Inflammation DefinitionInflammation is a protective mechanism your immune system uses to free your body from infection, damage, or illness. Everyone experiences inflammation, irrespective of whether or not they are aware of it. Without inflammation, you wouldn't be able to recover from numerous conditions. 
Your immune system may occasionally target healthy cells when you have autoimmune disorders, such as some arthritis-related conditions and inflammatory bowel disease. Inflammation DefinitionYour immune system is activated when your body comes into contact with an inflammatory substance (such as bacteria, viruses, or toxic substances) or sustains damage. Inflammatory cells and cytokines (substances that stimulate more inflammatory cells) are the first immune system response agents sent out. These cells produce an inflammatory reaction to absorb germs and other harmful substances or heal damaged tissue. Nevertheless, inflammation also impacts unseen bodily processes, and there may be discomfort, bruising, swelling, or redness. Types of InflammationThere are two primary types of inflammation: 

Some of the diseases related to chronic and acute inflammation: 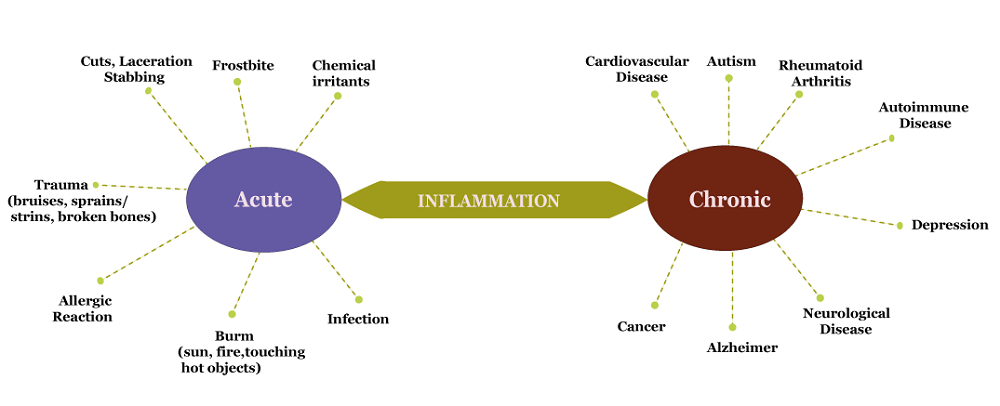
General Body ResponsesThe body may generally respond depending on the symptoms of inflammation. The following signs and indicators might be among them: 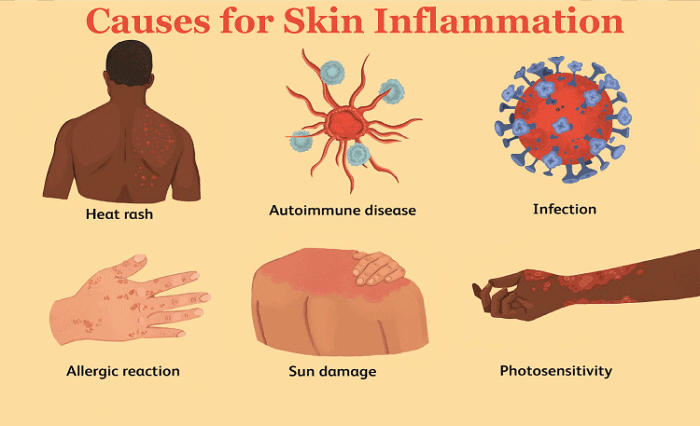
What Mainly Occurs When You Have Inflammation?There may be involvement from a wide variety of immune system cells when inflammation develops in your body. They discharge a range of substances referred to as inflammatory mediators. The hormones histamine and bradykinin are examples of inflammatory mediators. By widening (dilating) the tissue's tiny blood arteries, they increase the amount of blood that can reach the wounded tissue. Because of this, inflamed areas become red and hot to the touch. Moreover, these two hormones disrupt nerves and trigger the brain to receive pain signals. This serves a preventive purpose because the damaged bodily part is more likely to be shielded when an inflammation hurts. Also, because of the increased blood flow, more immune cells can be sent to the wounded tissue, which supports the healing process. 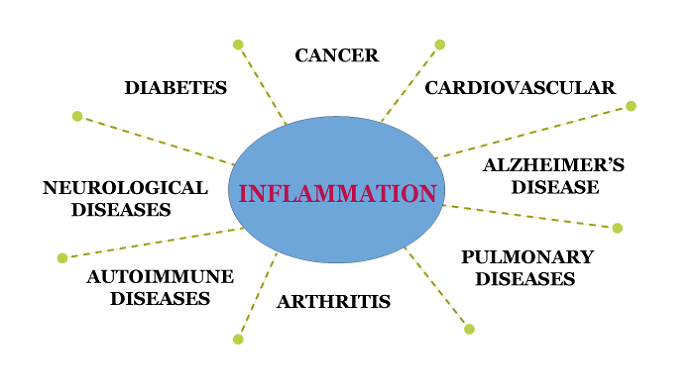
One other job of the inflammatory mediators is to facilitate the passage of immune cells through the tiny blood channels so that more of them may reach the area of tissue that is injured. Moreover, the immune system cells increase the fluid that enters the inflammatory tissue, so it frequently expands. After some time, the swelling returns to normal as the fluid is removed from the tissue. Also, when they are inflamed, mucous membranes