Linux Find FileThe find command in Linux is a robust tool that allows system administrators to manage and locate directories and files based on a huge range of search techniques. It can search files and directories by the type, name, or permissions, size, extension, etc. Besides locating directories and files, associating the find command along with others allows us for taking action over the outcomes. Including the -exec option allows system admins to execute external commands and implement actions like moving, deleting, copying, or modifying permissions of the file that are matching the described criteria like name, size, etc. The find command searches for various directories and files inside the directory hierarchy which is based on the user-provided expression. It could implement user-specific operations on all the matched files. Also, we can add with various other tools like sed or grep. Syntax-The basic syntax for Linux find command is as follows: Where,
Options in find commandThere are various options available in find command. Some of the important options are discussed and explained as follows:
Find directories and filesFind particular files by extension or nameTo search for a particular file, we can execute the below command through the root (/). This command includes the matching name for the file we are looking for. 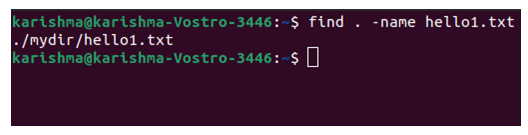
Remember that the outcomes contain the path. It's important when we do not know the directory in which the file is positioned, or when it's in multiple places. We can also find the file in other directories while still inside the current position. We need to facilitate the path for our directory in which we wish to search. 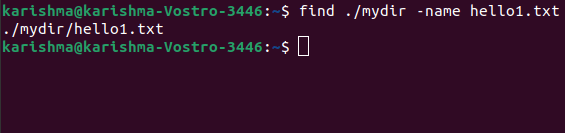
Looking for particular files in other directoriesIn this case, we will find for each of those files that are beginning with the file letters inside the newdir directory. 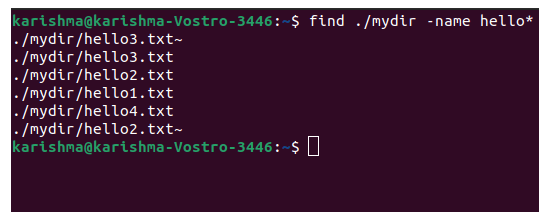
