How to Install WordPress in Ubuntu 16.04?Wordpress is an open source CMS (Content Management System). It is used to create dynamic websites using PHP and MySQL database. It works on cross-platform and can be installed on any operating system. WordPress was originally designed as a tool to release blogs. Still, it has derived to support releasing other web content, such as more classic websites, Internet forums and mailing lists, membership sites, media galleries, online stores, and learning management systems. WordPress is surrounded by the most famous content management systems, and it was utilized by 48% of the excellent 10 million sites as of October 2021. This content management system is specified in PHP (hypertext preprocessor) language and paired with a MariaDB or MySQL database. Some features are a template system and a plugin architecture called "Themes" within WordPress. WordPress needs to be installed to function on a web server, either as an Internet hosting service or executing the WordPress application package on a computer. WordPress was published on 27 May 2003 by Mike Little (an English developer) and Matt Mullenweg (an American developer). WordPress Foundation has WordPress Projects, WordPress, and other associated trademarks. Multi-blogging and multi-user in WordPressWordPress supported a single blog/installation prior to version 3, although two or more concurrent copies might be executed from distinct directories if set up to use different tables of the databases. WordPress Multisites (referred to as WPMU, WordPress MU, or WordPress Multi-User previously) was a WordPress fork designed to permit two or more blogs to be available in a single installation. Still, it could be commanded by a centralized manager. It can be possible with WordPress MU for those using websites to manage their blogging communities, as well as moderate and control every blog from one dashboard. WordPress MU includes eight new tables of data for all blogs. History of WordPressb2/cafelog, more generally called catalog or b2, was WordPress precursor. As of May 2003, it was supposed to have been installed on around 2,000 blogs. It was specified in PHP to utilize with MySQL via Michael Valdrighi, a WordPress contributing developer. Another project, i.e., b2evolution, is under active development; however, WordPress is an official successor. Matt Mullenweg started pondering the plan of forking b2/cafelog and many new aspects that he wished for in the new CMS as b2/cafelog development slowed down in a blog post written on 24 January 2003. A professional developer, Mike Little, was the first one to comment on this post blog showing interest in contribution. These two worked together to make the first WordPress version, i.e., version 0.70, which was published on 27 May 2003. A friend of Mullenweg, Christine Selleck Tremoulet, recommended the title WordPress.
Recognition and awards
WordPress release historyPrimary WordPress releases have been codenamed after acclaimed jazz musicians, initiating from the 1.0 version. Security updates are supported "as a courtesy" to every release as far back as the 4.0 version, although only the latest version is supported officially.
The 5.0 "Bebo" version of WordPress was published in December 2018. It is named in tribute to Bebo Valdes, the pioneering Cuban jazz musician. It added the new default "Gutenburg" block-based editor. It permits users to change their visible content in a user-friendly way as compared to the previous iterations. Blocks are philosophical markup units that form the layout or content of a web page. Content that was made on WordPress pages is mentioned under what's called a Classic Block. Many block-based editors are available before Gutenburg as WordPress plugins, such as Elementor. Comparisons were enabled between it and those plugins following the Gutenberg release.
It was made as an output of User preferences and aided website developers in managing their past plugins only suitable with the 4.9 version of WordPress, providing the time for plugin developers to get their plugins compatible and updated with the 5.0 version. If we install the Classic Editor plugin, it can bring back the "classic" editing practice that WordPress had up prior to the 5.0 version of WordPress. Until 2024, the support of the Classic Editor plugin will be available. It is active on 5+ million WordPress installations as of November 2022. Vulnerabilities of WordPressSeveral security problems have been found in the software, specifically in 2007, 2008, and 2015. In April 2009, WordPress had seven security advisories (unpatched), according to Secunia, with a "Less Critical" rating. Secunia manages an up-to-date list of the vulnerabilities of WordPress. Various high-profile SEO (search engine optimization) blogs, as well as various low-profile commercial blogs providing AdSense, were attacked and targeted with a WordPress exploit in January 2007. A different vulnerability on one of the web servers of the project site permitted an attacker to address exploitable code within the pattern of a back door to a few downloads of the 2.1.1 version of WordPress. This version introduced this problem; an advisory published during advised every user for upgrading immediately.
Support and Development
Mike Little and Matt Mullenweg were the project co-founders. The main lead developers are Andrew Nacin, Andrew Ozz, Matt Mullenweg, Mark Jaquith, Dion Hulse, and Helen Hou-Sandi. Also, WordPress is improved by its community, such as WP tester, an association of volunteers who check all releases. Early, they have access to release candidates, beta versions, and nightly builds. Bugs are documented in a unique mailing list or the Trac tool of the project. WordPress is nearly related to Automattic, the community discovered by Matt Mullenweg though largely improved by the community neighboring it.
