Install Yarn Ubuntu
Yarn is a system of software packaging integrated in 2016 for the runtime environment, i.e., Node.js JavaScript by Facebook. A replacement to the npm package manager, yarn was made as a collaboration of Tiled (the company beyond Ember.js), Google, Exponent (Expo.dev now), and Facebook for solving performance, security, and consistency problems with big codebases.
Yarn permits us to share and use code with other developers around the world. It does this job reliably, securely, and quickly so we do not ever need to worry.
Yarn permits us to use the solutions of the other developers to distinct issues, making it convenient for us to integrate our software. If we have issues, we can report problems or contribute on GitHub and we can use Yarn for keeping it all up to date when the issue is fixed.
Code is shared using something known as a package. A package includes every code being distributed and a package.json file (known as a manifest) that defines the package. Yarn is a fresh package manager that substitutes the previous workflow for an npm client or several other package managers while others are consistent with the npm registry. It includes the similar aspects set as previous workflows while implementing faster, more, reliably, and more securely.
General Architecture of Yarn
Yarn works from a core package (released as @yarnpkg/core) that discloses several base elements that create a project. A few of the elements are classes that we might identify from the API: Manifest, Cache, Workspace, Project, Configuration, and others. Each of those is given by the core package.
The core itself does not do much, it includes the logic needed for managing a project. To apply this logic using the command line, Yarn gives an indirection known as @yarnpkg/cli which does not do much either. However, it has two different very essential responsibilities: it injects the pre-built plugins of Yarn into an environment and hydrates an instance of a project based on the latest directory (cwd).
Yarn is a built-in modern way that permits most of the enterprise logic corresponding to the third-party interactions to be materialized in their package. For instance, the npm resolver is one plugin among many others. This architecture provides us a much easier codebase for working with (hence an enhanced stabler product and development speed) and provides plugin authors the capability for writing their external logic without needing to modify the codebase of Yarn itself.
Functionality of Yarn
Users can specify their plugins for Yarn:
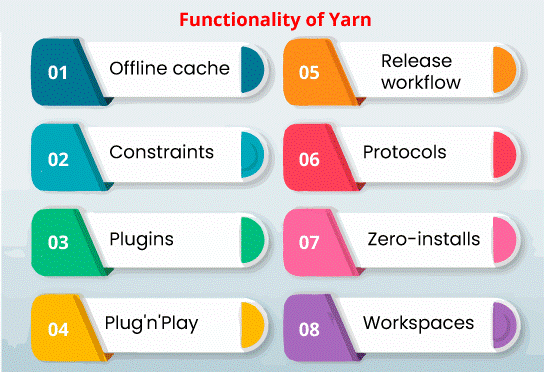
Offline cache
The downloaded packages are stored and cached as individual files.
Constraints
The constraints of Yarn permit users for enforcing rules for their dependencies or several fields around scoped workspaces.
Plugins
It can add new commands, linkers, features, and resolvers, and can register to a few events or be developed with each other, most aspects of Yarn are worked from plugins including yarn install and yarn add, which are pre-installed plugins as well.
Plug'n'Play
It permits users to execute Node projects without using the folder, i.e., node_modules, defining the location or way for resolving dependency package files using the Plug-n-Play-control file. This aspect is focused to set an unwell structured architecture of node_modules and outcoming in a faster Node.js software start-up time.
Release workflow
It automatically upgrades corresponding packages among several workspaces when the root packages are upgraded.
Protocols
Users can specify which protocol would be used for resolving certain packages. For instance, the git protocol is used to download a public package through a Git repository, and a patch protocol is used to create a patched copy of the real package.
Zero-installs
Zero-installs resolve the requirements of package installation when packages are needed to install if the codes are just newly fetched to the local.
Workspaces
Workspaces permit more than one project for working together in a similar repository and automatically use modifications to other relatives if source code is changed, permitting installation of more than one package by only executing yarn install once for installing each of them in an individual pass.
Terminologies of Yarn
- Build Script: It refers to operations run right after a package gets installed. The post-install scripts are typically configured from the manifest inside the scripts field. They should be left for native dependencies. Virtually, there is no cause for authentic JavaScript packages to utilize them. Build scripts have serious side effects on the projects of our users, so carefully weigh whether we actually need them.
- Dependency: Dependencies (listed inside the manifest dependencies field) specify a connection between two different packages. Yarn ensures that package A can access package B if the installation process is successful when A includes a dependency B.
Note: It is the only guarantee we make related to the regular dependencies. However, there is no assurance that package B will be a similar release to the one utilized in other application parts in particular.