Find for files by their extensionIn Linux, for finding a file along with a specific extension, include it to the command. 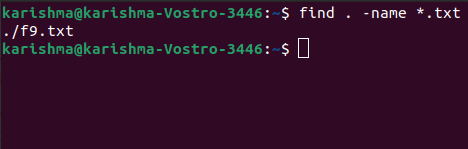
Find directories and files by nameApply the following command to search for directories and files beginning with the hello letters. In our system, we have hello1, hello2, hello3, and hello4 files. So let's execute the command: 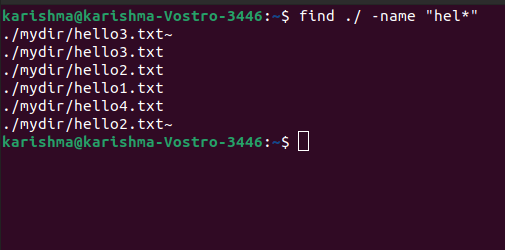
The above command will return all the directories and files that are starting with the hello letters. We need to describe it in this command to search directories or files only. Find only directory or filesFor only files, use the f type switch. 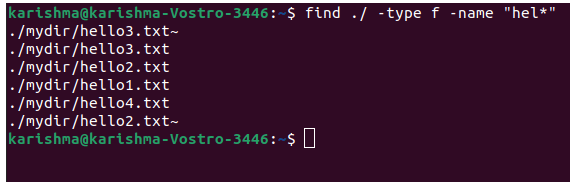
For only directories, use the d type option for locating only directories. 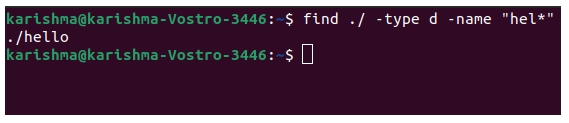
