Liver Cirrhosis DefinitionThe liver is one of the most vital organs in the body, performing essential functions such as detoxification, metabolism, and storage of nutrients. However, liver diseases such as liver cirrhosis can impair its function, leading to serious complications. In this article, we will delve into liver cirrhosis, a condition characterized by the scarring of the liver tissue that affects millions of people worldwide. Its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention will all be covered. Definition of Liver Cirrhosis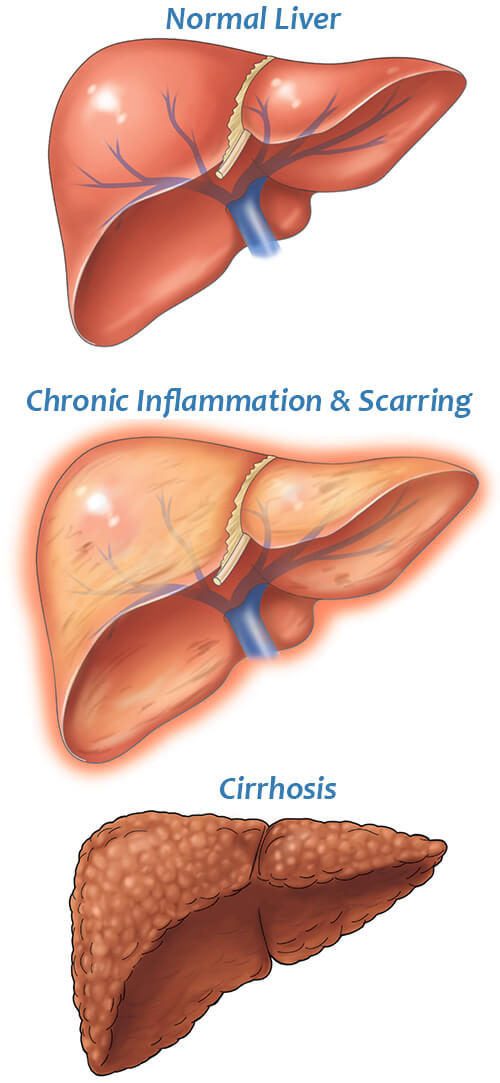
A chronic liver condition called liver cirrhosis happens due to sustained liver injury that results in the growth of scar tissue and the loss of liver function. The scarring is irreversible and can cause significant damage to the liver, impairing its ability to perform its critical functions. The liver performs a number of vital tasks, including the following:
When the liver is damaged, its ability to perform these functions is compromised, leading to a range of complications that can be life-threatening. Causes of Liver CirrhosisLiver cirrhosis can result from various causes, including:
Who Is At The Most Risk Of Getting Liver Cirrhosis?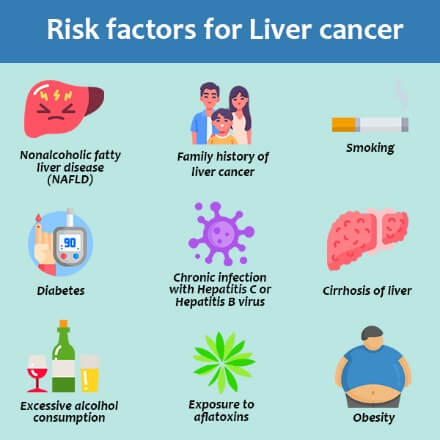
There are several factors that can increase a person's risk of developing liver cirrhosis. The following are some of the most common risk factors:
It is important to note that not everyone with these risk factors will develop liver cirrhosis, and some individuals without any risk factors may still develop the condition. Symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis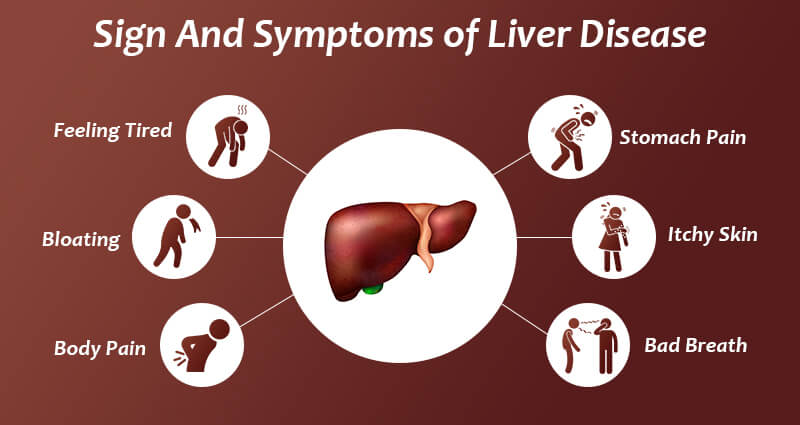
The symptoms of liver cirrhosis can vary depending on the severity and stage of the disease. In the early stages, the symptoms may be mild or non-existent, making it difficult to diagnose the condition. But, when the condition worsens, more severe symptoms, such include:
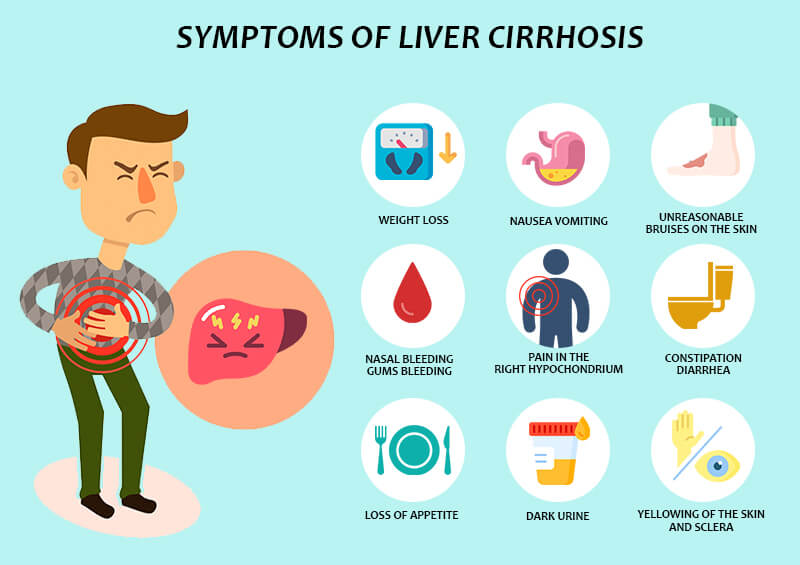
Is Liver Cirrhosis Cancer?No, liver cirrhosis is not a type of cancer. It is a chronic liver disease that occurs when healthy liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue, which can impair liver function. Liver cirrhosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including chronic alcohol consumption, viral hepatitis, and other diseases that affect the liver. Although liver cirrhosis is not a type of cancer, it can increase a person's risk of developing liver cancer, also known as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This is because the scar tissue that forms in the liver can lead to the development of