- Descriptor: It is a combination of a package range and package name. Descriptors are utilized to recognize a collection of packages instead of that one special package.
- Development Dependency: Dependencies (listed inside the manifest devDependencies field) specify a connection between two different packages. Development dependencies are quite the same as regular dependencies apart from they are only important for local packages only. Packages retrieved from remote registries like npm can't access the development dependencies; however, packages installed using local sources like portal : protocol or the workspaces will.
- Fetcher: A fetcher is a component loaded with extracting the complete package data from any reference. For instance, the npm fetcher will download tarballs of the package with the npm registry.
- Hoisting: Hoisting is the process of converting the dependency tree to improve it by deleting as several nodes as possible. There is no one way to determine how to convert the tree, and distinct package managers create distinct trade-offs. For this cause, no assurance can be made related to the ultimate hoisting layout, excluding that packages can always approach the dependencies they named in their manifests.
As the hoisting is massively connected to the Node resolution and the filesystem, its design makes it convenient to make a bug and access packages accidentally without them being correctly specified as dependencies. Hence, making their existence unpredictable without being observed at the time of the hoisting process.
- Linker: Linkers are some components that use both a package data store and dependency tree and produce disk artifacts particular to the platform they target in return. For instance, the Plug'n'Play linker produces one .pnp.cjs file.
- Locator: A locator is an aggregation of a package reference and a package name. Locators are utilized to recognize one unique package.
- Monorepository: It is a repository that includes two or more packages. For instance, Jest and Babel are such repository examples. They each include several small packages that all depend on one another.
- Manifest: It is a package.json file.
- Packages: They are dependency tree nodes. A package is a set of source code generally defined by a package.json at the root. The packages can specify dependencies, which are some other packages that require to be made present for it to work correctly.
- Peer dependency: Dependencies (listed inside the manifest peerDependencies field) specify a connection between two different packages.
- Peer-dependent Package: It is a package that mentions peer dependencies.
- Plugin: It is a new concept announced in Yarn 2+. Yarn can be developed and made more robust using plugins, whether it is via the addition of new linkers, fetchers, or resolvers.
- Plug'n'Play: It is an alternative installation plan that generates one file that's then inserted into the node to let understand where to search the installed packages rather than generating the classic node_modules directories. Starting from version 2, Plug'n'Play becomes the installation plan (default) for JavaScript projects.
- Portal: It is a dependency that utilizes the portal : protocol, indicating a package placed on the disk.
Opposed to the link : protocol, Yarn will configure its dependency map in a way that not just the dependency package can access a file referenced via the portal, although the portal itself can also access its dependencies.
- Project: This term is used to enclose every worktree that associate with a similar dependency tree.
- Range: It is a string that can be used to choose two or more versions of one package when merged with a package name. Typically, ranges follow semver, although they can use the supported protocols of Yarn.
- Reference: It is a string that can be used to choose one version of one package when merged with a package name. Typically, references follow semver, although they can use the supported protocols of Yarn.
- Resolver: Resolvers are the elements tasked with transforming descriptors in locators and also selecting the package manifests using the package locators. For instance, an npm resolver would inspect what releases exist on the npm registry and provide every candidate that fascinates the semver requirements. After that, it would check the npm registry to get the complete metadata related to the chosen resolution.
- Scope: It is a term connected inherited through the npm registry, used to define a group of packages that each belong to a similar entity. For instance, every Yarn package belongs to version 2 related to the berry scope in the npm registry. Traditionally, scopes are prefixed with a @ sign.
- Singleton Package: It is a package that is instantiated one time around the dependency tree. Singleton packages can be created easily with the help of peer dependencies by utilizing one of their properties while they are not a first-class citizen. Because packages reliant on by peer dependencies are assured to be the same item as the one utilized by their ancestor, across the whole dependency branch with the peer dependencies each way up to the closest workspace will assure that one item of the package is ever made- making it an existing package.
- Transitive Dependency: It is a package dependency we depend on. If we talk about react, our application relies on it, so it is a direct dependency. However, react also relies on prop-types which makes them a transitive dependency.
- Unplugged Package: Using Yarn PnP, almost every package is kept in its zip archives instead of not being wrapped on the disk. Then, the archives are mounted over the filesystem during runtime and accessed transparently. Mounts are read-only; hence, the archives do not get corrupted when something attempts to write on them.