Find case insensitive commandAll finds with -name option is case sensitive and these will not provide outcomes with the capital letters. We can apply the -iname option for getting all cases: 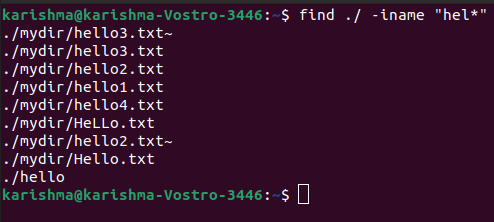
Find a file through more than one directoryFor finding the files in distinct directories, we can include their path inside the command. In this case, we will find it inside the newdir directory. 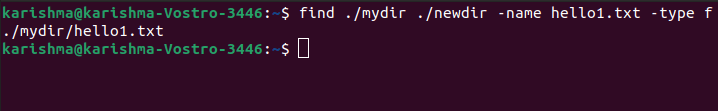
Find more than one file with distinct extensions from each directoryWe can apply the find command for locating more than one file that distributes the distinct extensions like *.pdf, *.txt, *.doc, etc. It could be separately done, a single extension at a time, or with the help of a single command that contains each desired extension. 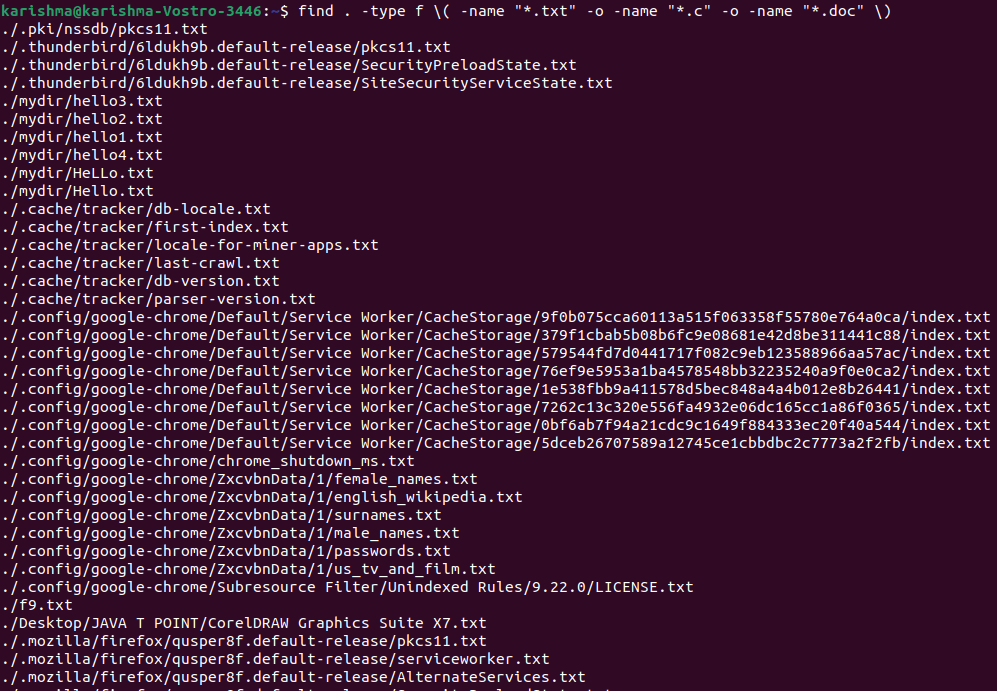
