Variable Directory (/var)The term 'var' is short for varible. Files that have an unexpected size and whose content is expected to change continuously (that's why it is named as variable) during normal operation of the system are stored here. For example, log files, spool files and cache files. Example: 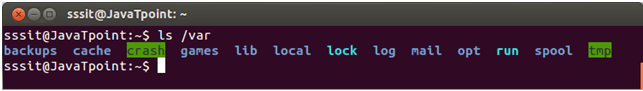
Look at the above snapshot, command "ls /var" displays '/var' content. We'll explain some of the /var sub-directories here:
/var/logThe '/var/log' directory contains all log files. Example: 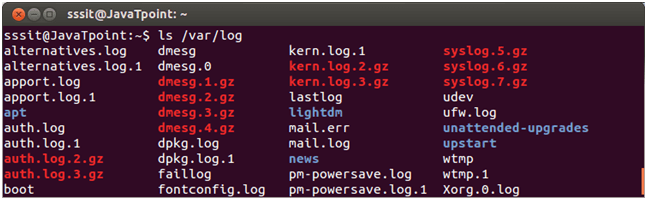
Look at the above snapshot, command "ls /var/log" displays the '/var/log' content. /var/cacheThe '/var/cache' directory stores application cache data. Cache data are locally generated by I/O or calculation. Cache must be able to regenerate or restore the data. These files can be deleted without any loss of data. Example: 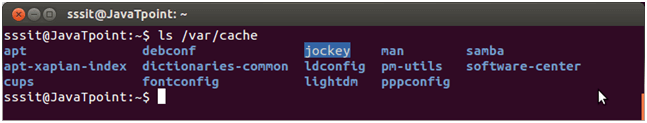
ls /var/cache Look at the above screenshot, command "ls /var/cache" displays the '/var/cache' content. /var/spoolThe '/var/spool' directory is used to spool the files waiting to be processed. For example, printing queues and mail queues. Example: 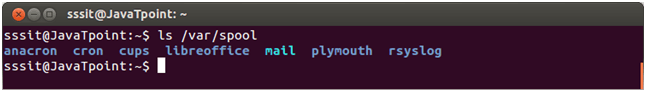
Look at the above screenshot, command "ls /var/spool" displays the '/var/spool' content. /var/libThe '/var/lib' directory stores the files that contains state information like databases. File's data modifies as their respective programs run.
Next TopicNon-Standard Directories
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










