Distinguish Between Micro and Macro EconomicsThe term "Economics" means study regarding how peoples, businesses, and governments make choices on the allocation of resources to meet their requirements. These groups are responsible for regulating how the resources are structured and coordinated to maximize productivity. They mainly deal with the production, consumption, and distribution of goods and services. Economics is divided into two main categories. Microeconomics and Macroeconomics. Microeconomics examines the behavior of specific customers and businesses, while Macroeconomics examines the behavior of the entire economy. What is Microeconomics?The study of choices made by individuals and businesses about the resource's allocation and prices of goods and services is known as Microeconomics. Microeconomics is concerned with the supply of goods and services, which defines the economy's price level. 
In order to analyze the economy, the microeconomy uses the bottom-up approach. In other terms, microeconomics aims to comprehend human decision-making and resource distribution. It does not determine what changes are occurring in the market; rather, it discusses why those changes occur. Microeconomics' main goal is to figure out how a business can maximize its output to reduce costs and succeed in its market. We can obtain huge information regarding microeconomics from the financial statements. Examples of Microeconomy; price of the product and Individual demand. Microeconomics Contains:
Importance of MicroeconomicsMicroeconomics has a wide range of theoretical and practical applications. As a result of this, even the Neo-classical economists focused on microeconomics. Although Keynes' popularity grew, the relevance of microeconomics has not diminished. 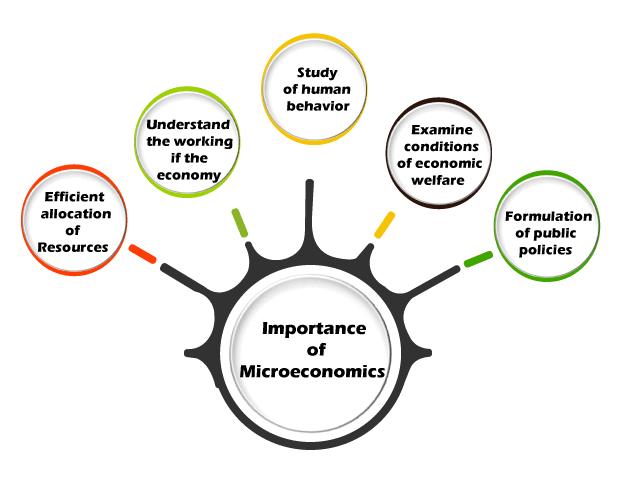
It is as follows: 1. Efficient Allocation of Resources Microeconomics assumes that consumers and producers function rationally. The producer investigates the various options and calculates the excepted advantages and costs of each option. The best use of resources comes from rational actions. Microeconomics instructs you on how to make the most efficient use of your resources. Microeconomics deals with the allocation of resources in the production of goods and services. It specifies which product should be produced, how much should be produced, and why it should be produced. 2. Understand the Working of the Economy Microeconomics knowledge is needed to understand how the economy works. The economy comprises the public as well as the private sector. The study of individual industry, wages, individual taxes, salary calculation, and foreign trade, is based on microeconomic principles. Correspondingly, various government operations can be evaluated using private-sector concepts. Such as the cost of national defense, price determination by the post office, etc., are analyzed with the help of the micro-economics. 3. Study of Human Behavior Microeconomics is a branch of economics that explores a wide range of human behavior. The law of diminishing utility, indifference curve theory, equip-marginal utility, each study human behavior. Economy theory may be used to explain a process in the economy. Positive economics is a term used to describe this type of descriptive theory. For example; When apples are in short supply, the price increases. According to the positive theory, one thing leads to another. The cause is a shortage of apples, and the result is a price increase. Economic theory may also be applied to determining what should occur. A normative theory is described as one that prescribes policy action. For example; When apples are in short supply, the price must increase. As a result, customers would eat less apple and instead opt for other fruits. (If they don't, they will have to wait in line.) Microeconomics is a discipline that is positive as well as normal science. 4. Examine Conditions of Economic Welfare The normative price theory is known as welfare economics. Welfare economics is the study of people's well-being as producers and consumers. It makes recommendations to improve people's welfare. It aids in the reduction of waste and enhancement of social welfare. It describes and analyses economic efficiency principles. 5. Formulation of Public Policies Microeconomics aids the government in formulating various economic policies that benefit the general public. It provides tools and foundations for the study of economic policy. The economy is influenced by economic policy. It results in a change in resource distribution, such as the public policy regarding loans, tax, price, subsidy, etc. A benefit-cost analysis is a useful technique that is often used in public policy decisions. Microeconomics supports the government in making the most efficient use of limited resources. What is Macroeconomics?Macroeconomics is an economics branch that shows a large picture. It examines the economy on a large scale, and many economic problems are taken into account. Macroeconomics measures and interprets the problems that an economy faces and the progress that it makes. Microeconomics is the study of the relationship between countries and how one country's policies affect the other. It delimits its scope by analyzing the effectiveness and failure of government policies. 
In macroeconomics, we usually survey the relationship between the nation's total manufacturing and the degree of employment, and other factors such as cost prices, rates of interest, profits, wage rates, etc., focusing on a single fictitious good and what occurs to it. Example of Macroeconomics; General price level, Poverty, Rate of unemployment, Aggregated demand as well as supply and National income and savings Macroeconomics contains:
Importance of Macroeconomics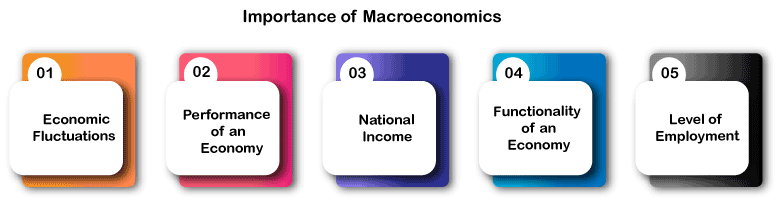
With the help of the following points, we can define the importance of Macroeconomics: 1. Economic Fluctuations With the help of macroeconomics, we can analyze the reasons of fluctuations in employment, income, output and try to control them or decrease their severity. 2. Performance of an Economy With the help of macroeconomics, we can examine the economy's performance. National Income (NI) estimates are used to measure the economy's performance over time by comparing the production of goods and services from one era to the next. 3. National Income The analysis of national income and social accounts has become increasingly important as a result of macroeconomic research. It is impossible to formulate the right economic policies without conducting a national income analysis. 4. Functioning of an Economy Macroeconomics theory helps you understand how an economic structure works. It assists us in comprehending the behavior pattern of aggregative variables in a vast and complex economic system. 5. Level of Employment Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that studies an economy's overall employment and production. Distinguish Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Next Topic#
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