Find files including certain textWe wish to access the files including certain types of text but can't recall its file location and name. This command permits us to find each file including our target text. To search for each file including the hello word, we can use the following command: 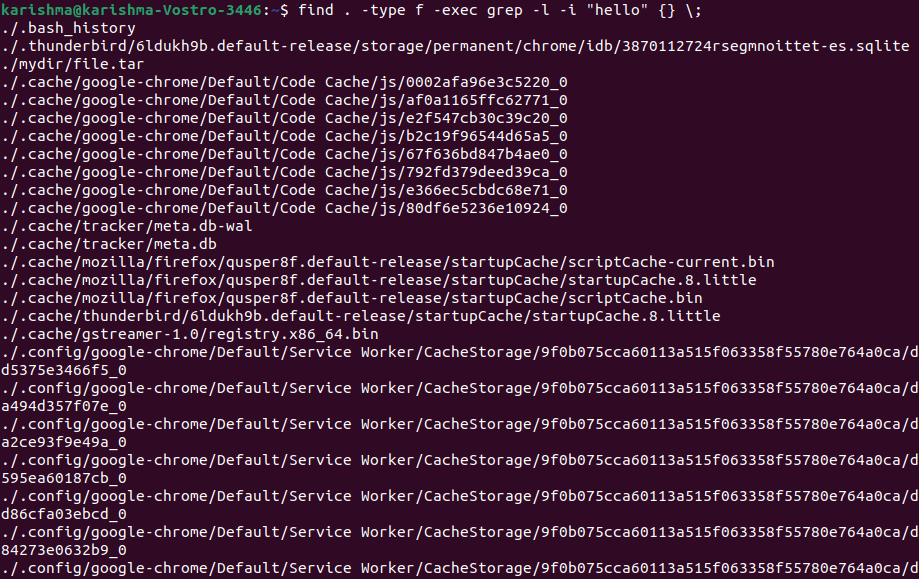
Option -i allows the command for ignoring cases and it will search that text whether it is capitalized or not i.e., hello, Hello, etc. To search for a file inside a particular directory, we can simply include them in our command. 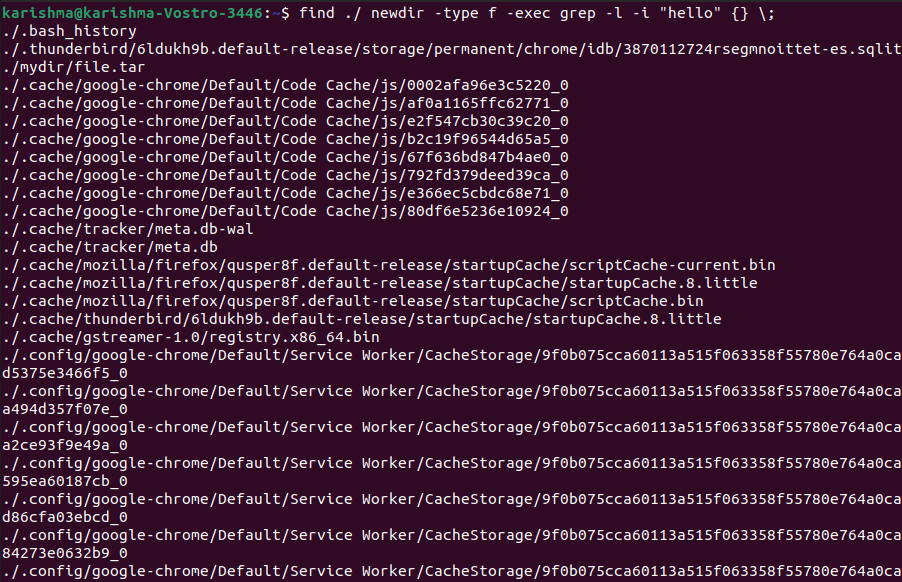
Find directories and files based on sizeWe can find all the directories and files that are greater, equal, or smaller than a specific size, in a spec range, or empty. Apply the proper size format based on the directory or file type we are looking for. Size options are: M- Megabytes G- Gigabytes c- bytes k- kilobytes Find files of a specific size- equal to 20MBTo find each 20MB file, we can use the following command: Find files bigger than a certain sizeWe can use the following command to find those files that are bigger than a certain size: 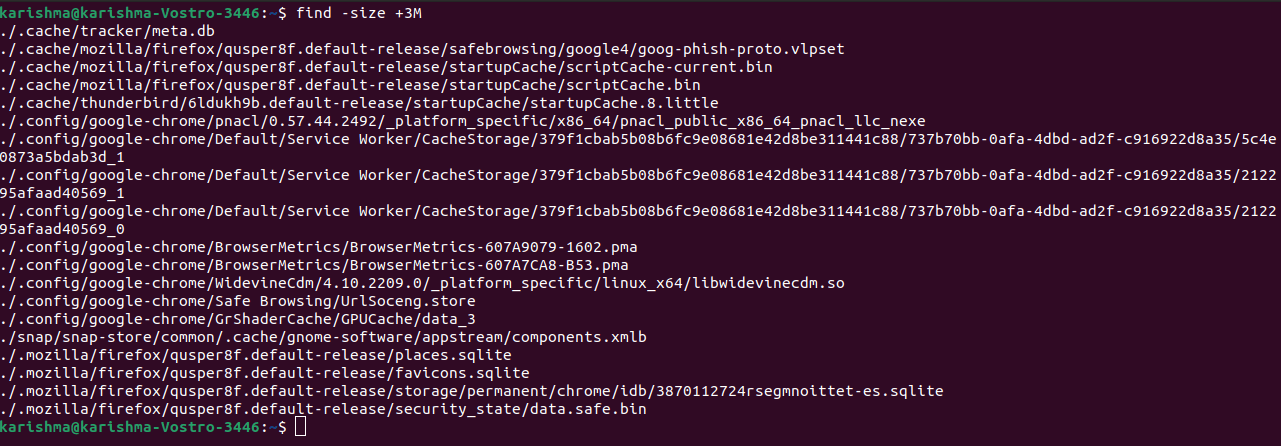