produce more fluid. The increased fluid will then contribute to swiftly flushing the viruses from your body. For example, this occurs when the nose's membranes are irritated and you have a stuffy nose. Causes of InflammationMicrobes, physical agents, chemicals, unsuitable immune reactions, and tissue loss are some of the reasons that can trigger inflammation. Bacteria and viruses are only a couple of the infectious substances that frequently cause inflammation. 
Inflammation is caused by bacteria and viruses that penetrate and damage bodily cells and endotoxins released by bacteria. Inflammation and tissue damage can result from physical trauma, burning, radiation harm, frostbite, and corrosive chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and oxidizing agents. As previously discussed, an inappropriate and harmful inflammatory response might be sparked by immune reactions that are not working properly. When tissues lack oxygen or nutrients and begin to die, inflammation may also develop. This condition is frequently brought on by a reduction in blood supply to the affected area. Symptoms of Inflammation
Acute inflammation could cause:
It may be more difficult to recognize the signs of chronic inflammation than those of acute inflammation. Chronic inflammatory symptoms can include:
Diseases Linked To InflammationInflammation is associated with the disease method of several conditions, including: 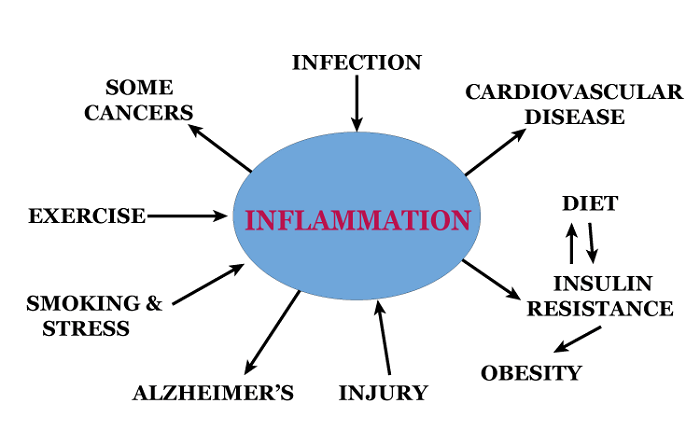
Diagnosing InflammationMore substances known as biomarkers will enter the bloodstream whenever inflammation occurs in the human body. C-Reactive Protein (CRP) is a typical example of a biomarker. 
CRP levels are typically higher in senior citizens and those with comorbid diseases, including obesity and cancer. The healthcare professional may check the CRP levels to determine whether the body is inflamed. How Is Inflammation Treated?It's not always necessary to cure inflammation; rest, ice, and proper wound care frequently cure the pain in a few days for acute inflammation. 
Your healthcare professional may suggest the following when you have chronic inflammation:
Domestic remediesSome methods to relieve protracted (long-term) inflammation include:

Consider taking supplements that contain green tea, capsaicin, curcumin, omega-3 fatty acids, and white willow bark to treat inflammation naturally. Furthermore, magnesium and the vitamins B6, C, D, and E have some anti-inflammatory properties. Before beginning any supplement, discuss it with your physician. SurgeryIf joint damage from inflammation is severe, surgery can be necessary. Popular techniques include:
Next TopicInformation Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










