JDBC Driver
JDBC Driver is a software component that enables java application to interact with the database. There are 4 types of JDBC drivers:
- JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
- Native-API driver (partially java driver)
- Network Protocol driver (fully java driver)
- Thin driver (fully java driver)
|
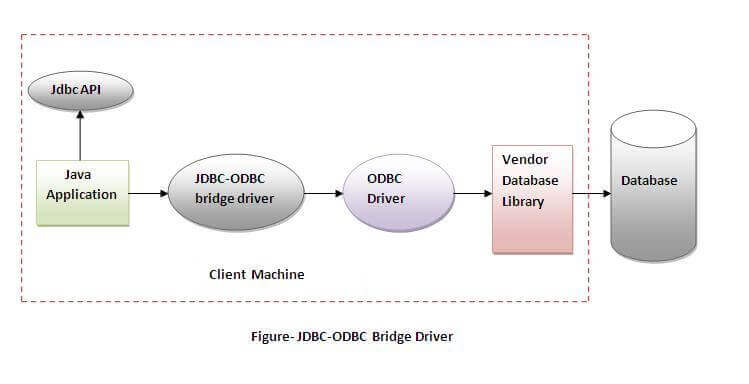
1) JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
| The JDBC-ODBC bridge driver uses ODBC driver to connect to the database. The JDBC-ODBC bridge driver converts JDBC method calls into the ODBC function calls. This is now discouraged because of thin driver.
|
In Java 8, the JDBC-ODBC Bridge has been removed.
Oracle does not support the JDBC-ODBC Bridge from Java 8. Oracle recommends that you use JDBC drivers provided by the vendor of your database instead of the JDBC-ODBC Bridge.
Advantages:
- easy to use.
- can be easily connected to any database.
Disadvantages:
- Performance degraded because JDBC method call is converted into the ODBC function calls.
- The ODBC driver needs to be installed on the client machine.
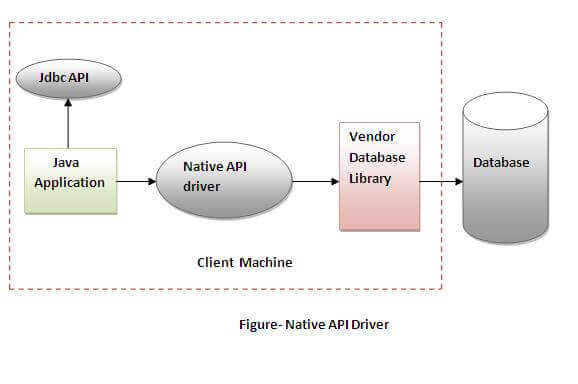
2) Native-API driver
| The Native API driver uses the client-side libraries of the database. The driver converts JDBC method calls into native calls of the database API. It is not written entirely in java.
|
Advantage:
- performance upgraded than JDBC-ODBC bridge driver.
Disadvantage:
- The Native driver needs to be installed on the each client machine.
- The Vendor client library needs to be installed on client machine.
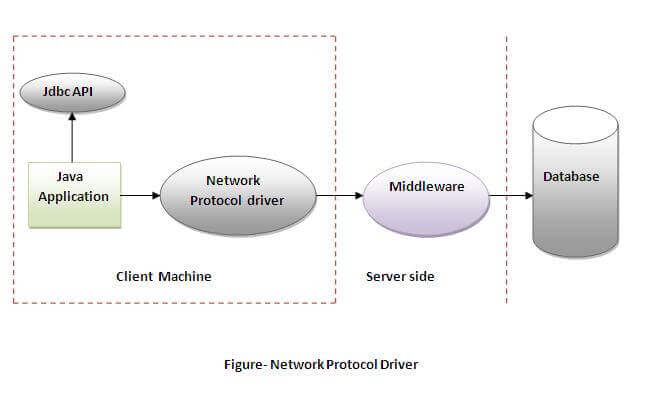
3) Network Protocol driver
The Network Protocol driver uses middleware (application server) that converts JDBC calls directly or indirectly into the vendor-specific database protocol. It is fully written in java.
Advantage:
- No client side library is required because of application server that can perform many tasks like auditing, load balancing, logging etc.
Disadvantages:
- Network support is required on client machine.
- Requires database-specific coding to be done in the middle tier.
- Maintenance of Network Protocol driver becomes costly because it requires database-specific coding to be done in the middle tier.
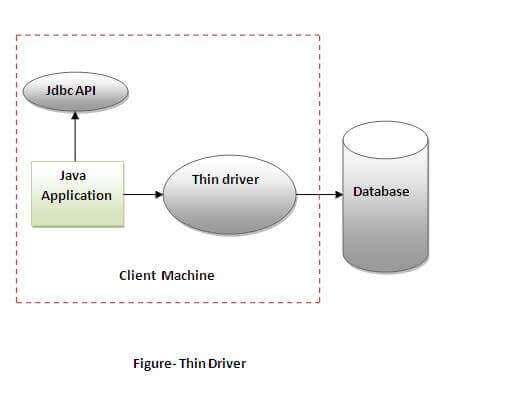
4) Thin driver
| The thin driver converts JDBC calls directly into the vendor-specific database protocol. That is why it is known as thin driver. It is fully written in Java language.
|
Advantage:
- Better performance than all other drivers.
- No software is required at client side or server side.
Disadvantage:
- Drivers depend on the Database.
|




 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










