Linux/Unix: chroot CommandWhat are the chroot commands?The "chroot command" is a Unix/Linux command. It is used to change the root directory to a new directory in the Linux/Unix operating system. The new directory is known as chroot jail and jail directory. It is an effective and simple command for the user toolset. Once you are inside two root directories, you cannot use any directory above it. If you create a fake root-directory for a user, it loses access to the real root directory. Usually, the following changes are made to the root for system maintenance:
Syntax of chroot command The chroot command in Linux has the following syntax.
The chroot command requires a parameter to run the command, and this parameter gives way to the new root directory. You can use these available options to get the result you want. Option:
Creating a chroot.jailA chroot jail is a virtual directory. It is created by converting the root directory to a new directory. It acts as a dummy root directory for your chroot jail. 1. Create a Directory In this command, first we create a fake root directory using the mkdir command. This command is shown below. 
This command creates a directory at the given address that we use for the chroot jail directory, and before running this command, we add the required files to the new directory. 2. To add Required Root Directories in chroot jail Firstly, in this command, we create the required directories (/ bin, / lib, and / lib64) in the chroot jail directory. The required directories are specified in the bracket ("{}"), as you can see in the below command syntax. 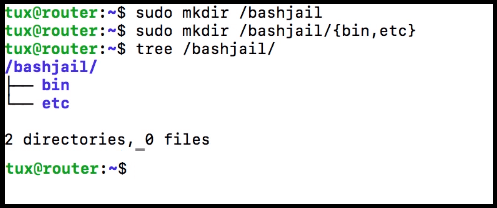
3. Move the Binary Files We create a minimalistic Linux environment for this command, and we use the ls, bash touch, and rm commands to enhance the functionality of the virtual environment. 
Note: In this command, we use the cp command and the -v tag to see what is being copied at that time.4. To find the Command Dependencies We can find out the dependency of a command using the ldd command. Now, we'll copy directories one by one in our chroot jail using the cp command. We check the copy of all dependency libraries. If there is a problem with dependency libraries, chroot jail will not run properly. 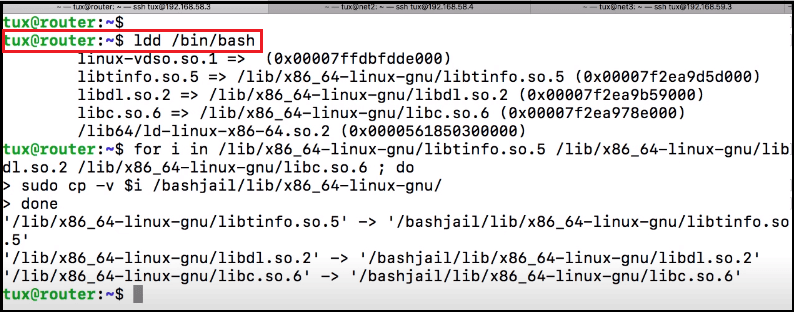
We will repeat these steps inside the Chroot jail with all the commands we want to allow.
Next TopicLinux Watch Command
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