nodules, which can become cancerous over time. It is important to note that not everyone with liver cirrhosis will develop liver cancer, and there are ways to reduce the risk of developing this condition. Regular check-ups and screenings can help detect liver cancer early and increase the chances of successful treatment. Can Cirrhosis Cause Pain?Indeed, cirrhosis can cause discomfort, particularly as the condition progresses. Up to 82% of those with cirrhosis report experiencing discomfort, and more than half of them believe it lasts for a long time (chronic). The majority of liver disease sufferers complain of stomach discomfort. Your right upper abdomen, just below your ribs, may feel sharp or dull throbbing when your liver is hurting. In addition to swelling from fluid retention, cirrhosis-related liver and spleen enlargement can produce generalized abdominal pain and discomfort. Both the disorders that cause cirrhosis and the diseases that are already present can cause pain and vice versa. For instance, cirrhosis exacerbates the pain in your bones and joints if you have non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease, obesity, and osteoarthritis. Your entire body experiences inflammation as a result of cirrhosis. General discomfort can be brought on by inflammation and your body's response to inflammation. Are There Stages Of Cirrhosis?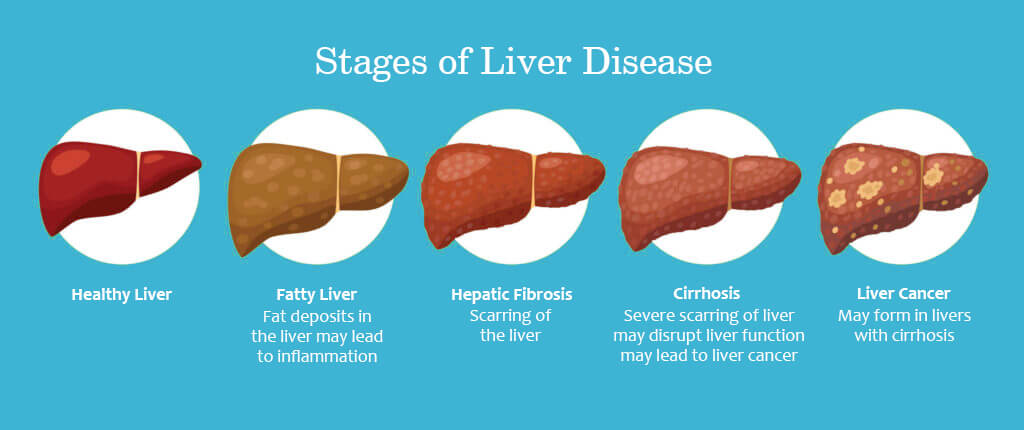
Compensated cirrhosis and decompensated cirrhosis are terms used to describe the progression and severity of liver cirrhosis. Let's see the difference between them in detail. Compensated cirrhosis refers to a stage of liver cirrhosis in which the liver is still able to perform its normal functions, despite the presence of scarring. In this stage, there may be few or no symptoms, and the individual may not be aware that they have liver cirrhosis. However, although liver function may still be relatively normal, there is a high risk of complications and disease progression. Regular monitoring and treatment are essential to prevent further damage and improve outcomes. Decompensated cirrhosis, on the other hand, refers to a more advanced stage of liver cirrhosis in which the liver is no longer able to function properly. In this stage, symptoms and complications are more severe and may include ascites (fluid build-up in the abdomen), jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), hepatic encephalopathy (a condition that affects brain function), and bleeding disorders. Decompensated cirrhosis is considered a medical emergency, and treatment may involve hospitalization, medication, and/or a liver transplant. It is important to note that the progression from compensated cirrhosis to decompensated cirrhosis can happen slowly over time, and the speed of progression can vary depending on the underlying cause of the cirrhosis and other factors. Regular monitoring and treatment can help slow the progression of liver cirrhosis and improve outcomes for individuals with the condition. How Are The Complication Of Cirrhosis Treated?