However, in some cases, keeping a package read-only might be hard. For those cases, Yarn can not wrap respective packages and keep them in their individual folders. These types of packages are called "unplugged". In some scenarios, packages will be unplugged:
- If the package includes native files implicitly
- If the package mentions post-install scripts implicitly
- If the package fixes its preferUnplugged field to true explicitly
- By fixing the unplugged field to true explicitly
- Virtual Package: A peer-dependent package might have two or more dependency sets because these packages effectively specify a horizon of potential dependency sets instead of one static group of dependencies. The package will require to be instantiated for all such sets at least once when it happens.
- Because JS modules and Node-land are instantiated according to their path, and because PnP makes it, so the packages are introduced only once in any provided project; a single way to represent those packages is to provide them two or more paths multiple times.
- Virtual packages come in very handy in these types of situations.
- Virtual packages are specially designed instances of a peer-dependent package that codify the group of dependencies that this specific instance should utilize.
- All virtual packages are provided a special filesystem path that guarantees that the scripts it indicates will be instantiated using their correct dependency set.
Previously, virtual packages were operated with symlinks, but it changed recently, and they are operated by a virtual file system layer. It avoids the requirements of creating several confusing symlinks, developing Windows compatibility, and preventing problems that would come with third-party tools called realpath.
- Workspace: Generally saying, workspace is a Yarn aspect used for working on two or more projects stored in a similar repository. In the case of the vocabulary of Yarn, workspace is local packages that are related to a project directly.
- Worktree: It is a private workspace that includes child workspaces within the current project.
- Yarn: It is a tool of the command line used for handling programming environments. It is specified in JavaScript, mostly used with other projects of JavaScript but has aspects that make it compatible to be used in many situations.
Lifecycle Scripts of Yarn
- prepack is a lifecycle script that is called before all calls to the yarn pack.
- postpack can be called after the yarn pack, even if the call is completed or not.
- prepublish can be called before the same commands and yarn npm publish.
- postinstall can be called right after the dependency tree changes of the package are specified to the disk.
Comparison with npm
- Yarn installs all packages in parallel but npm Installs a single package at a time.
- Yarn can apply checksum to ensure data integrity but npm applies SHA-512 for checking the data integrity of the downloaded packages.
- Yarn connects package versions strongly.
- Yarn can install packages using the local cache.
Architecture of Yarn
Dependencies get positioned in the node_modules directory in our project within the Node ecosystem. Although, this file structure can be distinct from the real dependency tree because duplicate dependencies are combined. An npm client installs several dependencies into the directory, i.e., node_modules non-deterministically. It means that the structure of the directory, i.e., node_modules can be different from a single person to another based on the sequence dependencies installed. These differences can lead to "works on my machine" errors that take time for hunting down.
Yarn resolves these problems around non-determinism and versioning by applying lockfiles and the install algorithm that's reliable and deterministic. These lockfiles can lock the dependencies (installed) to a particular version and make sure that all installs outputs are in a similar file structure across every machine in the node_module directory. The written lockfile applies a compact format with ordered keys for ensuring that modifications are basic and review is easy.
The installation process is divided into three different steps which are mentioned below:
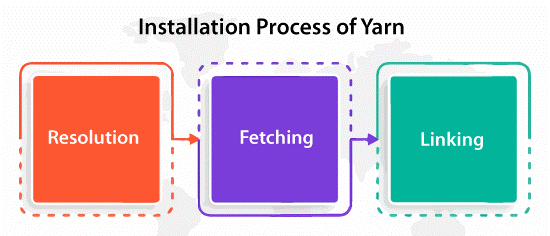
- Resolution- Yarn begins resolving dependencies by creating claims to the registry and looking up all dependencies recursively.
- Fetching- Yarn next looks in the universal cache directory to check if the package required has already been installed. If it has not, Yarn fetches a tarball for that package and sets it in the universal cache so it can implement offline and would not require installing dependencies multiple times. Also, dependencies can be positioned in the source control.
- Linking- Yarn finally connects everything by copying every file required from the universal cache into the local directory, i.e., node_modules.
By cleanly dividing these steps and having deterministic outputs, Yarn can parallelize operations which increases resource utilization and enables the installation process faster. Yarn decreased the installation process by a sequence of magnitude on a few Facebook projects from many minutes to just some seconds. Also, Yarn applies a mutex for ensuring that more than one active CLI instances do not pollute and collide with each other.
Yarn indicates strict guarantees across package installation during this whole process. We have control on which lifecycle scripts are run for which packages. Also, package checksums are stored within the lockfile for ensuring that we get a similar package all the time.
Install architecture of Yarn
What happens if we run the yarn install command can be explained in some distinct steps:
Initially, we type the "resolution step":
- We first load the entries saved in the lockfile, based on data and the latest project state. The core executes an internal algorithm for finding out which entries are not available.
