What is the Full Form of NFONFO: New Fund OfferNFO stands for New Fund Offer. Mutual funds are one of the most popular new fund offers presented by an investing business. A new fund offer, or NFO, is the initial subscription offering for each new fund an investing company offers. 
Key LessonsAn investment business's initial selling of fund shares to investors is referred to as a new fund offer (NFO). NFOs are used to raise money for the fund and draw investors, much like an IPO on the stock market. Despite being advertised, NFOs are less common aggressively than IPOs and focus on a small number of exclusive investment groups. Therefore, compared to IPOs, new fund issuance may be less obvious to individual investors. Before choosing to invest in an NFO, investors should look at the fee ratio and past fund performance supplied by the investing business. Investors interested in learning about new fund launches can keep an eye on the press releases of various investment businesses and news sources that compile the most recent fund news. An Acquaintance of NFOsAn NFO is equivalent to an initial public offering (IPO). Both are efforts to generate money to expand operations. They may include aggressive marketing activities designed to persuade investors to buy units in the fund with new fund offerings. New fund offerings frequently have the potential for large returns once they start trading publicly. Types of New Fund OffersNew exchange-traded funds are first made available through a new fund offering. The most prevalent category of new fund offerings is mutual funds. Closed-end mutual funds or open-end can both provide new fund offers. Below are specifics on investing in a few of the most well-liked new fund-providing categories. 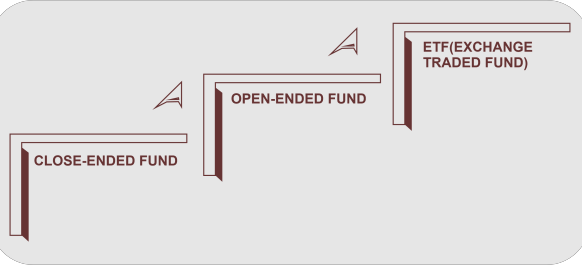
Open-End FundOn a predetermined launch day, an open-end fund will make new shares available for purchase as part of a new fund offer. There is no share cap for open-end funds. These funds can be purchased and sold via a brokerage company on their original launch. The fund business and affiliates of the fund firm do not manage the stock and trades on an exchange. Open-end mutual funds provide their daily net asset values after the market closes. Fund firms can introduce fresh fund offerings for fresh strategies or extend the share classes of current strategies. Closed-End FundThe purchase of closed-end money happens through a brokerage company on the day of its commencement. Closed-end fund issuances are typically among the most well-publicized new fund issuances since they can only issue a limited number of shares during their new fund offer. On an exchange, closed-end funds are traded daily with daily price quotations. DCF's new fund offer resulted in a $140 million profit. Exchange-Trade FundA sort of investment fund that they may openly trade on the stock market is an exchange-traded fund. A fresh fund offer also includes the introduction of new exchange-traded funds (ETFs). The "goal is to strive to deliver current income while preserving minimum price volatility," according to Vanguard. The money in the fund should maintain a 0 to 2-year dollar-weighted average maturity. The expenditure ratio for VUSB is only 0.10%. Alerts and LaunchesNew fund offerings are frequently not publicly advertised, making it difficult to find them. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) requires businesses to submit a new fund offering registration form, which provides one monitoring tool. Investors interested in learning more about new fund offers may also receive notices from their brokerage firm before the launch date. A useful place to find out about new fund offers is news organizations and news aggregators. For example, sources like the Closed-End Fund Center may provide details about fresh fund launches. 
Businesses will also issue press statements on fresh fund offerings. For instance, you may read Vanguard's statement about the debut of their most recent ETF on their website. When trading started on the first exchange-traded fund (ETF) tied to bitcoin, ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF(BITO), in October 2021, it became one of the most talked-about debuts in recent years. Advantages And Disadvantages of NFOAlthough investing in a new mutual fund may seem like an exciting approach to diversifying your portfolio, there are certain things to consider before making a choice. Many investment firms may launch a new fund when the market is strong, and investors are keen to participate in the newest new company or sector of the economy. But just because a certain technology or sector is flourishing right now doesn't guarantee that it will continue to do so in the future. 