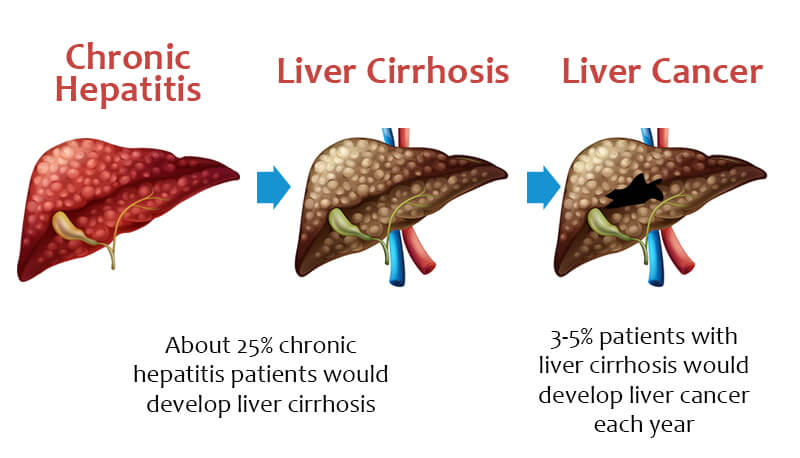
The treatment of complications of cirrhosis depends on the specific complication and its severity. Some common complications and their treatments are listed below:
It is important to note that treatment for complications of cirrhosis is typically aimed at managing symptoms and preventing further damage rather than reversing existing damage. Regular monitoring and management of the underlying cause of cirrhosis are also essential to prevent further complications and improve outcomes. Diagnosis of Liver CirrhosisDiagnosing liver cirrhosis requires a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. The following are some of the tests used to diagnose liver cirrhosis:
What Are A Child-Turcotte-Pugh Score and MELD Score?Two widely used scoring systems to evaluate the severity of liver disease and forecast outcomes in cirrhotic patients are the Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) score and the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score. 1. Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) Score: The CTP score is a clinical scoring system that measures the severity of cirrhosis based on five clinical parameters: bilirubin levels, serum albumin levels, prothrombin time, presence of ascites, and hepatic encephalopathy. Each parameter is scored on a scale of 1 to 3, with higher scores indicating more severe disease. The scores for each parameter are added together to give a total score ranging from 5 to 15. CTP scores are used to predict the prognosis and survival of patients with cirrhosis, with higher scores indicating a worse prognosis. 2. Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score: The MELD score is a more objective scoring system that was developed to predict the survival of patients awaiting liver transplantation. It takes into account three laboratory values: serum bilirubin levels, serum creatinine levels, and the international normalized ratio (INR) of prothrombin time. The MELD score ranges from 6 to 40, with higher scores indicating a higher risk of mortality. The MELD score is used to prioritize patients for liver transplantation, with those with the highest scores given priority. Both the CTP and MELD scores are used to assess the severity of liver disease and to guide treatment decisions in patients with cirrhosis. While the CTP score is more comprehensive and takes into account additional clinical parameters, the MELD score is more objective and has been shown to be a more accurate predictor of mortality in patients with cirrhosis. Treatment of Liver Cirrhosis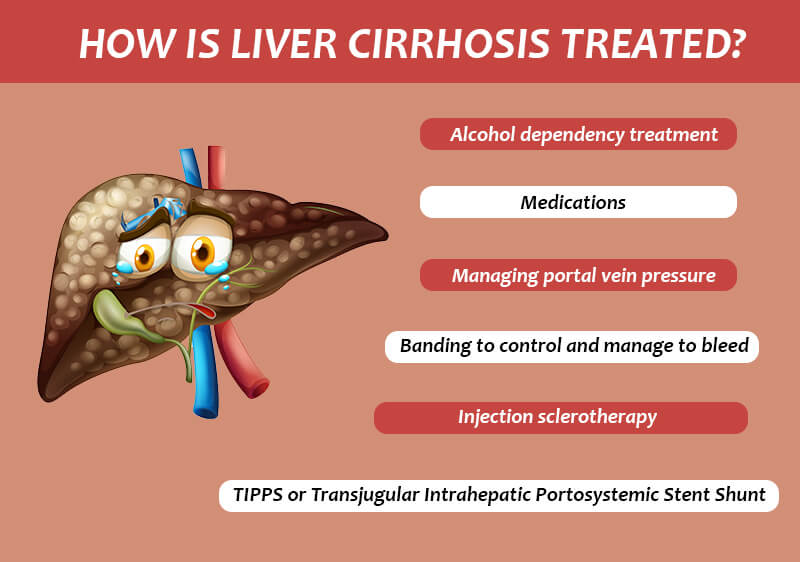
