Ionic Bond DefinitionThe topic's name indicates that it is related to Chemistry; it is for a reader from a science background, it is quite easy for him to understand this concept of bonding because the primary and basic concept while studying chemistry. But those from a non-scientific background can also relate to it because it is considered the fundamental topic while studying the concept of Chemical bonding. What is Chemical Bonding?Chemical Bonding is the formation of chemical bonds among atoms by sharing an electron or by forming different types of bonds like covalent bonds and many other types. Still, specifically, in this article, we are talking about we are discussing the ionic Bond. The atoms lose and gain the electron and form various chemical bonds to attain a stable noble gas configuration, and it is a normal tendency of an atom to gain a stable noble gas configuration because every atom wants to reach a stable noble gas configuration; moreover, they do this to get new and stable chemical and physical properties. Different Types of Chemical BondsIonic Bond: This is a special type of chemical Bond that is formed by the mutual sharing of electrons by two or more atoms to get a stable physical or chemical state because in a stable state, if the newly formed compound is stable, then it will not further dissociate with any other chemical compound if the newly formed compound is chemically or physically unstable then it will further dissociate until it attains a stable state. While forming an ionic bond, there must be an atom with an excess number of electrons, and it needs to release a few electrons to attain a stable noble gas configuration. This atom releases an electron, known as a cation, and acquires a positive charge. At the same time, there is a need for an electron-deficient atom, and hence it needs a few more electrons to attain a stable noble gas configuration. The atom accepts the cation's released electron, completes its octet, and attains a noble gas configuration; after accepting the electron, it attains a negative sign, an anion. Example of Ionic Bond: let us take a simple example of an ionic bond NaCl known as salt in simple language, known as Sodium Chloride in scientific language. Its formation is the best example of stable chemical and physical properties of ionic bonds. As mentioned above, to form an Ionic Bond, there must be an electron-deficient atom and an atom with an excess number of electrons. In this case, Na (Sodium) has excess electrons, and Cl (Chlorine) is electron deficient. 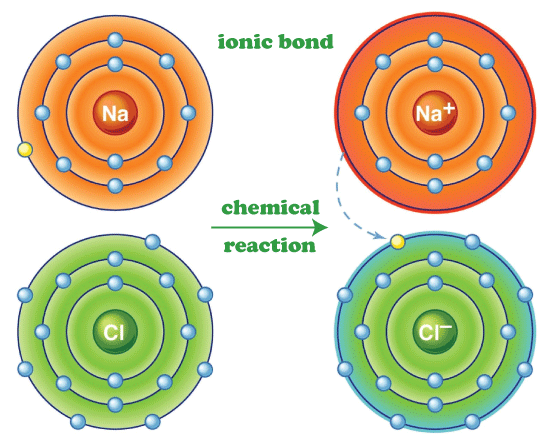
The atomic number of Na (Sodium) is 11, and the number of valence electrons in the Na (sodium) is 1. It has only one electron resisting it to attain a stable noble gas configuration, so to become stable, Na (Sodium) loses one electron and gets a positive charge over it. On the other hand, Cl (Chlorine), whose atomic number is 17, and the number of valence electrons on Cl (Chlorine) is 7. Moreover, there is only one electron that is resisting it from becoming stable and getting a noble gas configuration, so it accepts the electron from some external source means that an atom that has an excess number of electrons, like Na (Sodium), shares the electron and forms an ionic bond, that is highly stable in both means that is physical and chemical, they did not dissociate further to form any other form of a chemical compound. Covalent Bond: The next type of chemical bonding is the Covalent Bond; this is a special type of chemical bonding which includes the mutual sharing of an equal number of electrons from both sides. Their bonds are known as bonding pairs or bond pairs. One of the best examples of a Covalent Bond is the formation of CH4 in which C (Carbon) shares an equal number of electrons from all four Hydrogen and hence forms a covalent bond. Hydrogen Bonds: In this type of chemical bonding, the Hydrogen forms a pair with the highly electronegative atom of the other compound, and the bonding electron pair is slightly more shifted towards the electronegative atom. Some examples of electronegative atoms are Nitrogen, Oxygen and fluorine. These chemical bonds formed are weak and can easily be broken during a chemical reaction.
Next TopicMoment of Inertia Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