- For all missing entries, the resolution step queries the plugins with the help of the interface, i.e., Resolver, and prompts them whether they'd know about the package that would be the same as the given descriptor.
- Once all packages that range through the dependency tree have been fixed into metadata, the core establishes the tree within the memory one last time for generating what the known as 'virtual packages'.
We type the "fetch step" once the resolution step is done:
- Now that we have the same package set that builds up our dependency tree, we can iterate on it and for all of them, we can begin a new claim to the cache for knowing whether that package is anywhere to be detected. If it is not we do like we did in the above step and we prompt our plugins.
- The interesting thing about the fetchers: they negotiate with the core from an abstraction layer on fs. We do it so that our packages could come from several different sources. It could be from the zip archive for packages that are downloaded through a registry or from an actual directory over the disk for portal : dependencies.
Once every package is ready for consumption, the "link step" comes finally:
- The packages we use should be installed over the disk in a few ways for working properly.
- Doing it means that fresh linkers could be made for other programming languages pretty simply- we just require to write our logic about what should happen through the packages given by Yarn.
- Something else that is cool is that the packages from in the dependency tree do not need to all be of a similar type. The design of our plugin permits instantiating more than one linker simultaneously. The packages can rely on one another linkers. We can have a package of JavaScript relaying on the Python package.
Elements of Yarn
The four major elements of Yarn are listed and discussed below:
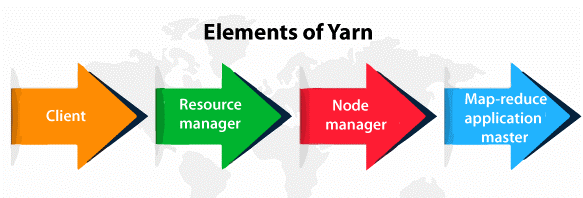
- Client- It is responsible to submit MapReduce.
- Resource manager- It is liable for the resource management in the cluster.
- Node manager- It is responsible to introduce and monitor computing containers in the cluster.
- Map-reduce application master- It is responsible to check every running operation. Application master implements in the resource manager and containers, and the node managers are liable for scheduling it.
Advantages of using Yarn
The following are some main advantages of using Yarn which is listed and explained below:
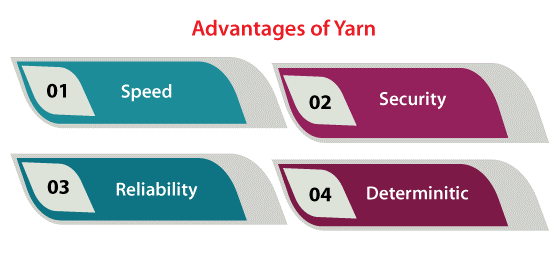
- Speed- Caching all downloaded packages. It ignores the requirement for re-downloading them later. Yarn additionally increases resource utilization by simultaneous processes, permitting faster installs.
- Security- The integrity of all install packages is checked by checksums. It is done before a package code is run.
- Reliability- Yarn provides baseline installation around every system due to a deterministic manner and the lockfile format of installing operations.
- Deterministic- Similar dependencies will be installed in a similar manner on any machine, despite the installation order.
Here are some more advantages:
- Supports both bower and npm workflows, permitting to mix registries
- Users can limit licenses of the installed modules and provide license details
- Easy-to-read CLI result
- Offline mode permits for package re-installation without the internet connection
- Developed network performance by queuing requests in an effective manner (and ignoring request waterfalls)
- Consolidated installation structure separate from installation sequence
- Developed network resilience by preventing respective failed requests from delaying the whole installation, rather, failed requests are retired automatically.
- More emojis
- Duplicate elimination by resolving mismatched dependency versions to a single version.
- Discloses a consistent public JS API along with logging abstracted for consumption by build tools
- Minimal, readable, pretty CLI results
- Yarn applies a bash-like compact shell for making package scripts compact across macOS, Linux, and Windows
- Yarn is the foremost and first Node API that could be used programmatically
- Yarn is completely type-checked and specified in TypeScript.
- Yarn by default supports Node but it is not restricted to it- plugins can also add support for several other languages
Installing Yarn in Ubuntu
Yarn is a JavaScript package manager which is npm-compatible that automates the managing, updating, installation, and uninstalling process of npm packages. It assists in catching all parallelizing processes and downloaded packages and for speeding up the installation process. Whether we are a hobbyist or enterprise users implementing one-shot projects, Yarn got us covered.
In this article, we will explain how we can install Yarn in Ubuntu.
