IPS - Intrusion Prevention SystemIntrusion Detection and Prevention System is another name for Intrusion Prevention System. It's a network security program that looks for harmful activity on a network or system. Intrusion prevention systems' main functions are detecting malicious behavior, collecting information about it, reporting it, and trying to block or stop it. Because intrusion prevention systems and intrusion detection systems both monitor network traffic and system operations for malicious behaviour, intrusion prevention systems are used in conjunction with intrusion detection systems (IDS). 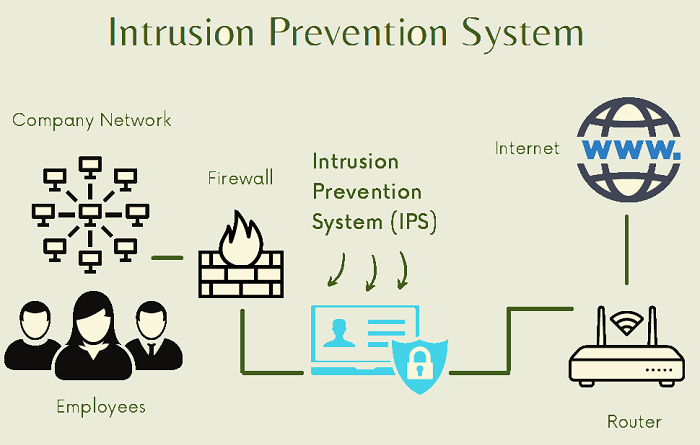
IPS normally logs information about observed events, notifies security administrators about significant occurrences, and generates reports. Many IPS can also try to prevent a threat from succeeding if it has been discovered. They utilize various response strategies, including the IPS interrupting the attack, modifying the security environment, and changing the substance of the attack. Why is Intrusion Prevention Systems important?To enable secure and trusted information exchange across diverse businesses in today's networked business environments, a high level of security is required. After traditional technologies, an intrusion prevention system serves as an adjustable safeguard technology for system security. Lower expenses and higher performance flexibility result from avoiding incursions by an automated approach that does not require IT intervention. Because cyber-attacks are only going to get more complex, defensive technology must keep up. Advantages of Intrusion prevention systemThe following are some of the advantages of intrusion protection systems:
Drawbacks of Intrusion prevention systemsThe following are some of the disadvantages of intrusion protection systems:
Classification of Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) is arranged into four kinds:
How do intrusion prevention systems detect malicious activity?Intrusion prevention systems detect malicious activity in a very different way by utilising different techniques, but the two most common are signature-based detection and statistical anomaly-based detection. In its signature-based detection mechanism, intrusion prevention systems use a dictionary of individually identifiable signatures detected in the code of each exploit. There are two types of signature-based detection approaches for intrusion prevention systems: exploit-facing and vulnerability-facing. Detecting harmful activity by identifying individual vulnerabilities is the goal of exploit-facing methodologies, whereas detecting malicious activity by detecting common attack patterns is the goal of vulnerability-facing methods. Difference between Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)The following features differentiate Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) from Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS):
Detection Method of Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
How Do IPS Work?An intrusion prevention system detects malicious activity and recognizes attack patterns by actively examining routed network data. The IPS engine regularly scans network traffic for known attack patterns and compares it to its own signature database. An IPS is intended to guard against a wide range of threats, including the following:
The IPS thoroughly inspects every packet that travels across the network in real-time. If the IPS detects any malicious or suspicious packets, it will take one of the following actions:
Types of PreventionTo defend the network from unauthorized access, an intrusion prevention system is usually set up to use various methods. These are some of them:
IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) - Proactive Network SecurityIPS systems provide proactive protection against some of the most well-known network exploits of today. When properly configured, an IPS protects against malicious or undesired packets as well as brute force attacks. The Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) from Forcepoint provides robust intrusion prevention and detection for any network, allowing you to respond to threats in minutes rather than hours and protect your most valuable data and application assets. What has been the evolution of IPS technology?Because firewalls lacked deep packet inspection (DPI) capabilities in the early 2000s, IPS was considered a separate technology from firewalls. As a result, IPS sits in front of the firewall, monitoring traffic and taking its security measures. However, because early effective IPS solutions - like antivirus manufacturers - relied primarily on maintaining a signature database, the process of scanning traffic had a few issues. First, DPI-based matching could cause network traffic to slow down, and second, legitimate traffic was a serious worry. Later generations of IPS systems included faster inspection, the use of machine learning for detection, and the addition of user and application control, where only certain accounts can access some or all of an application (called "next-generation IPS"). IPS soon made its way into next-generation firewalls (NGFW), allowing it to do even more things based on DPI and user activity, like blocking known malware, modifying URL filtering, and reconfiguring VPNs and the firewall itself. Furthermore, advancements in user and application-based security-enabled enterprises to monitor, detect and enforce internal compliance with security policies as part of their overall security strategy. The advantages of a next-generation firewallIt's critical to think about a next-generation firewall when adopting IPS. Most NGFWs include IPS technology (replacing the need for a separate solution) and offer a number of advantages to the organisation, including improved network security, increased user productivity, improved bandwidth management, optimization, simplified management, and lower total cost of ownership. Traditional firewalls only filter traffic into and out of the business network, whereas NGFWs, with their DPI and IPS capabilities, assist in combating particular cyberattacks on apps. The issues of an IPS are strongly intertwined with those of an NGFW, making it a very realistic option for most enterprises looking to increase their cyberthreat prevention while also enhancing adherence to corporate security policies. Why is Next-Generation Protection Important?Ransomware usually infiltrates a network and spreads in one of several ways:
Blocking network exploitsNext-generation firewalls must have IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) technology. It searches network traffic for specific exploits, patterns, and abnormalities that suggest an attack using deep packet inspection. Attacks often use malicious inputs to compromise a host program or service, such as the Eternal Blue exploit used by WannaCry and Not Petya, to gain sufficient control to execute malware such as ransomware. Types of Network threats:
Selecting the most effective intrusion prevention systemThe market for intrusion protection systems is extremely diverse. As a result, selecting the best intrusion detection system is a difficult task. There are many necessary steps that are important for reducing the complexity of selecting the best intrusion prevention system (IPS) i.e., Setting a budget, defining the specifications that your new system must meet, and researching the many intrusion prevention systems in the market. Keep in mind that an intrusion prevention system is a stand-alone security solution. While an intrusion prevention system (IPS) can help detect malicious network activity, a comprehensive security strategy should include data protection, endpoint security, incident response, and other technologies and resources. ConclusionAn IPS can be used as a programming tool or as a piece of equipment. In a perfect world (hypothetically), IPS relies on the simple rule that filthy traffic enters and clean traffic exits. Intrusion prevention systems are essentially intrusion detection systems that have been expanded. The main difference is that, unlike intrusion detection systems, Intrusion Prevention Systems can block and prevent successfully detected blockages. An IPS, for example, can drop vengeful packages, obstructing traffic from a responsible IP address, and so on.
Next TopicIAS - Indian Administrative Service
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










