List of AcidsAcids are those substances or molecules that have a pH value of less than 7 (including negative values) and release hydrogen-ion while reacting with metals and other substances. Or, it can also be said that substances or molecules having pH values less than 7 are acidic in nature. Acids are generally sour in taste, promote chemical reactions, form salts when react with bases, liberate Hydrogen-ion while reacting with metals, and turn blue litmus paper to red. Generally, acids are categorized into the following two categories according to the pH value of the acidic molecule:
There are many popular acids that are used in daily life, and these most popular acids include both categories of acids (strong and weak acids). Following is a complete list of popular acids that can be seen and are used in everyday life: 1. Citric AcidChemical formula- C6H8O7 Other names- 2- Hydroxy-1,2,3- propanetricarboxylic acid Ph level- 3-6 Molar Mass- 192.124g/Mol 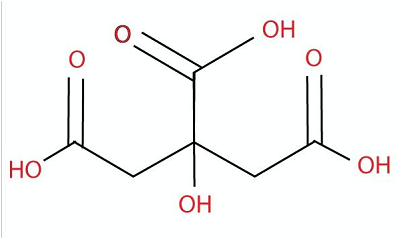
Citric acid is a natural acid derived from citrus fruits like oranges and lemons that gives the acid tart and sour taste. It is a weak organic acid that appears as odorless and colorless crystals. Uses:
Although, the acid produced is different from the acid found naturally. 2. Hydrochloric AcidChemical formula- HCl Other names- Marine acid, Spirit of salt, chloronium Ph level- 3.01 Molar Mass- 36.458g/Mol 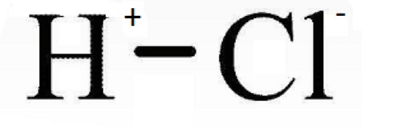
Hydrochloric acid is a highly corrosive strong acid that is found in diluted form as muriatic acid. It is a colorless solution with an extraordinary pungent smell. This acid is naturally produced in the stomach of humans that aids in the digestion of food. Hydrochloride acid is artificially manufactured for numerous commercial and industrial applications. It is formed synthetically by various manufacturing procedures like dissolving hydrogen chloride gas in water. Uses:
3. Acetic AcidChemical formula- HC2H3O2 Other names- ethanoic Acid, AcOH, CH3COOH, methane carboxylic acid Ph level- 2.5 Molar Mass- 60.052 g/mol 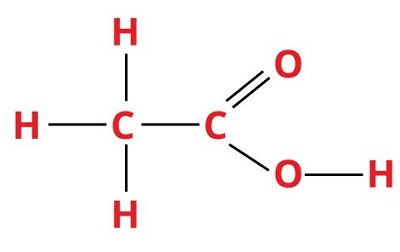
Acetic acid is an organic compound and one of the simplest carboxylic acids found in vinegar. It is the main ingredient of vinegar, as vinegar consists of about 5- 10% acetic acid. It is a weak acid that basically exists in an aqueous form that is clear, colorless, and with a pungent odor. Glacial acetic acid is formed when acetic acid is dissolved in water. Acetic acid is manufactured first and foremost as a predecessor to polyvinyl acetate and cellulose acetate, along with household vinegar. Uses:
4. Boric AcidChemical formula- H3BO3 Other names- Acidum boricum, hydrogen orthoborate Ph level- 9.1 Molar Mass- 61.83 g/Mol 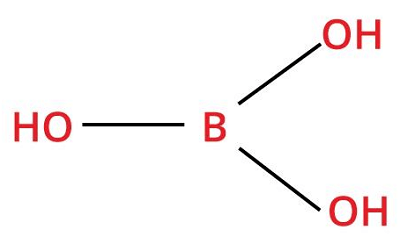
Boric acid is a weak acid by nature and is soluble in water easily. It occurs in nature and does not possess any distinctive smell, and it exists both in white powdered form and in the colorless crystal. Boric acid can be made by reacting borax with hydrochloric acid. Uses:
5. Nitric AcidChemical formula- HNO3 Other names- Aqua fortis, Eau forte, Acid nitricum, Hydrogen nitrate, Spirit of niter Ph level- 3.1 Molar Mass- 63.01 g/Mol 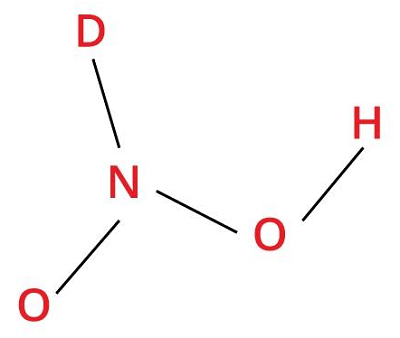
Nitric acid is a strong and highly corrosive mineral acid with a highly pungent smell and bitter taste. It is a colorless liquid when in its purest form but gradually acquires yellow color from the decomposition of water into nitrogen oxides. This acid can dissolve metals like copper, silver, and iron. Nitric acid is a potent oxidizing agent, as it readily accepts electrons from other substances. Uses:
6. Hydrofluoric AcidChemical formula- HF Other names- Hydrofluoride, flurohydric acid, hydrogen fluoride, hydrogen monofluoride Ph level- 3.27 Molar Mass- 20.0063 g/Mol 
Hydrofluoric acid is an organic compound formed when hydrogen fluoride is dissolved in water. This acid is colorless and highly corrosive. However, it does not completely dissociate into the water and is therefore considered a 'weak' acid. It can cause deep burns to human skin when it comes into contact. Uses:
7. Carbonic AcidChemical formula- CH2O3 Other names- acid of air, kihydroxyketone, dihydrogen carbonate, aerial acid Ph level- 4.18 Molar Mass- 62.03 g/Mol 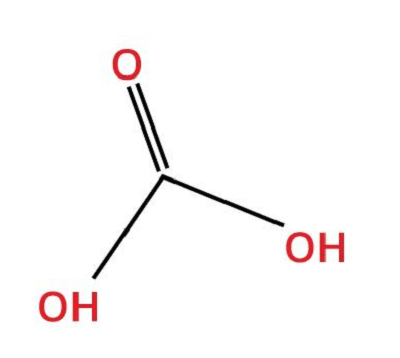
Carbonic acid is the solution of carbon dioxide in water (carbonated water). It is a weak acid and the only acid excreted by the lungs as gas. It is unique as it contains the carbon but is an organic compound and is the most common type of acid because of the abundance of carbon dioxide and water. Carbonic acid is also found in the bloodstream as the CO2 in blood bonds with the water in the blood. This acid can cause erosion based on the chemical constitution of the material. It is also one of the primary reasons for the low pH level of the water. Uses:
8. Oxalic AcidChemical formula- H2C2O4 Other names- hydrogen oxalate, Acidum oxalium, oxiric acid, ethanedionate, ethanedioic acid Ph level- 3 Molar Mass- 90.03 g/Mol 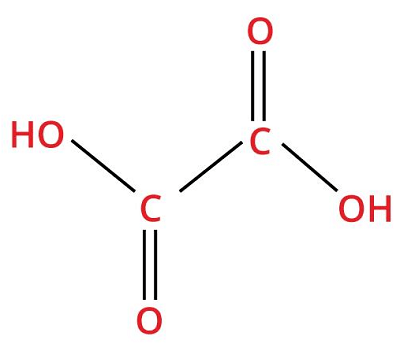
Oxalic acid belongs to a family of carboxylic acids and is a weak organic compound. It is a naturally derived chemical found in legumes, leafy greens, and other plant food we consume through our diet. However, excessive intake of oxalic acid can cause harm to the human body. Oxalic acid is produced by the oxidation of carbohydrates and can also be prepared in the laboratory by oxidizing sucrose in the existence of nitric acid and vanadium pentoxide as a catalyst. Uses:
9. Sulfuric acidChemical formula- H2SO4 Other names- dipping acid, Terra Alba, battery acid, matting acid, oil of vitriol Ph level- 1.87 Molar Mass- 98.079 g/mol 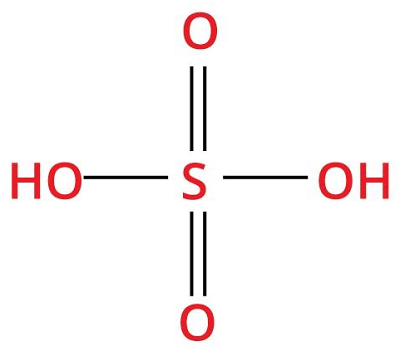
