How to Use ANY keyword in SQLIn this SQL article, you will learn how to use the 'ANY' keyword in the database tables. What is Any in SQL?The ANY is an operator in SQL. This operator compares the given value to each subquery value and returns those values that satisfy the condition. ANY operator is mainly used in the HAVING or WHERE clause with the INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and UPDATE SQL statements. It always evaluates to TRUE if at least one subquery value matches according to the given condition. The syntax for using ANY operator in Structured Query Language: In the syntax, the ANY operator is followed by the SQL comparison operator, which helps compare the column value with the subquery. Following are the SQL comparison operators used with the ANY operator in queries: 1. Equal operator (=) The equal comparison operator with ANY operator evaluates to TRUE when the column's value is equal to any value of the subquery. Syntax: 2. Not Equal operator (!=) This comparison operator with ANY operator evaluates to TRUE when the column's value is not equal to any value of the subquery. Syntax: 3. Greater Than operator (>) This comparison operator with ANY operator evaluates to TRUE when the column's value is greater than the smallest value of the subquery. Syntax: 4. Less Than operator (<) This comparison operator with ANY operator evaluates to TRUE when the column's value is less than the largest value of the subquery. Syntax: 5. Greater Than Equal To operator (>=) This comparison operator with ANY operator evaluates to TRUE when the column's value is greater than or equals the smallest value of the subquery. Syntax: 6. Less Than Equals To operator (<=) This comparison operator with ANY operator evaluates to TRUE when the column's value is less than and equals to the largest value of the subquery. Syntax: If you want to use the SQL ANY operator in the tables for performing operations, you have to follow the given steps in the same manner:
Now, we are going to explain the steps in detail with a SQL example: Step 1: Create the Simple new databaseFirstly, you have to make a new database in Structured Query Language. So, let's start. The following query creates the new College Database in SQL server: Step 2: Create the New tableNow, use the below SQL syntax, which helps in creating the new table in the database: The following query creates the Teacher_Info table in the College Database: The following query creates the Department_Info table in the College Database: Step 3: Insert the ValuesThe following INSERT queries insert the records of teachers in the Teacher_Info table: The following INSERT queries insert the records of departments in the Department_Info table: Step 4: View the Table's DataThe following query shows the data of the Teacher_Info table.
The following query shows the data of the Teacher_Info table. 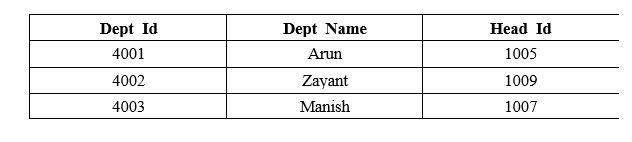
Step 5: Use ANY operator to view the Table's dataThe following query uses ANY operator with an Equal comparison operator: This query shows the details of a teacher from the Teacher_Info table. Here, the teacher is also the head of the department from the Department_Info table. The output of the above SELECT query with Equal operatoris shown in the below table:
The following query uses ANY operator with less than operator and GROUP BY clause: This query shows the details of all teachers whose salaries are less than the average salary of every department. The output of the above SELECT query with less than operator is shown in the below table:
The following query uses ANY operator with greater than operator and GROUP BY clause: This query shows the details of all teachers whose salaries are greater than the average salary of every department. The output of the above SELECT query with Greater Than operatoris shown in the below table:
Next TopicHow to use CHECK in SQL
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