It is a non-profit enterprise that was founded for supporting WordPress projects. The goal of the enterprise is to ensure open access to the software projects of WordPress forever. The enterprise manages and owns WordCamp, WordPress, and associated trademarks. Matt Mullenweg structured the enterprise in January 2010 to manage and own the WordPress project trademarks. From 2006 onwards, Automattic previously pretended as a short-term WordPress trademark owner. From the start, he wanted later for placing the trademarks of WordPress with the WordPress Foundation, which didn't available in 2006 and finally took longer to begin than expected.
WordCamp is usual, organized conferences to cover everything associated with WordPress. The initial such event was organized, i.e., WordCamp 2006, in San Francisco in August 2006, which had 500+ attendees. Outside San Francisco, the initial WordCamp was held in September 2007 in Beijing. There have been 1022+ WordCamps since then in 75+ cities in 65 countries worldwide.
At the event, i.e., the State of Word 2021, Matt Mullenweg introduced the WordPress Photo Directory on 14 December 2021. It's an open-source directory of images for open images managed by the WordPress project. It aims to facilitate an open replacement to closed image banks, including Adobe Stock, Pixbaby, and Unsplash, whose licensing conditions have become limited in recent years.
WordPress.org is the main support website for WordPress. This website introduces both WordPress Forums, which is a running online association of WordPress users, and WordPress Codex, which is an online WordPress manual, and a living archive for WordPress documentation and information. Installation of WordPressIn this tutorial, we are installing wordpress in the Ubuntu 16.04. This whole process includes the following steps. Prerequisites
