone, barytes, pyrite and lead. 18) UttarakhandUttarakhand is situated in the northern region of India at the foothills of the Himalayan mountain ranges. The capital of Uttarakhand is Dehradun. Its geographical area is 53,483 sq. km. the literacy rate is 78.8 per cent and its population as per 2011 census is 1.0 crores. 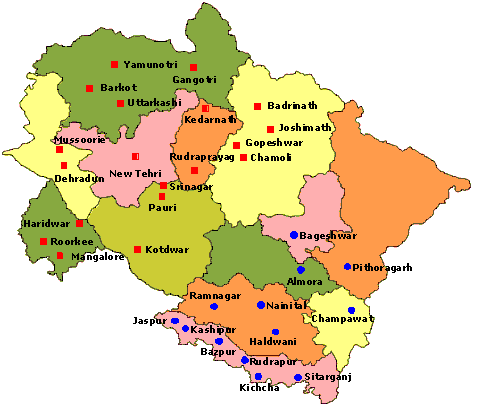
Neighbouring states of Uttarakhand: In the north, it shares borders with Tibet; in the east with Nepal; in the west and northwest with Himachal Pradesh and in the south with Uttar Pradesh. Formerly, it was a part of Uttar Pradesh. Later, on 09 November 2000, it was carved out of northern Uttar Pradesh and thus became a full-fledged state. As of June 2020, the chief minister of Uttar Pradesh is Trivendra Singh Rawat and its governor is Baby Rani Maurya and it has 33 districts. The major rivers of Uttarakhand are Alaknanda, Ganga, Yamuna and Bhagirathi. Major crops of the state include wheat, rice, sugarcane, maize, soybean, groundnuts and pulses including fruits and vegetables. The major minerals that are found in Uttarakhand are limestone, magnesite, steatite and tungsten. 19) PunjabPunjab is situated in the northern part of India. The capital of Punjab is Chandigarh. Its geographical area is 50,362 sq. km. the literacy rate is 76.7 per cent and its population as per the census of 2011 is 2.77 crores. 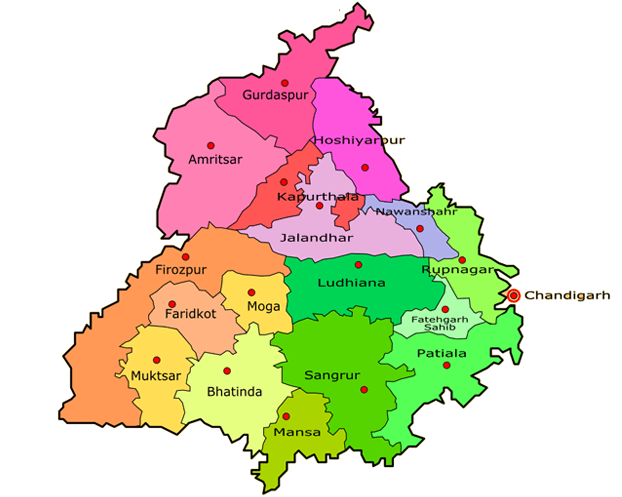
Neighbouring states of Punjab: on the west, it is bordered by Pakistan; in the north by Jammu and Kashmir; in the east, by Himachal Pradesh; in the south and southeast by Haryana and in the southwest it shares borders with Rajasthan. The state in its current form was formed on 01 November 1966 when a part of it was separated from it to form the new state of Haryana. The current chief minister of Punjab as of June 2020 is Amarinder Singh and its governor is Vijayendra Pal Singh Badnore. Punjab is also known as the 'Bread Basket of India'. It is the state where the first green revolution of the country occurred. The major rivers of the state are Sutlej and Beas; the major crops are wheat, rice, cotton, maize, and sugarcane, and the major minerals include quartz, silica sand, quartzite, potash, etc. 20) HaryanaHaryana is one of the northernmost states in India. The capital of Haryana is Chandigarh. Its geographical area is 44,212 sq. km. the literacy rate is 75.5 per cent and its population on the basis of the 2011 census is 2.54 crores. 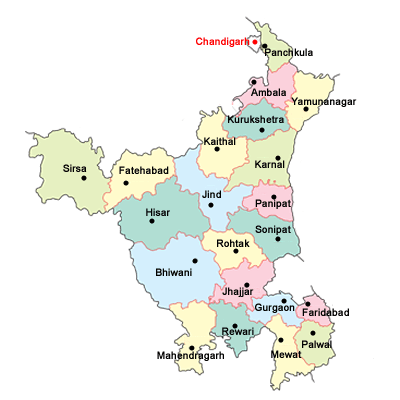
