HTML DefinitionThe collection of markup symbols or codes entered into a file to be displayed on the Internet is known as Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML). The markup instructs web browsers to display the text and pictures on a web page. 
HTML determines the web page's structure, and an interactive web page cannot be created using just this framework. So, to create your HTML appealing and add interactivity, you'll need assisting technologies like JavaScript and CSS. HTML DefinitionHypertext: Hypertext is the text arranged to link similar elements (sometimes with embeds like images, too). Markup: It is a style manual for typesetting anything that will be printed, whether in hardcopy or digital form. Language: The language which a computer system utilizes to comprehend orders is known as language.
There are several uses for HTML, including:
HTML cannot provide dynamic functionality, so it is not regarded as a programming language and is currently regarded as a recognized web standard. The HTML standards are developed and updated often by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). Hypertext Markup Language FundamentalsHTML is just a set of shortcodes entered into a text file. An HTML text file is saved, and a web browser is used to see it. Following the author's instructions for writing the codes that result in visible representation, the browser examines the file and converts the content into a visual form. 
While writing HTML, tags must be utilized appropriately to convey the author's intent. These tags power the capabilities of HTML, and tags distinguish normal text and HTML code. The words included within angular brackets (<>) are called tags, enabling the appearance of graphics, pictures, and tables on the website. Various tags have different purposes. JavaScript and Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) applications may be employed when web interfaces need to be made more dynamic. Web pages are made more powerful and accessible by CSS and JavaScript, respectively. HTMLBasic ElementsAn HTML element is a component within a tag that can contain name-value combinations known as attributes. A text file is additionally marked with HTML content specifying how the page should be presented. A unique, distinctive HTML syntax is maintained to show the markup different from the HTML file's real content. These unique elements are referred to as HTML tags. 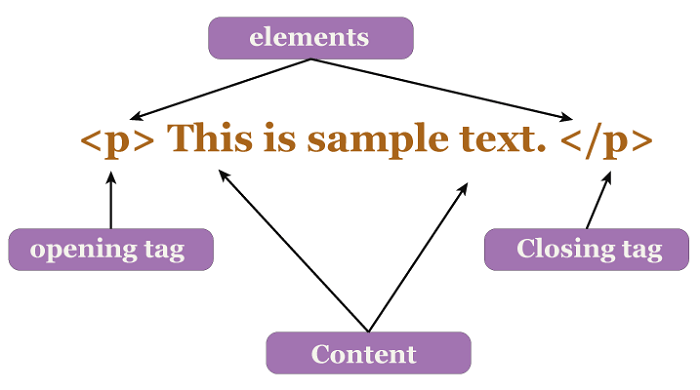
There are always starting tags, middle content, and closing tags for HTML components. The opening tag contains attributes that can provide the element with further details. There are two methods to characterize an element: 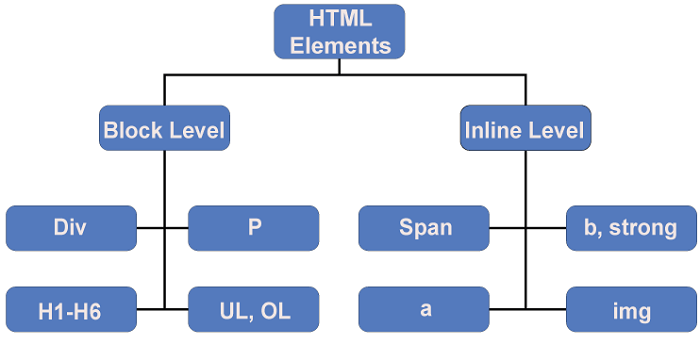
HTML TagsLike keywords, HTML tags specify how a web browser will structure and display the text. Using tags, a browser can differentiate between plain text and HTML content. The opening tag, content, and closing tag are the three essential components of an HTML tag. Yet, certain HTML tags are not closed. 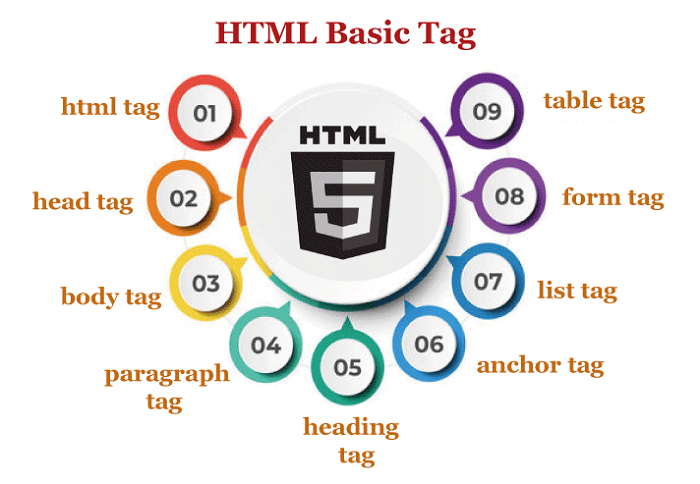
A web browser views an HTML document from left to right and top to bottom. To generate HTML documents and display their characteristics, HTML tags are employed. Every HTML tag has a unique set of features. A web browser needs a few basic tags in an HTML file to distinguish between ordinary text and HTML text. According to the needs of your code, you may incorporate as many tags as you like.
