Linux Commands to Check Disk SpaceThere are many ways by which we can check the Linux system disk space. We can use a third-party app which displays the available disk space. Another way is the command-line by the Linux Terminal, some of which are df and du, where du means disk space used and df means disk space free. 1. Using du CommandWe can check the disk space with the help of the du command. The full-form of du is "Disk Usage." The du command shows the usage of disk. The du command will show you the disk usage for specific directories in Linux. Syntax: 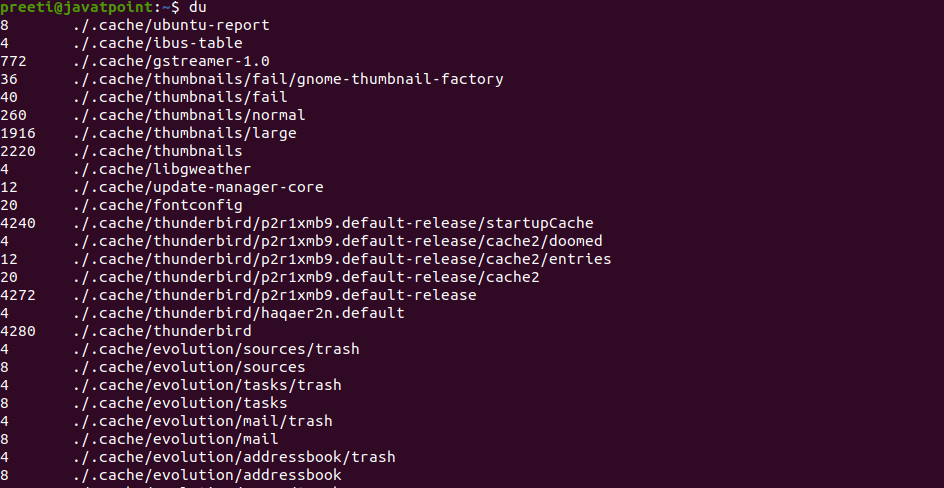
Syntax: 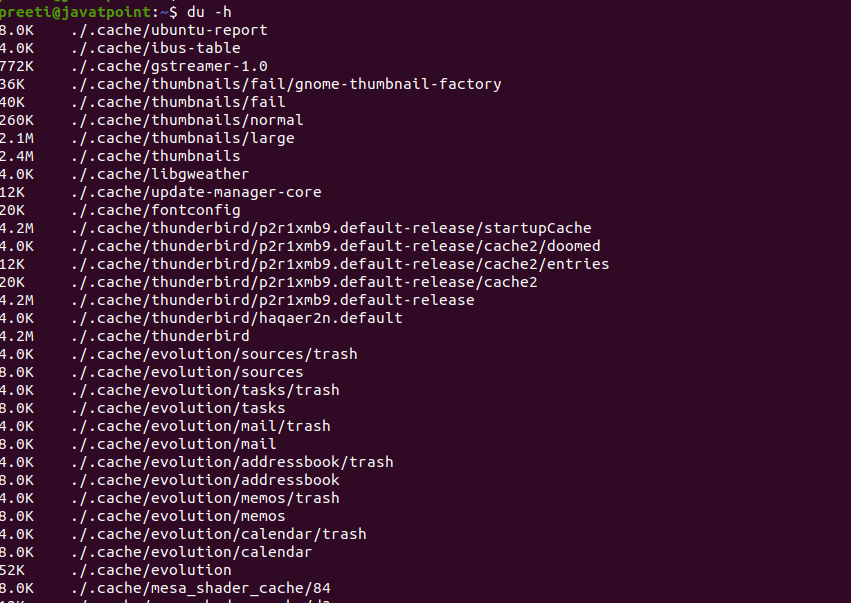
Syntax: 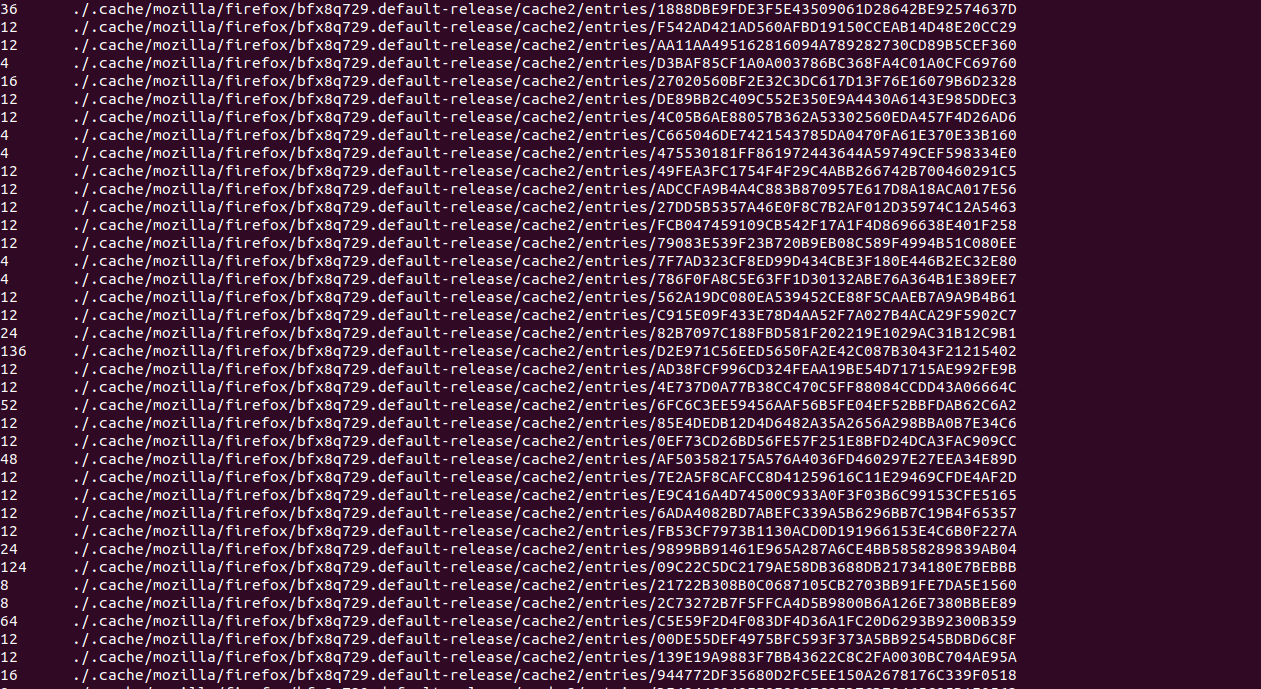
Syntax: 
Syntax 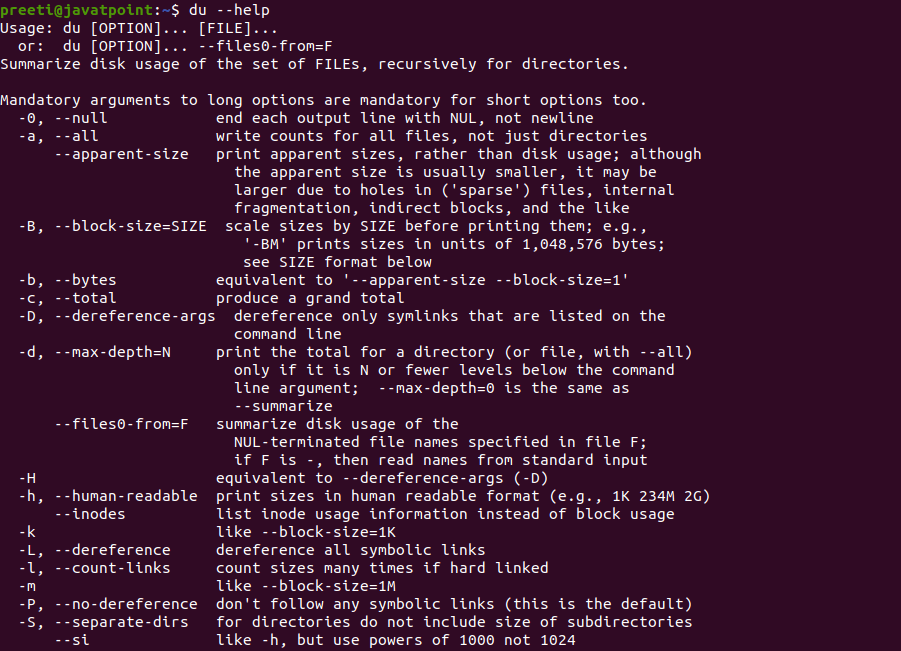
2. Using the df optionThe full-form of df command is "disk-free,". Using this command, we can check the used and available disk space in the Linux system. Syntax: When we use this command with no parameter, then this command will show you the information related to all the mounted file systems: 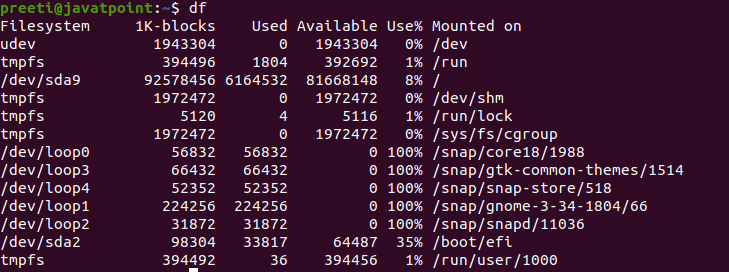
The following columns are contained in each line:
If we want to show the information for a particular file system only, we can pass the name or the mount point of the file system to the df command. For example, if we need to display the space which is available on the file system mounted to the root directory (/) then we can use the df/dev/nvme0n1p3 or df/. Syntax: 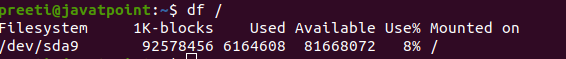
Show Disk Space Usage in Huma Readable FormatBy default, this command will display the disk space in 1-kilobyte blocks, and the size of available and used disk space will display in kilobytes. If we want to show the details of disk drives in a human-readable format such as gigabytes, megabytes, kilobytes etc., then we have to use the df command along with the option -h. Syntax: 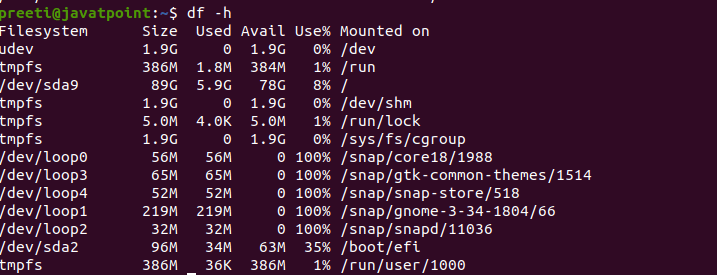
File System TypesIf we notice all the command output, we can see no Linux file system type specified in the results. In order to check the file system type of our system, we can use the 'T' option. The 'T' option will show the file system type with other information. We can use the -T option to tell df to display the file system types: Syntax: 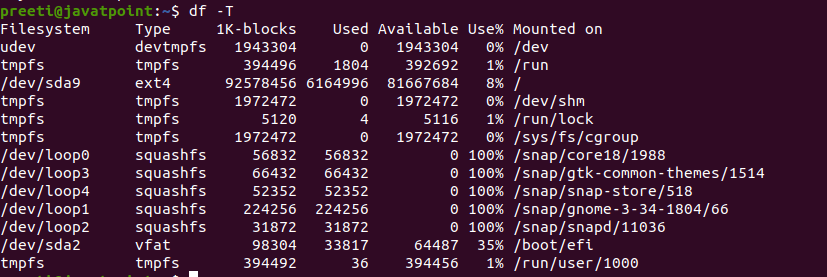
The output contains an extra column named "Type: which displaying the filesystem's type. Display Inode UsageAn inode is a data structure in Linux and Unix file systems including information of a file or directory like owner, size, device node, pipe, socket, etc. If we invoke this with the -i option, then the df command prints information related to the filesystem inodes usage.. 
