Normalization in Machine LearningNormalization is one of the most frequently used data preparation techniques, which helps us to change the values of numeric columns in the dataset to use a common scale. 
Although Normalization is no mandate for all datasets available in machine learning, it is used whenever the attributes of the dataset have different ranges. It helps to enhance the performance and reliability of a machine learning model. In this article, we will discuss in brief various Normalization techniques in machine learning, why it is used, examples of normalization in an ML model, and much more. So, let's start with the definition of Normalization in Machine Learning. What is Normalization in Machine Learning?Normalization is a scaling technique in Machine Learning applied during data preparation to change the values of numeric columns in the dataset to use a common scale. It is not necessary for all datasets in a model. It is required only when features of machine learning models have different ranges. Mathematically, we can calculate normalization with the below formula:
Example: Let's assume we have a model dataset having maximum and minimum values of feature as mentioned above. To normalize the machine learning model, values are shifted and rescaled so their range can vary between 0 and 1. This technique is also known as Min-Max scaling. In this scaling technique, we will change the feature values as follows: Case1- If the value of X is minimum, the value of Numerator will be 0; hence Normalization will also be 0. Put X =Xminimum in above formula, we get; Xn = Xminimum- Xminimum/ ( Xmaximum - Xminimum) Xn = 0 Case2- If the value of X is maximum, then the value of the numerator is equal to the denominator; hence Normalization will be 1. Put X =Xmaximum in above formula, we get; Xn = Xmaximum - Xminimum/ ( Xmaximum - Xminimum) Xn = 1 Case3- On the other hand, if the value of X is neither maximum nor minimum, then values of normalization will also be between 0 and 1. Hence, Normalization can be defined as a scaling method where values are shifted and rescaled to maintain their ranges between 0 and 1, or in other words; it can be referred to as Min-Max scaling technique. Normalization techniques in Machine LearningAlthough there are so many feature normalization techniques in Machine Learning, few of them are most frequently used. These are as follows:
Standardization scaling is also known as Z-score normalization, in which values are centered around the mean with a unit standard deviation, which means the attribute becomes zero and the resultant distribution has a unit standard deviation. Mathematically, we can calculate the standardization by subtracting the feature value from the mean and dividing it by standard deviation. Hence, standardization can be expressed as follows: 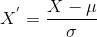
Here, µ represents the mean of feature value, and σ represents the standard deviation of feature values. However, unlike Min-Max scaling technique, feature values are not restricted to a specific range in the standardization technique. This technique is helpful for various machine learning algorithms that use distance measures such as KNN, K-means clustering, and Principal component analysis, etc. Further, it is also important that the model is built on assumptions and data is normally distributed. Difference between Normalization and Standardization
When to use Normalization or Standardization?Which is suitable for our machine learning model, Normalization or Standardization? This is probably a big confusion among all data scientists as well as machine learning engineers. Although both terms have the almost same meaning choice of using normalization or standardization will depend on your problem and the algorithm you are using in models. 1. Normalization is a transformation technique that helps to improve the performance as well as the accuracy of your model better. Normalization of a machine learning model is useful when you don't know feature distribution exactly. In other words, the feature distribution of data does not follow a Gaussian (bell curve) distribution. Normalization must have an abounding range, so if you have outliers in data, they will be affected by Normalization. Further, it is also useful for data having variable scaling techniques such as KNN, artificial neural networks. Hence, you can't use assumptions for the distribution of data. 2. Standardization in the machine learning model is useful when you are exactly aware of the feature distribution of data or, in other words, your data follows a Gaussian distribution. However, this does not have to be necessarily true. Unlike Normalization, Standardization does not necessarily have a bounding range, so if you have outliers in your data, they will not be affected by Standardization. Further, it is also useful when data has variable dimensions and techniques such as linear regression, logistic regression, and linear discriminant analysis. Example: Let's understand an experiment where we have a dataset having two attributes, i.e., age and salary. Where the age ranges from 0 to 80 years old, and the income varies from 0 to 75,000 dollars or more. Income is assumed to be 1,000 times that of age. As a result, the ranges of these two attributes are much different from one another. Because of its bigger value, the attributed income will organically influence the conclusion more when we undertake further analysis, such as multivariate linear regression. However, this does not necessarily imply that it is a better predictor. As a result, we normalize the data so that all of the variables are in the same range. Further, it is also helpful for the prediction of credit risk scores where normalization is applied to all numeric data except the class column. It uses the tanh transformation technique, which converts all numeric features into values of range between 0 to 1. ConclusionNormalization avoids raw data and various problems of datasets by creating new values and maintaining general distribution as well as a ratio in data. Further, it also improves the performance and accuracy of machine learning models using various techniques and algorithms. Hence, the concept of Normalization and Standardization is a bit confusing but has a lot of importance to build a better machine learning model.
Next TopicAdversarial Machine Learning
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