Neighbouring states of Haryana: On the east, it is surrounded by Uttar Pradesh; on the west by Punjab; on the north by Himachal Pradesh and in the south by Rajasthan. Haryana was formed on 01 November 1966. It was carved out from Punjab when Punjab was reorganized. The current chief minister of Haryana as of June 2020 is Manohar Lal Khattar and its governor is Satyadeve Narayan Arya and it has 22 districts. Haryana is also called "The Home of Gods." The major rivers of this state are Ghaggar, Yamuna, Sahibi and Krishnavati and major crops include wheat, rice, sugarcane, cotton, maize, barley, millet, etc. The main minerals found in Haryana are china clay, limestone, quartz, and quartzite. 21) KeralaKerala is situated in the southern region of India. It has lots of beautiful locations blessed with natural beauty and is known as "God's own country". The capital of Kerala is Thiruvananthapuram. Its geographical area is 38863 sq. km. the literacy rate is 94.6 per cent and its population as the 2011 census is 3.34 crores. 
Neighbouring states of Kerala: On the south and east it shares boundaries with Tamil Nadu; on the north with Karnataka, and on the west with Lakshadweep sea coastline. Kerala was formed on 01 November 1956. The current chief minister of Kerala as of June 2020 is Pinarayi Vijayan and its governor is Arif Mohammad Khan and it has 14 districts. The major rivers that flow through Kerala are the Periyar, the Bharatapuzha and the Pamba. Its major food crop is paddy and the main cash crops include coconut, tea, coffee, rubber, pepper, cardamom, ginger, nutmeg, cinnamon, etc. The major minerals found in Kerala are rutile, zircon, gold, iron, graphite, monazite and sillimanite. 22) MeghalayaMeghalaya is situated in the northeast part of India. Its capital is Shillong, the geographical area is 22,429 sq. km. the literacy rate is 74.4 sq. km. and its population as per the 2011 census is 29.6 lakh. 
Neighbouring states of Meghalaya: On the north and east, it shares borders with Assam and on the south and west with Bangladesh. Meghalaya became a full-fledged state on 21 January 1972. It was carved out from Assam. The current chief minister of Meghalaya as of June 2020 is Conrad Sangma and its governor is Tathagata Roy and the total number of districts is 11. The major rivers that flow through Meghalaya include Ajagar, Chagua, Didram, Dudnai, Krishnai, Bhogai, Bandra, Simsand, etc. The major crops grown here include rice, maize, bananas, potatoes, and pineapple. The main minerals found in this state are coal, uranium, granite, clay, glass sand, limestone, etc. 23) ManipurManipur is located in the Northeast region of India. The capital of Manipur is Imphal. Its geographical area is 22,327 sq. km. The literacy rate is 76.9 per cent and the population as per the census of 2011 is 27 lakh (2721756). The map of Manipur is given below: 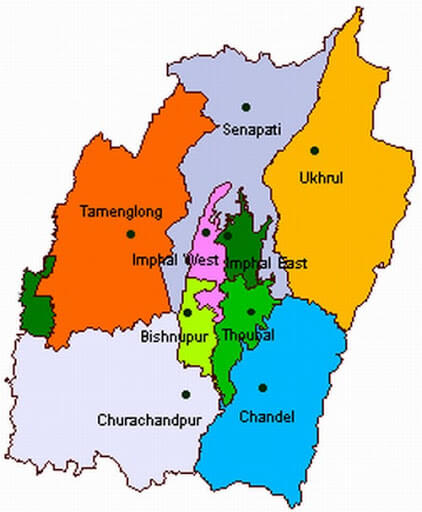