Sulphuric acid is a highly corrosive and strong mineral acid prepared from sulfur dioxide, and it behaves as a dehydrating agent and an oxidizing agent at higher concentrations. It is an oily liquid with no odor, can be colorless to slightly yellow, and to make people aware of its composition; it may be dyed dark brown. Sulfuric acid is water-soluble, and heat is released when it is dissolved in water. Sulfuric acid can cause severe chemical and thermal burns through an exothermic dehydration reaction. Uses:
10. Phosphoric acidChemical formula- H3PO4 Other names- Trihydrogen phosphate, orthophosphoric acid, Acidum phosphoricum Ph level- <2 Molar Mass- 97.994g/mol 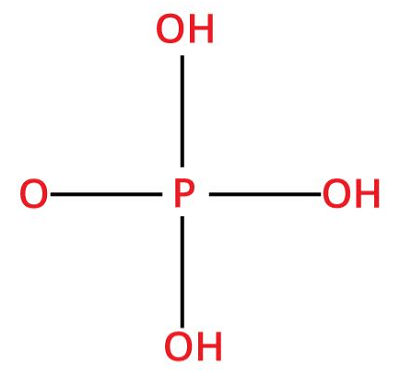
Phosphoric acid is among the most applicable and essential mineral acids. This acid is generally found in the aqueous form (about 85%). It is a sticky, colorless, odorless, non-volatile, and non-toxic solution that has a melting point of 42.4°C. Pure phosphoric acid is commonly found in the form of a white crystalline solid. This acid is categorized as a weak acid, but still, it can irritate or burn the skin and can be harmful to the eyes as well as membranes in the nose. Uses:
11. Perchloric AcidChemical formula- HClO4 Other names- hydroxidotrioxidochlorine, hyperchloric acid Molar Mass- 100.46 g/mol 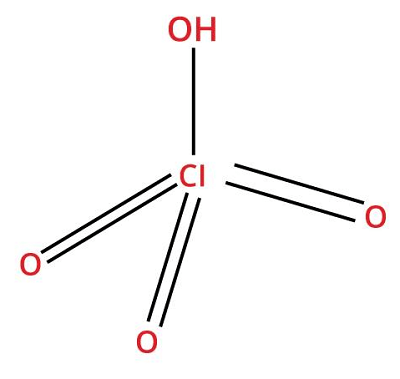
Perchloric acid (50-72%) is a solution with no color or odor. It is a strong acid that is highly corrosive to tissues and metals. Closed containers rupture violently when exposed to heat for a long time. Uses:
12. Formic AcidChemical formula- CH2O2 Other names- Methanoic acid, aminic acid, Formylic acid Ph level- 3.47 Molar Mass- 46.03 g/mol 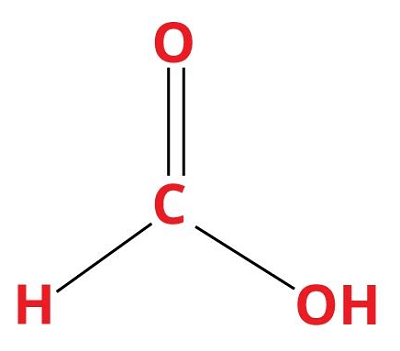
Formic acid is a weak acid that is naturally produced in the stings of bees and ants. It is a colorless solution with a pungent and penetrating odor. It is a water-soluble acid. Its melting point is 8.4°C, and its boiling point is 100.8°C. This acid is harmful at high concentrations, whereas very effective at low concentrations. Uses:
13. Chloric AcidChemical formula- HClO3 Ph level- 1.5 to 3.5 Molar Mass- 84.45914 g/mol 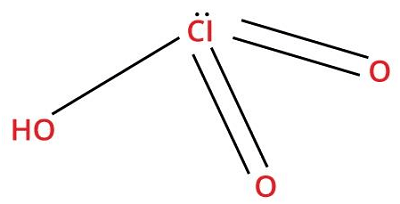
Chloric acid is a strong acid and a strong oxidizing agent. It appears as a colorless solution with a pungent smell. It accelerates the burning of flammable items and, when it comes in contact, catches fire. It is highly corrosive to tissues and metals. Uses:
14. Benzoic AcidChemical formula- C6H5COOH Other names- benzene carboxylic acid Ph level- 2.5 to 4.0 Molar Mass- 122.3°C 
Benzoic acid is an organic compound and a weak acid. It is called an aromatic carboxylic acid as it contains a carboxyl group attached to a benzene ring. This compound has an agreeably pleasing fragrance due to the presence of an aromatic ring. Under normal conditions, this acid appears as a colorless and crystalline solid. It is a water-soluble compound. The density of this compound decreases to 1.075 grams per cubic centimeter at a temperature of 130°C. Uses:
Next TopicList of Arab Countries
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