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic and irreversible condition, and treatment focuses on managing the symptoms and preventing complications. The following are some of the treatments used to manage liver cirrhosis:
Prevention of Liver CirrhosisLiver cirrhosis can be prevented by taking measures to protect the liver and prevent liver damage. Some actions that can be performed to avoid developing liver cirrhosis include:
ConclusionLiver cirrhosis is a serious and chronic liver disease that can lead to significant liver damage and impair the liver's critical functions. Many things, such as drinking alcohol, viral infections, and genetic disorders, might contribute to the condition. The symptoms of liver cirrhosis can be mild in the early stages, but as the disease progresses, they can become severe and life-threatening. A thorough review of the patient's medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic testing is required for the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis. Treatment focuses on managing the symptoms and preventing complications, while prevention involves taking measures to protect the liver and prevent liver damage. By making lifestyle changes such as limiting alcohol consumption, practising safe sex, maintaining a healthy diet, and avoiding exposure to toxins, individuals can reduce their risk of developing liver cirrhosis. It is important to note that liver cirrhosis is a chronic and irreversible condition, and there is no cure for it. But, with the right care, people may manage their condition while still leading healthy lives. Working closely with a healthcare professional is crucial for creating a treatment plan and maintaining regular condition monitoring. In conclusion, liver cirrhosis is a serious and potentially life-threatening liver disease that can result from several factors. It is crucial to be aware of the risk factors and take steps to prevent liver damage. Early diagnosis and proper management can help individuals with liver cirrhosis live a full and productive life. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider for regular check-ups and to seek medical attention if any symptoms arise.
Next TopicLymph Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