Neighbouring states of Manipur: On the east, it is bounded by Myanmar (Sagaing region), on the north by Nagaland; on the west by Assam and on the south, it shares borders with Mizoram and Myanmar. Manipur became a part of India in October 1949. It became a Union Territory in 1956 and a full-fledged state in 1972. The current chief minister of Manipur as of June 2020 is Nongthombam Biren Singh, and the governor is Najma Heptulla. It has 16 districts. Barak is the biggest river in Manipur and the major crops grown here include paddy, sugarcane, potato, tobacco, mustard, pulses. Yaosang is the main festival of Manipur, it is celebrated for five days. The major minerals found in the state include chromite, limestone, nickel, petroleum and serpentinites. 24) MizoramMizoram is situated in the northeast of India. The capital of Mizoram is Aizawl and its geographical area is 21,087 sq. km. The literacy rate is 91.33 per cent and its population as per the census of 2011 is 10 lakh (1091014). The map of Tripura with neighbouring states is shown below: 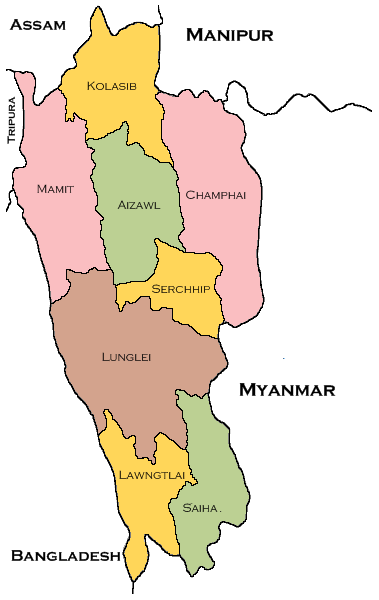
Neighbouring states of Mizoram: On the west, it is bounded by Bangladesh; on the east and south by Myanmar; to the northwest by Tripura; on the north by Assam and on the northeast it is bordered by Manipur. Formerly, Mizoram was a union territory. It became a state on 20 February 1987. The current chief minister of Mizoram as of June 2020 is Zoramthanga and its governor is P.S. Sreedharan Pillai and it has 11 districts. The main rivers of Mizoram include Tlawng, Tian, Tut, Tuichawng, Teirei, Serlui, and the main horticulture crops of this state include orange, banana, grapes, passion fruit, pineapple and papaya. Furthermore, the main minerals found in Mizoram are lignite, sandstone, clay, coal, etc. 25) NagalandNagaland is a north-eastern state situated in the farthest east side of India. Its capital city is Kohima, the geographical area is 16,579 sq. km, the literacy rate is 79.55 per cent and its total population as per the 2011 census is 19.8 Lakh (1978502). The map of Nagaland with neighbouring states is shown below: 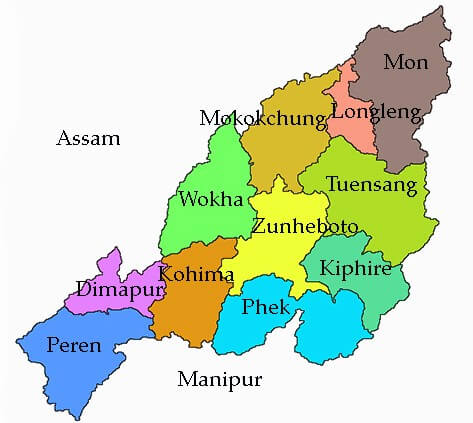
Neighbouring states of Nagaland: In the east, it is bounded by Myanmar; in the north by Arunachal Pradesh; in the west, by Assam and in the south by Manipur. It became the 16th state of India on 01 December 1963. The current chief minister of Nagaland as of June 2020 is Neiphiu Rio and its governor is Ravindra Narayana Ravi. It has 12 districts. The major rivers of Nagaland are Dikhu, Doyang, Tizu, Dhansiri, Dzu, Zungki, Langlong and Dzuza. The main crops grown here include rice, maize, millet, pulses and the main minerals found in Nagaland include coal, nickel, cobalt, chromium, limestone, copper, magnetite, zinc, platinum, petroleum and natural gas. 26) TripuraTripura is a north-eastern state in India. Its capital city is Agartala, the geographical area is 10491 sq. km. the literacy rate is 87.8 sq. km. and the population as per the 2011 census is 36.74 Lakhs (3673917). See the map of Tripura: 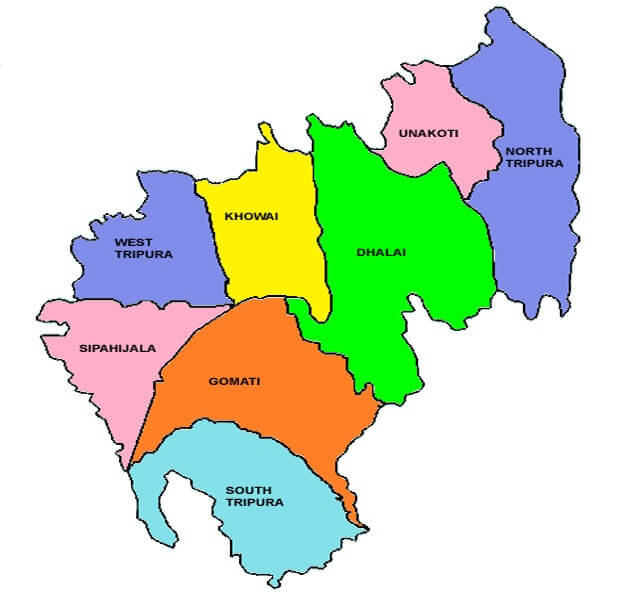
