Linux Memory DirectoryMemory directory contains files of the whole system. All the device information, process running indata or system related information are stored in this directory. Memory directory contains the following directories.
/devThe term 'dev' is short for device. As you know in Linux operating system everything is a file. It appears to be an ordinary file but doesn't take up disk space. Files which are used to represent and access devices are stored here including terminal devices like usb. All the files stored in '/dev' are not related to real devices, some are related to virtual devices also.
/procThe term 'proc' is short for process. Same as '/dev', '/proc' also doesn't take up disk space. It contains process information. It is a pseudo filesystem that contains information about running processes. It also works as virtual filesystem containing text information about system resources.
Example: 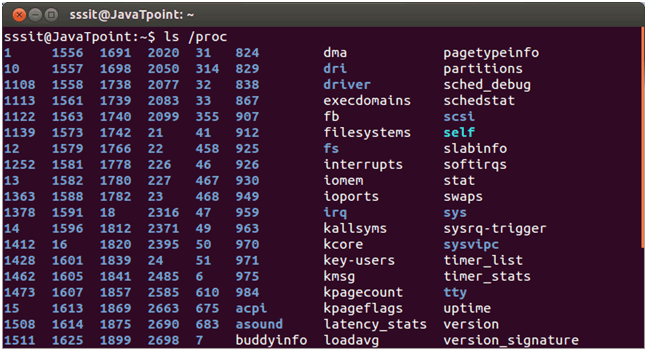
Look at the above snapshot, command "ls /proc" displays content of '/proc'. Many files are named as numbers and some named files are also there. The '/proc' has some file properties like date, which keeps on updating as shown in the below snapshot. 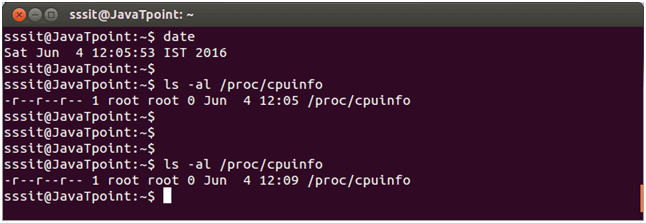
Also most of the files in '/proc' are of 0 bytes yet they contain a lot of data. Most of the files are readable only, some require root privileges and some are writable.
Example: 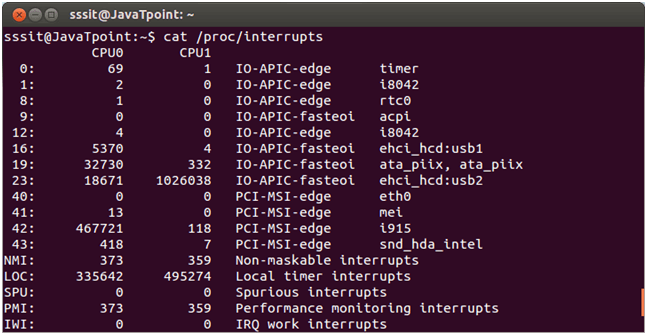
Look at the above snapshot, when a system have two CPUs, files will look like this. /sysThe term 'sys' is short for system. Basically it contains kernel information about hardware. It was created for Linux 2.6 kernel. It is a kind of '/proc' and is used for plug and play configuration.
Next TopicUnix System Resources
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










