Javascript promise chainingPromise Chaining is a straightforward idea that allows us to initialize a second promise inside of our.then() method and then execute our results as a consequence. The value returned by the earlier promise is then captured by the function within. There are instances when we need to run two or more related asynchronous operations, with the first operation beginning with the outcome of the prior one. Promises come in handy when we need to manage multiple asynchronous tasks sequentially. We employ promise chaining for this. With the methods then(), catch(), and finally, we can carry out an action once a promise is fulfilled (). Syntaxes for promises in a chainFirst syntax Sometimes we wish to carry out several asynchronous tasks in succession. Also, we must transmit the outcome of the prior stage to the subsequent one. We can employ the following syntax in this situation: Second syntax Use the following syntax if we need to convey the result from the previous job to the subsequent one without passing the result: How to operate promise chaningThe syntax shows the javascript promise chaining operation and working procedure. Explanation
Examples The following examples show the chaining operation of the promise function. The following example avoids multiple handlers and uses promise chaining. Example 1 The basic promise chaining function shows two promises value as an output. We use the three promises and then() method. Output The image displayed promise chaining functions output. 
Example 2 The javascript promise chaining function shows multiple promises value with the operation as an output. We use various promises and then() methods with the required time. Output The image displayed promise chaining functions output. 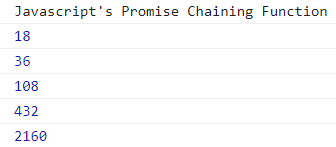
Example 3 The javascript promise chaining function shows multiple promises value with the operation as an output. We use various promises and then() methods with the required time. Output The image displayed promise chaining functions output. 
Multiple handlers for promise chaningIt does not work on the promise chaining when we repeatedly call the then() method on a promise. One promise has several handlers. These handlers don't have any connections. Also, unlike the promise chain, they execute separately and do not pass the output from one to another. Example The following example uses a single promise for multiple handlers. The output shows the initial promise value for each handler. Output The image displayed promise chaining functions output. 
ConclusionThe promise chaining shows multiple outputs using the "then()" method. The method uses the promise variable. It works for single input and multiple outputs using equations. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