Additionally, a new fund offer frequently includes a greater cost-to-income ratio. The fund has no history of success, which is one of the biggest risks of investing in an NFO (or failure). While some bullish investors may view this as a chance to make significant gains, investing in a fund whose performance you cannot monitor carries significant risk. A new mutual fund plan for the general public on the financial markets with the intention of a first-time subscription is referred to as an NFO or new fund offer. Asset management firms (AMCs) provide NFOs as new mutual fund products that weren't previously available as part of their portfolios. In other words, investors are given a short window of opportunity to participate in a new mutual fund scheme based on a new investing approach. Of the basket of goods, both closed-ended and open-ended mutual fund schemes are offered NFOs. In the case of the former, investors cannot make investments after the NFO period has ended and must remain invested until the maturity term. Still, the latter can let people invest in the scheme's units when it reopens for a subscription. The risk of an investor is prepared to accept and the value proposition being given are two aspects that affect whether or not they invest in NFOs. The following might be viewed as mutual fund NFO characteristics:
Closed-ended funds plans offer NFOs for a brief period, after which investors are prohibited from purchasing more units until the scheme reaches maturity. This could also make it easier for fund managers to choose and keep track of assets (such as equities or bonds). They may undertake any purchase of units during the NFO window for open-ended mutual fund schemes after it closes. Net asset value for that specific scheme. Investors can buy units at comparably low cost before the fund's NAV is established, thanks to a new fund offering in this case. Only through NFOs may investments in close-ended funds be made. Investors may be able to avoid giving in to panicky feelings and maybe obtain returns that are proportionate to the risk involved by the time the plan matures, thanks to the characteristics of some close-ended funds regarding the holding period till maturity. The timing of NFO launches is crucial since it can provide a range of outcomes depending on an investor's entrance point. One's investing profile may not necessarily match the NFO's investment aim. Investors may benefit from being aware of all the information. A fund's NFO carefully reads the scheme information materials (SID). This may help investors even more in choosing wise investments. If one thinks NFOs provide anything extra compared to other current funds and can assist close any gaps in their investment portfolio, they may want to consider investing. Mutual Funds New Fund Offer or NFOAn asset management business establishes a new fund on a first-subscription basis using a New Fund Offer (NFO) to finance the purchase of securities. The Operation of the New Fund OfferIn a new fund offer, there is just a little window of time during which you may subscribe to the plan. Investors may purchase the mutual fund scheme's units during the specified term and pay an offer fee to subscribe to the NFO. The standard price is Rs. 10. Investors can acquire fund units at the set price after the tenure expires. In general, NFO subscribers have produced significantly higher returns after listing. Why is the NFO an Excellent Opportunity?Through an NFO, the fund house raises money from the general public to purchase assets such as equity shares, bonds, and other marketable financial instruments. As a new product, NFO is less costly than the present funds. They resemble initial public offers (IPOs), in which shares are offered for sale to the general public before being listed on a stock exchange. 
Additionally, they are a too-good-to-miss prospect due to the massive marketing techniques employed to sell them. Before choosing one, you occasionally need to use your good sense and intelligence. Who Decides to Make a New Fund Offer Investment?Most investors search for mutual fund investment opportunities when markets are down. They want to invest in the market because they think it will keep expanding, whether for gold or real estate. However, they also choose profitable investments offered at a lower cost. Asset management firms (AMCs) attempt to profit from this investor mindset. This explains why individuals prefer to pursue NFOs that appear to be less expensive. Investors elect to subscribe to NFOs after determining they are a good investment. Consequently, the fund companies may accomplish their objective of growing their Asset Under Management (AUM). Considerations for InvestorsFund House CredibilityIt is crucial for investors who wish to invest in NFOs to research the fund house thoroughly. Make sure the fund manager has a long history of operation, say, between five and ten years, in the mutual fund sector. You may utilize it to analyze the fund house's performance during market ups and downs. The NFO could deliver on its promises if the fund firm has a solid track record. Funding GoalsThe fund's goals specify, among other things, the asset mix, level of risk, projected returns, and liquidity. It aids in your impression of the NFO's feasibility. Simply put, it indicates that potential investors should read the offer document to comprehend the fund manager's plans better a person's financial decisions. Investor process deficiencies are shown if investors cannot understand the NFO's goals. Financial TargetsThe New Fund Offer's Theme The Indian mutual fund industry is flooded with mutual fund programs. As a result, it is advised to carefully read the small print when presented with an NFO to understand the fund's topic. The investment topic needs to be durable and distinct from what is offered by the current programs. This information may or may not be mentioned in the offer agreement. You can analyze the fund following a projected rate of return that you establish. If you have already put money in the fund, you might want to think about evaluating it every three years during the first three years. For example, to understand the returns trend, you may contrast the mutual fund's performance with the index and peer funds. Risk Element 
Investing in NFOs could be dangerous. NFOs don't have a performance history, unlike existing funds, where you can easily verify the asset allocation and associated risks. You won't be able to forecast without any standards or measurements. Additionally, you won't be able to determine the fund manager's plans for using your money for the fund's performance. Investment Cost The exit loads may impact your results if the lock-in period exceeds your investment horizon. It is advisable to determine if the expenditure ratio is less than or the same as SEBI requires. Cost of Minimum SubscriptionNFOs typically include specifics and a minimal investment need for subscribers. It might range from 500 to 5,000 rupees. When narrowing down your potential investments, this might be your main criterion as an investor. Reassessing alternatives may be advisable if the minimum subscription cost exceeds what you can afford. In such circumstances, you may consider choosing a systematic investment plan (SIP), a cheaper and more practical option in an already-existing high-performing scheme. Additionally, Investment Horizon NFOs have lock-in durations of three to five years. It's possible that you won't be able to redeem your units before maturity if you've joined a mutual fund scheme. In rare circumstances, you could additionally be assessed an exit load (pre-exit cost) for the same. Make sure your investment horizon and goals are in sync with your investments. If your chosen NFO occurs to be longer than your investment horizon, it is suggested that you reassess your alternatives. How Do I Buy Mutual Funds?Investing in mutual funds is hassle-free and paperless. You may begin your investing journey by using the steps below:
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