Find files smaller than 10MB in our current directoryWe can use the following command to find those files that are smaller than 10MB in our current directory: 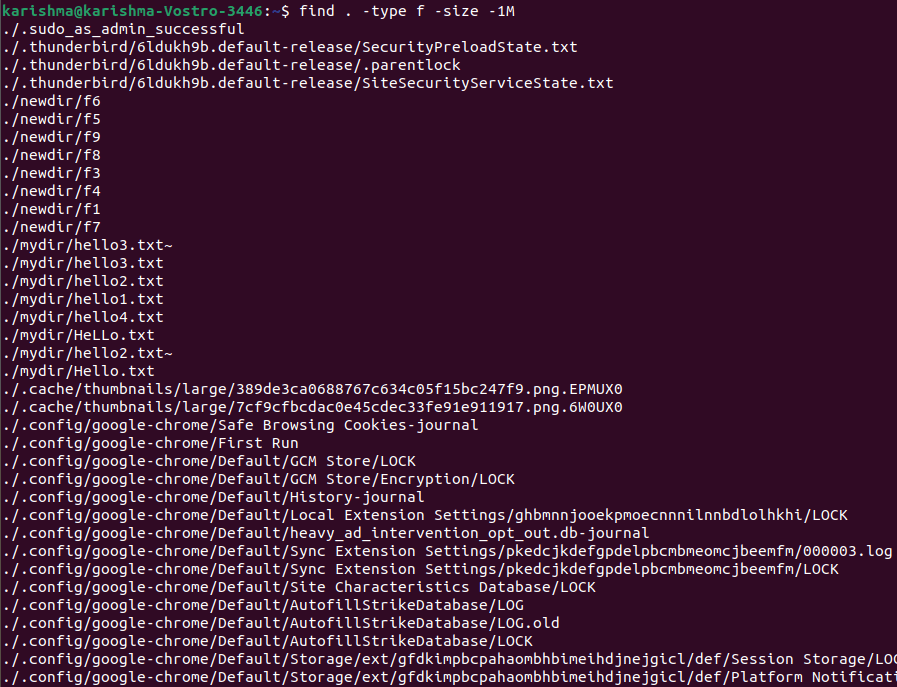
Find files that contain sizes between 1-3MBIf searching files in a certain range like between 1 and 3 MB, we can use the following command: 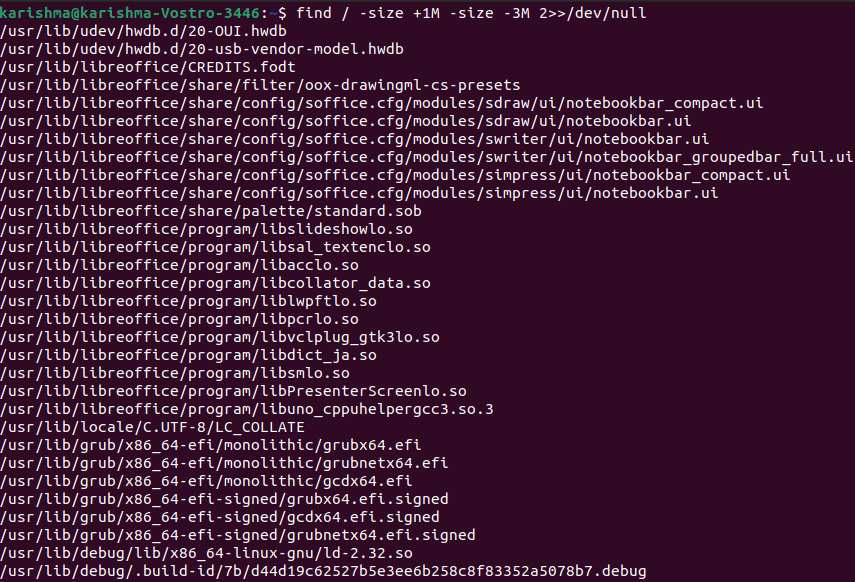
Find directories bigger than 10kbWe can use the following command: 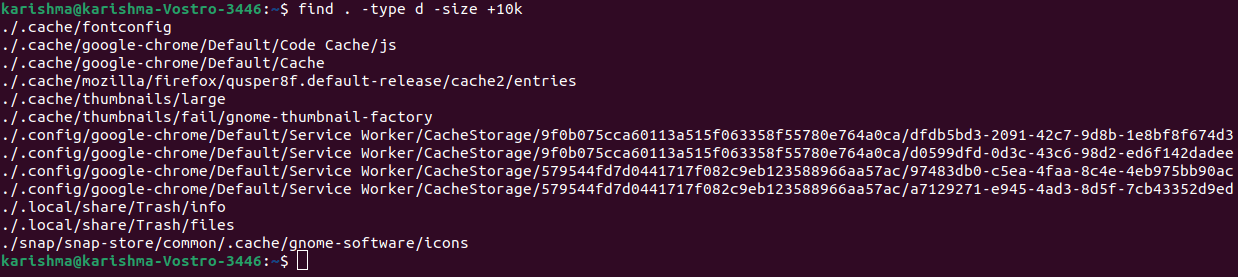
Find empty directories and filesFor filesWe can use the following command to find an empty file: 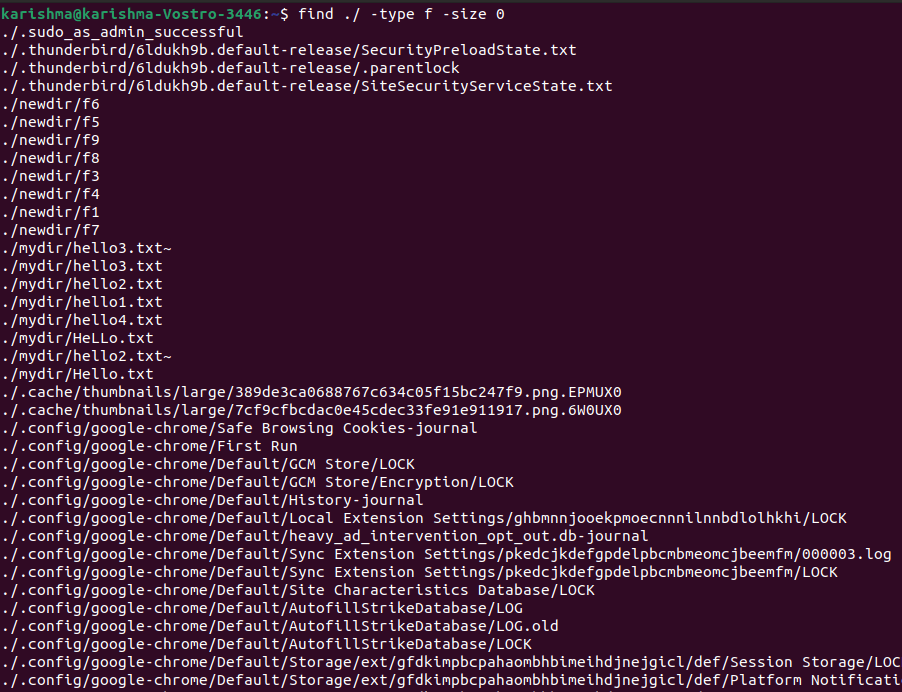
Or, For directoriesWe can use the following command to find an empty directory: 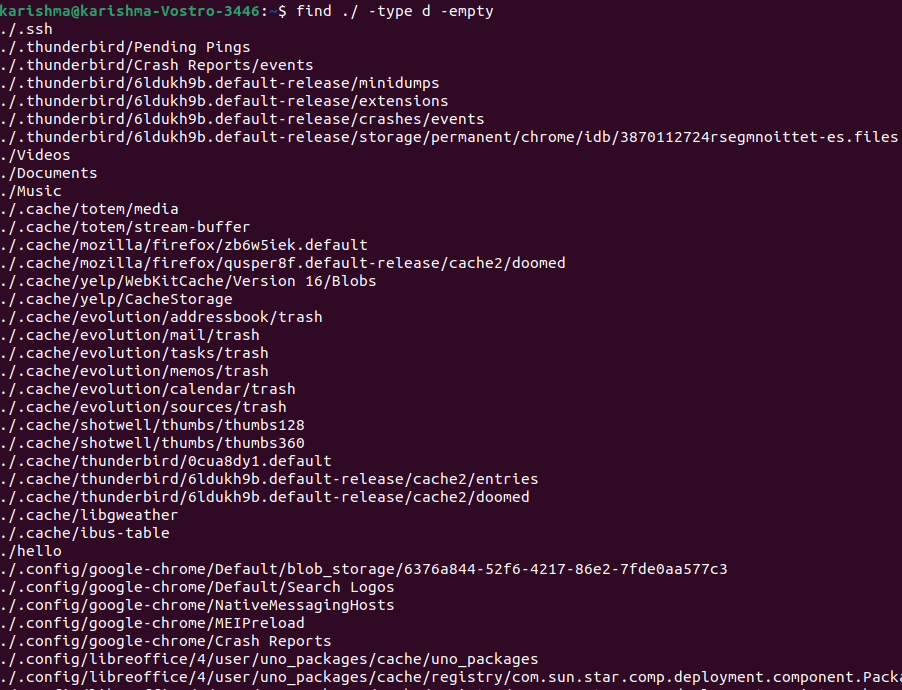