1) Download Wordpress Change current working directory to the /var/www/html/ and run the following command. 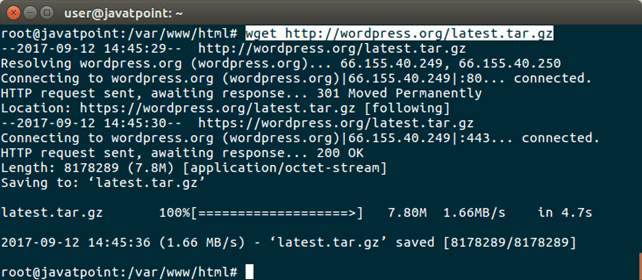
It will download a zip folder that contains wordpress template. Extract the folder by using the following command. 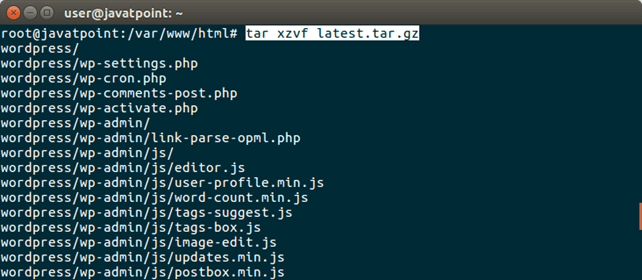
2) Create a Database We are creating a database wordpress in MySQL as given in the following screen-shot. 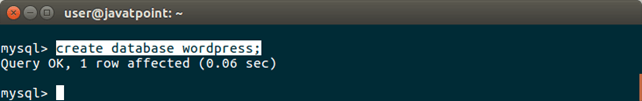
3) Access Wordpress From Localhost 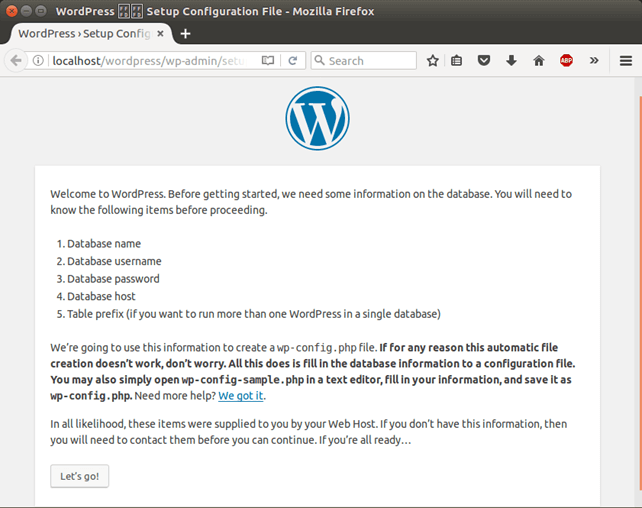
Click on let's go! 4) Provide Database Details 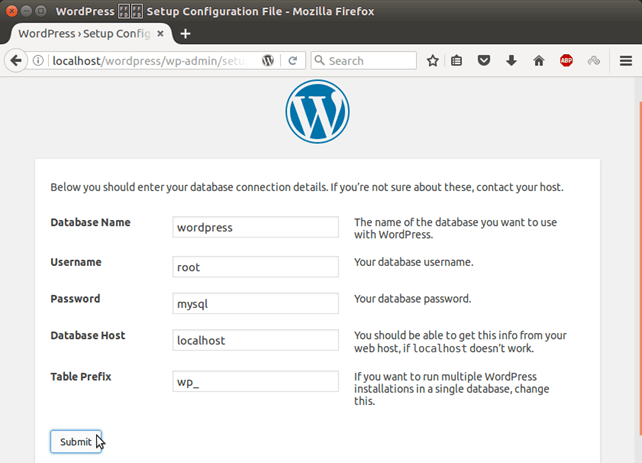
Provide database name, database username and password. Specify database host, if database is located at the localhost, enter localhost. Click on submit, it shows php code. 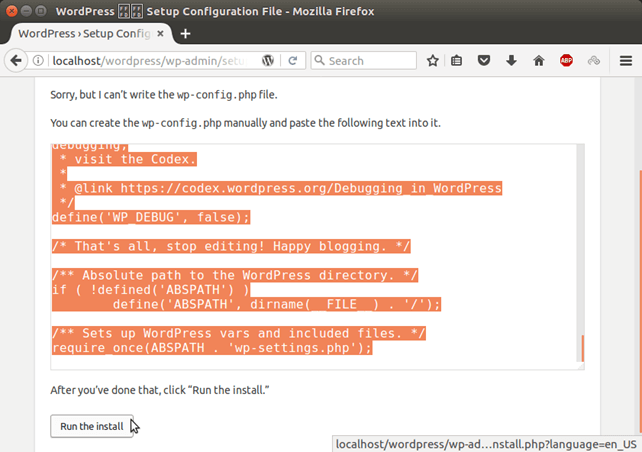
Create a file wp-config.php inside the wordpress folder. Copy that code and paste into the created file. After this, click Run the install. 5) Provide Login Details Fill login details into the following form. 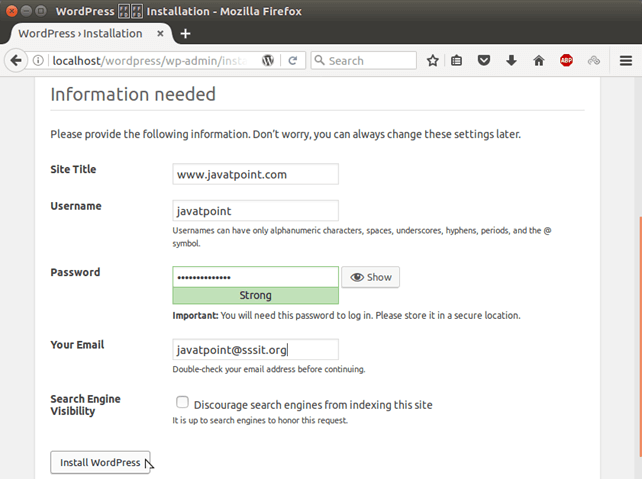
After providing all details. Click on the button Install WordPress and it will show a success message after doing some internal configuration and installation. 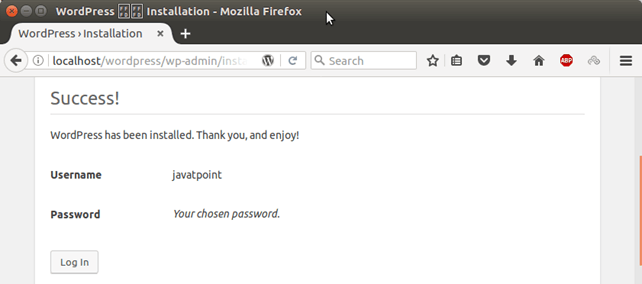
6) Login into Wordpress Login into the wordpress by providing login details. 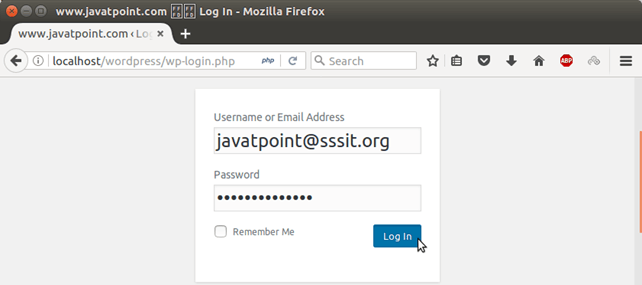
After login, it shows a dashboard that looks like below. 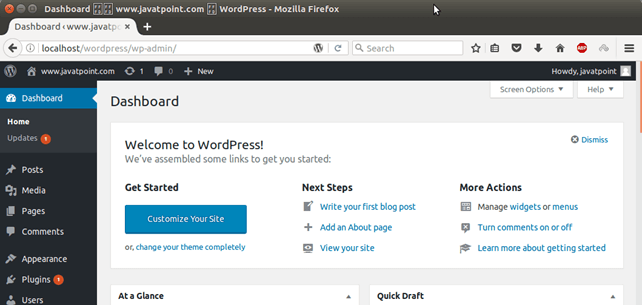
Now, we have installed wordpress in Ubuntu 16.04 successfully.
Next TopicHow To Install Node.JS In Ubuntu
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










