Linux Source CommandSource is a built-in shell command. It is used for reading and executing a file's content (generally command set) and it is passed as any argument inside the shell script (current). The command after getting the specified file's content passes it towards the TCL interpreter like a text script which gets executed. The arguments become the positional parameters if filename is run when they are supplied. Otherwise, these positional parameters endure unchanged. In $PATH, the entries are used for finding the directory having FILENAME. But, if the file is not available in $PATH, it will find a file inside our current directory. In Linux, the source command includes no option and the file is the argument only. Syntax of the source command: Notes:
Examples: 1. For passing hello2.txt as the argument which is saved inside our home directory. All commands enlisted within the file will be run line by line. 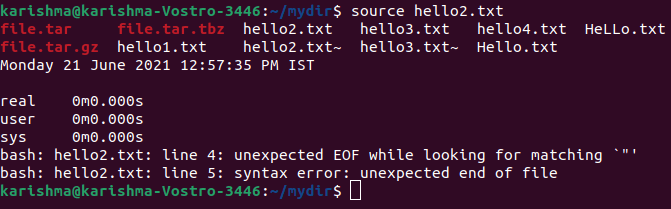
2. For passing the path_name of any file as the argument. The file's content is mentioned as follows: 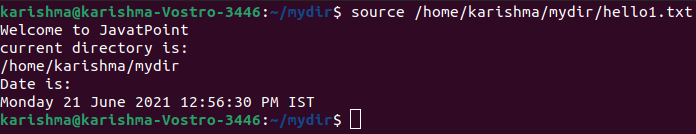
Next TopicLinux Terminal Shortcuts
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