Neighbouring states of Tripura: On the north, west and south, it is bordered by Bangladesh and in the east, it shares boundaries with Assam and Mizoram. On 26 January 1950, Tripura was given the status of a 'C' category state. Later, on 01 November 1956, it became a union territory and finally, it became a state on 21 January 1972 as per the North-East Reorganization Act, 1971. As per June 2010, the current chief minister of Tripura is Biplab Kumar Deb and its governor is Ramesh Bias and the state has 8 districts. The major rivers of Tripura are Bijay, Deo, Dhalai, Gumti, Feni, Juri, Haora, Longai, Manu and Muhuri. The main food crop is rice and the main horticultural crops are pineapple, potato, jackfruit, sugarcane, natural rubber and chilli. Besides this, the main minerals found in Tripura include glass sands, plastic clay and limestone and oil and natural gas. 27) SikkimSikkim is situated in the north-eastern region of India. The capital city of Sikkim is Gangtok. Its geographical area is 7,096 sq. km. The literacy rate is 81.42 sq. km. and its population as per the 2011 census is 36.74 Lakhs (3673917). 
Neighbouring states of Sikkim: On the north, it is bounded by Tibetan Plateaus; on the east by Chumbi Valley of Tibet and Bhutan; in the west by Nepal and in the south by West Bengal. On 16 May 1975, Sikkim became the 22nd state of India. The current Chief Minister of Sikkim as of June 2020 is Prem Singh Tamang and its governor is Ganga Prasad and the total number of districts in this state is 4. The major rivers in Sikkim are Teesta and Rangeet and the main food crops include wheat, rice, barley, maize, buckwheat, potatoes, tea, etc. Whereas, the major cash crops are large cardamom, turmeric, baby corn, buck heat, cherry, ginger, etc. Besides this, the main minerals found in Sikkim include copper, lead and zinc and silver. 28) GoaGoa is situated in the western part of India and its capital city is Pana Ji. Its geographical area is 3702 sq. km. the literacy rate is 88.7 per cent and its population as per 2011 census is 14.59 Lakhs. 
Neighbouring states of Goa: On the west, it shares borders with the Arabian Sea; on the north with Maharashtra; on the south and east by Karnataka. Goa became a full-fledged state of India on 30 May 1987. The current chief minister of Goa as of June 2020 is Pramod Sawant and its governor is Satya Pal Malik and it has 2 districts. The major rivers of Goa are Tiracol, Baga, Mandovi, Zuari, Saleri, Talpona, Galgibaga, Sal and Chapora, and the major food crops include paddy, ragi, maize, jowar, bajra and main cash crops include coconut, mango, cashew nut, pineapple, banana, and jackfruit. The main minerals include iron, bauxite and manganese, etc.
Next TopicBest Honeymoon Places in India
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