Installation process
We can follow the following steps for installing Yarn in the Ubuntu system:
Step 1- Updating system repositories
We need to click "Ctrl+Alt+T" for opening the terminal window of Ubuntu and execute the following command for updating system repositories:
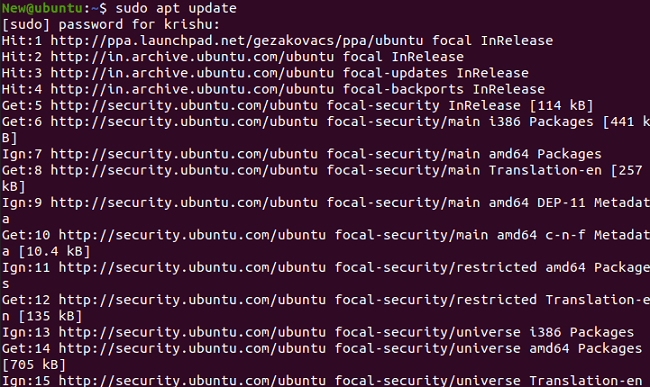
Step 2- Installing CURL in Ubuntu
We need to run the below command for the installation of CURL after updating Ubuntu system repositories:
The following result indicates that we have installed CURL on the system successfully.
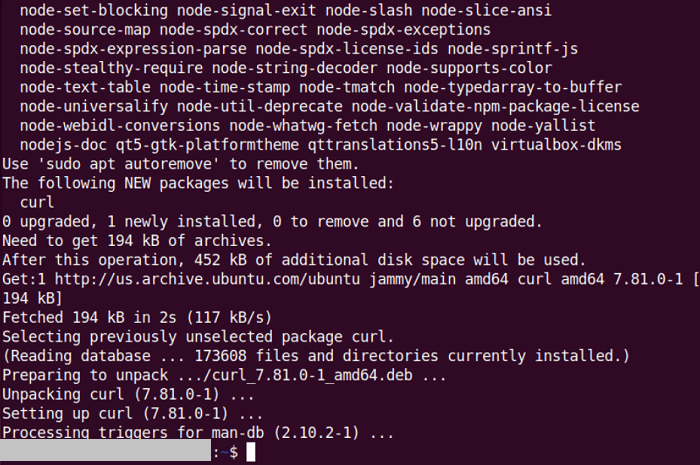
Step 3- importing Yarn GPG Key
We need to use the "curl" command to import the Yarn GPG Key to the system repositories of Ubuntu in the next step.
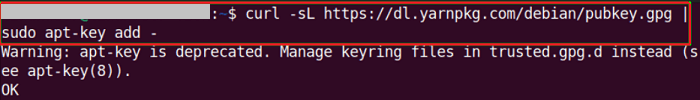
Step 4- Enabling the Yarn repository
We need to enable the Yarn repository on our Ubuntu system after importing the Yarn GPG Key. We need to use the below command in the terminal window for this goal

Step 5- Installing Yarn in Ubuntu
If we have carefully pursued the above steps, our Ubuntu system is ready for the installation process of Yarn. We need to run the following command to do so:
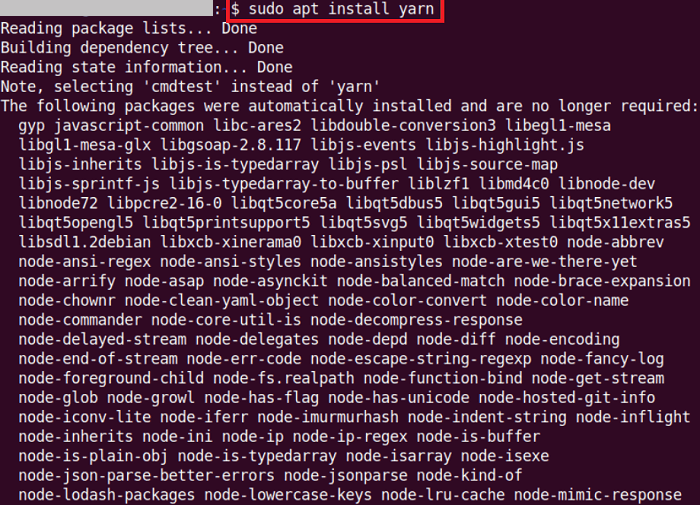
We need to enter the "y" button for permitting the installation process to proceed and wait for some time.
Step 6- Checking the Yarn version
For verifying if Yarn is installed or not successfully, we need to check its installed release on our Ubuntu system.
As we can see the yarn version is currently installed on our system in the following screenshot.
|










 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