The above command will display the details of inodes on the file system which is mounted to the root directory of the system in a human-readable format. When we use the -i option, then each output's line contains the following columns:

Display Information of /home File SystemIf we want to see the information of only the device /home file system in the human-readable format, then we can use the following command: 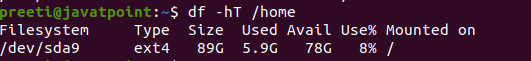
Display Information of File System in BytesIf want to see the information and usage of file system in 1024-byte blocks, then we can use the '-k' option. Syntax: 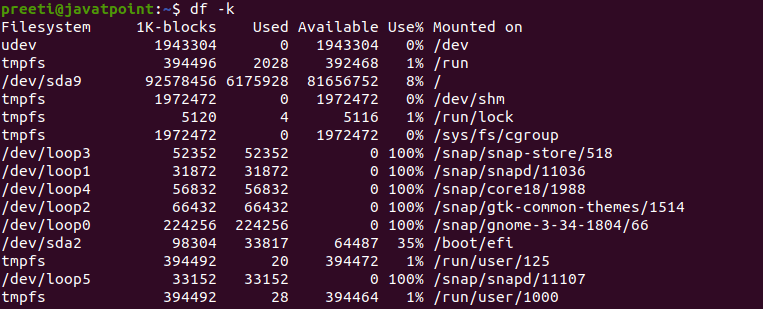
Display Information of File System in MBWe can use the '-m' option in order to show the information of all file system usage in MegaByte (MB). 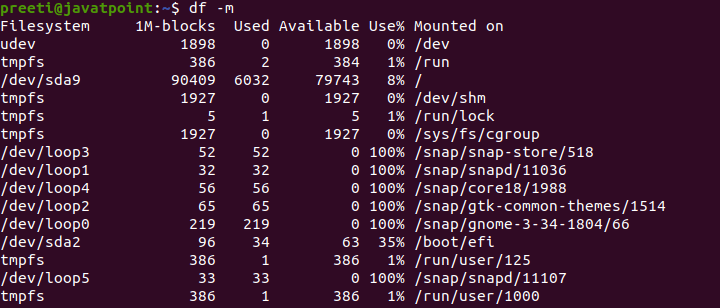
Display Information of File System in GBWe can use the 'df -h' option if we want to show information of all file system statistics in Gigabyte (GB). Syntax: 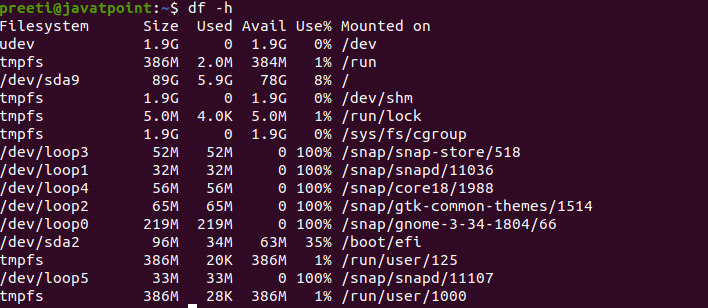
Next TopicManjaro Vs. Ubuntu
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