Common HTML TagsThe layout of a page is determined by its HTML tags, which also specify how each element will be seen in the browser. HTML tags that are often used include:
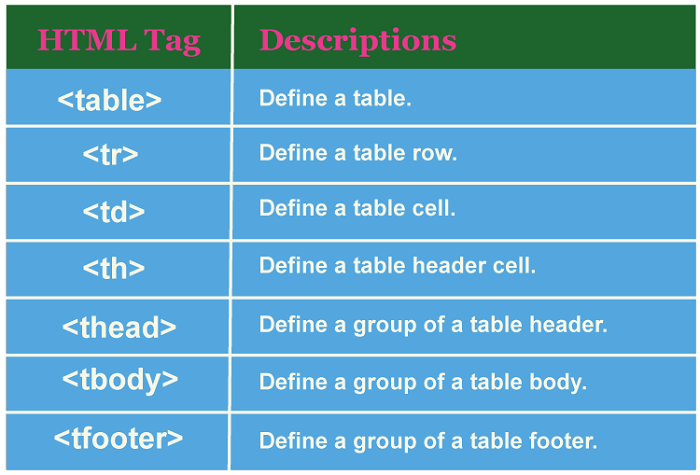
As previously indicated, the information they enhance is surrounded by opening and closing tags.
The same rules apply to closing tags, except they include a backslash to signify that the provided HTML element has ended.
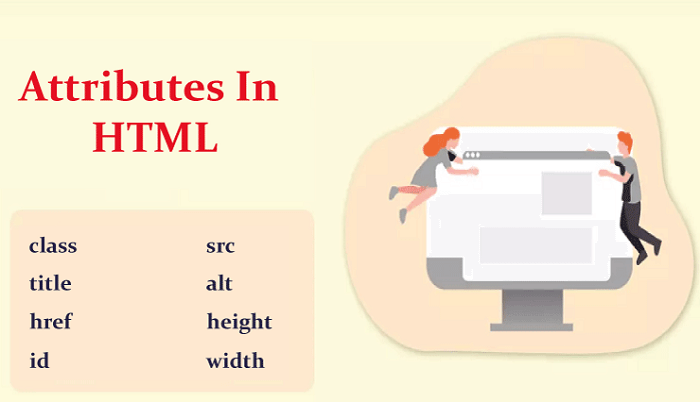
HTML Attributes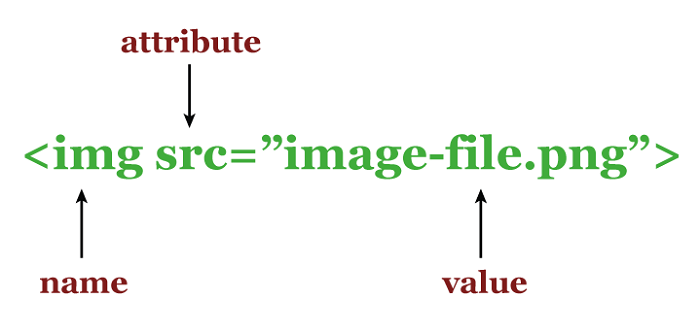
Using and Implementing HTMLAs HTML is entirely text-based, it is possible to modify an HTML file by opening it in an application like Notepad++, Vi, or Emacs. An HTML file may be created or edited in any text editor, and as long as it has a ".html" file extension, any web browser, including Chrome or Firefox, can view the file as a webpage. 
There are several WYSIWYG "what you see is what you get" editors available for use by professional software developers to create web pages. WYSIWYG editors are offered as plugins or standard components by NetBeans, IntelliJ, Eclipse, and Microsoft's Visual Studio, making HTML very simple to use and implement. Although contemporary online browsers sometimes come with web developer plugins that show issues with Html documents, such as a blank ending tag or syntax that doesn't produce well-formed HTML, these WYSIWYG editors also offer HTML debugging capabilities. Both Chrome and Firefox come with HTML developer features that let you immediately examine a webpage's whole HTML file, edit HTML while browsing, and update HTML while the browser is open. CSS, HTML, and JavaScriptAlthough it may be used to build webpages, HTML has several restrictions regarding completely responsive elements. As a result, adding text components and organizing them inside a website should be the primary uses for HTML. Combining HTML with CSS and JavaScript enables more complicated functionalities (JS). 
An HTML file can have a link to a cascading style sheet (CSS)or JS file, often at the top of the page with a defined file path, that contains information on the display of HTML elements, including the colors and fonts to use. Moreover, JavaScript enables website designers to incorporate more dynamic features like pop-up windows and image sliders. Tags known as class attributes are employed to link HTML components to their matching CSS or JS elements. The same fundamental approach is used with JS sheets but with different functionality. For example, a user may add code to the CSS file with a class property that makes text red if they want a specific quantity of text to be that color. Finally, they may add the same class property to all of the text in the HTML page that they wish to be red. Difference Between HTML and HTML5There were 18 tags in the original HTML, and since then, more tags and properties have been introduced to the markup with each subsequent edition. 
HTML5 includes new types of form controls, which is the primary distinction (difference) between HTML and HTML5. Also, HTML5 added several semantic elements like "article," "header," and "footer" that precisely define the content. XML vs. HTMLUnlike HTML, Extensible Markup Language, or XML, enables users to customize their markup. 
Just one predetermined tag can be used in HTML to indicate certain data. As XML documents only include syntax and content, they are designed to be simple to read and contain user-defined tags. Benefits and drawbacks of HTMLThe following are some benefits of utilizing HTML: 
A few drawbacks to take into account are: 
Next TopicInertia Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share