Find files by modification time or ageWith this option, we can find those files that were created before n days: 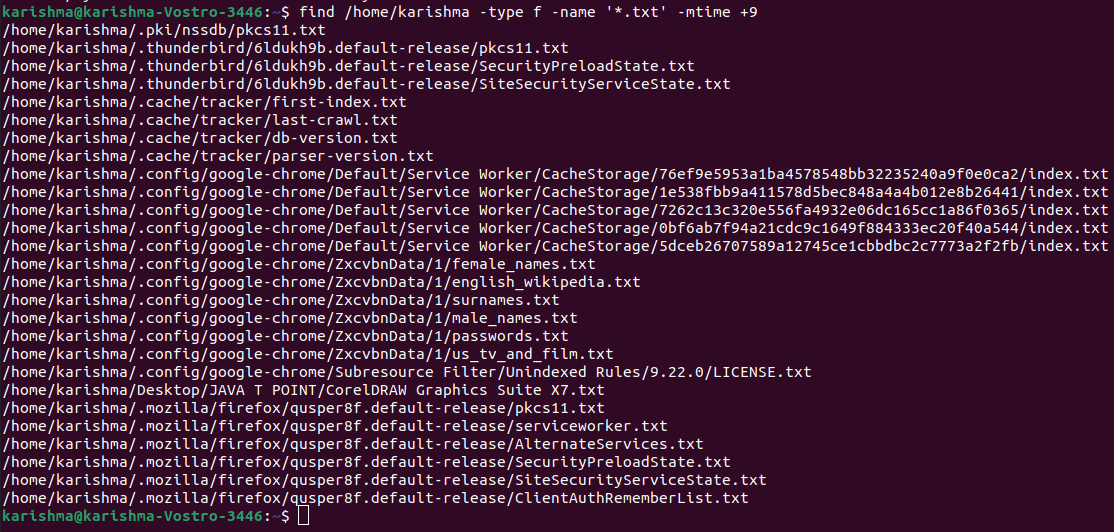
Where, -mtime +9 will search those txt files that were created before 9 days. Find a file by modification dateIt looks search those files that are modified in the last n hours. 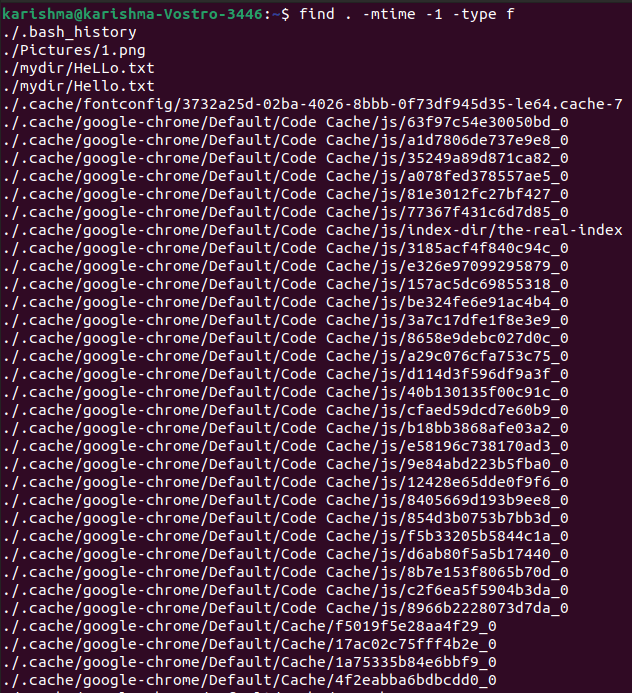
We can also use the following command to search those directories that are modified in the last n days: 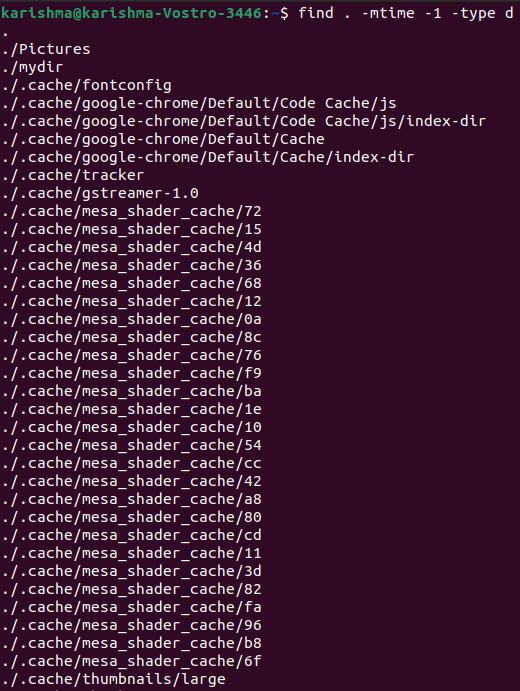
Find files according to modification or accessFind files according to time or date accessed. It permits us to look at files that haven't or have been accessed at a particular time. To look at files that haven't been accessed in the last 15 days in our home directory, we can use the following command: 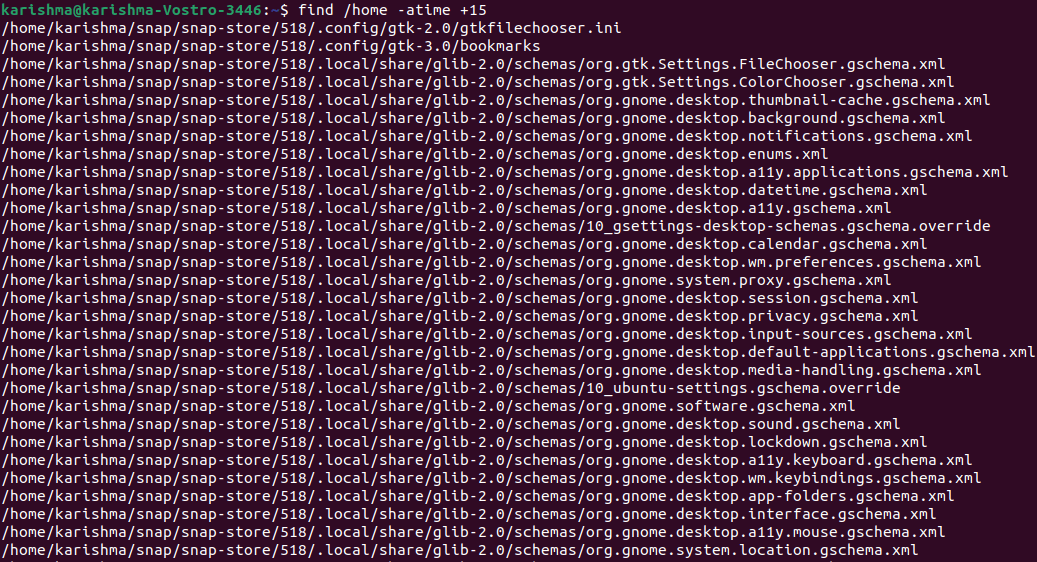
We can use the following command to see files that are accessed 15 days ago exactly: 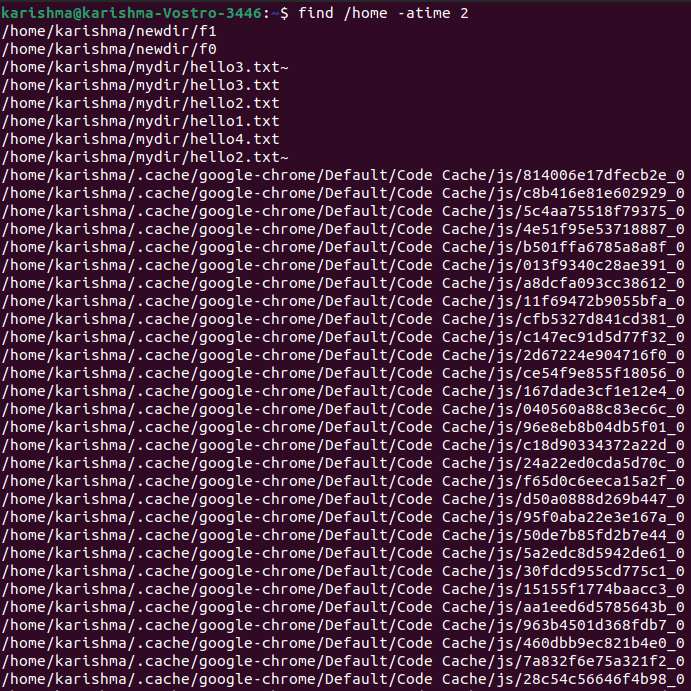
Also, we can use the following command to see files that are accessed in the last 15 days: 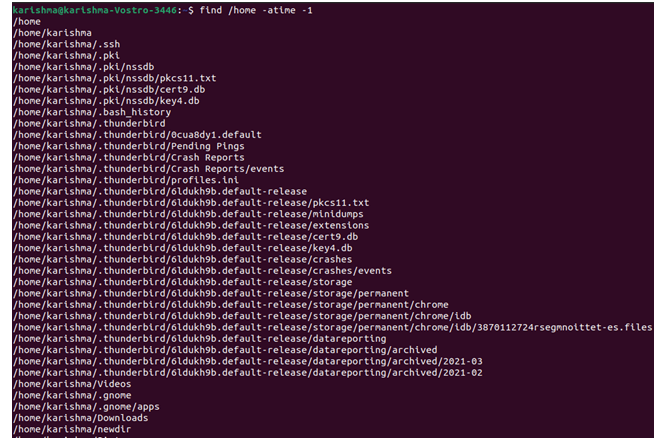
Find files changed in the last n daysWe can also consider files within the /home directory that changed in the last 1 days with the help of the following command: 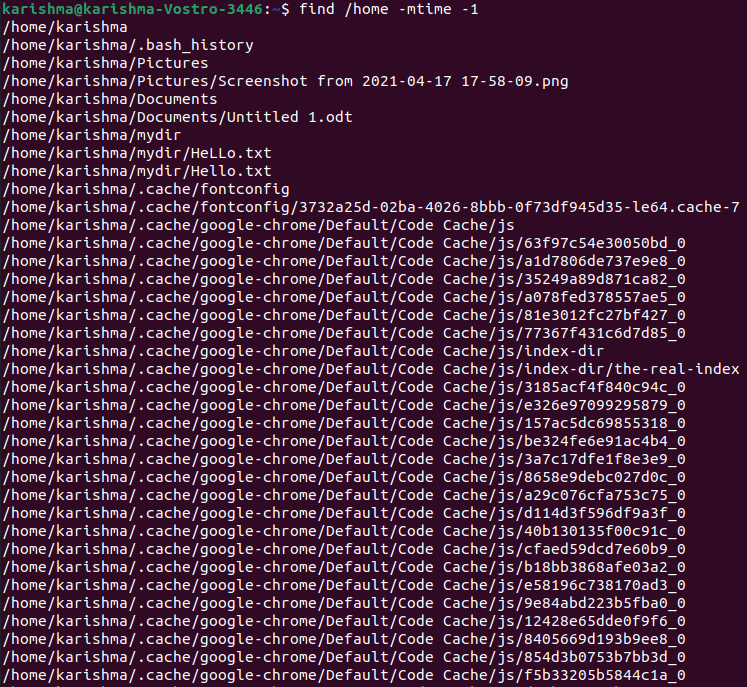
Find files changed in a particular timeFor example, each file changed between 7 and 16 days ago within our home directory. 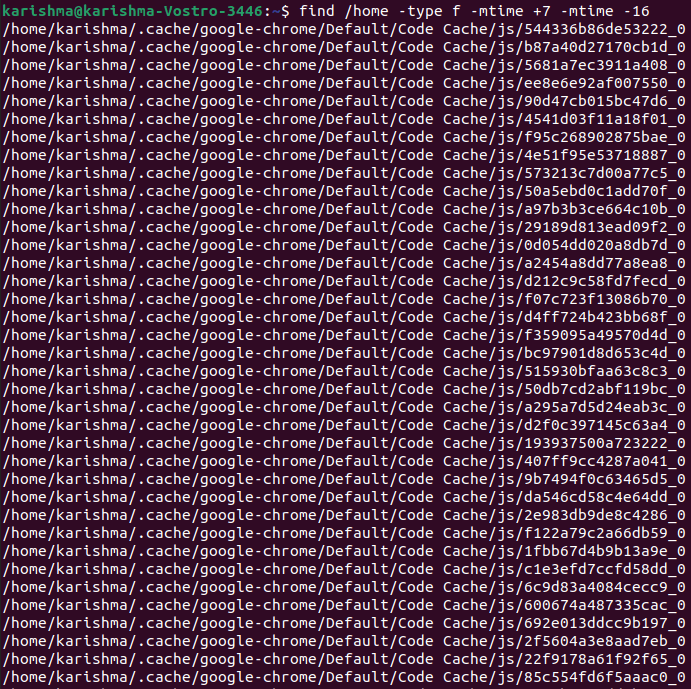
Directories and files accessed in the last n minutesFor files:To see files accessed in the last 15 minutes, we can use the option -amin. The command is as follows: 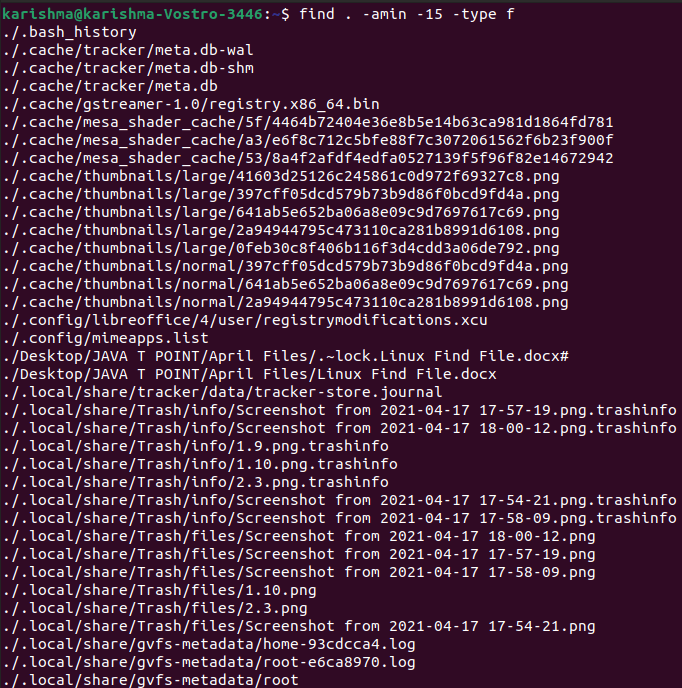
For directories:To see directories accessed in the last 15 minutes, we can use the option -amin. The command is as follows: 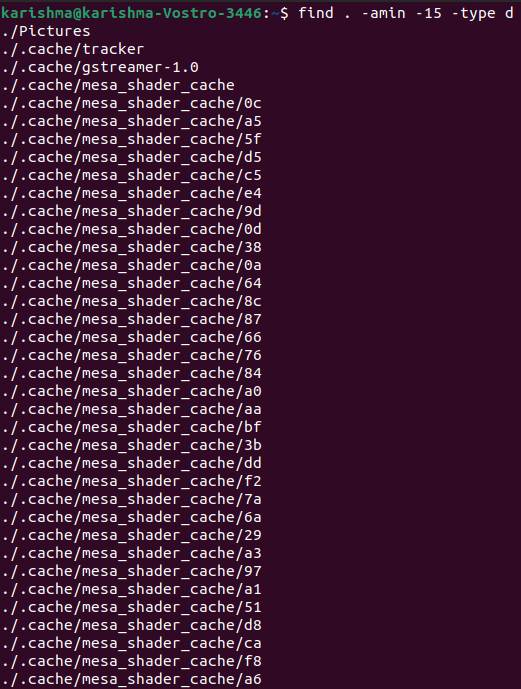
Next TopicEcho command
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










