Noun PhrasesWhat exactly is a phrase?Before we begin with noun phrases, we need to grasp what a phrase is. Below is a quick recap of the same. A phrase is merely a group of words that forms a sentence. For instance, "in the stormy night" or "amid the busy crowd." You can combine phrases to form a complete sentence, but a phrase by itself does not make a sentence.In the English language, there are various common phrases. Examples include verb phrases, adjective phrases, prepositional phrases, absolute phrases, adverb phrases, and noun phrases. 
What are Noun Phrases?Noun phrases are collection or combination of words that function as nouns. In a statement, they typically serve as the subjects, objects, or prepositional objects. While this may be difficult to grasp, seeing these useful phrases in practice is the best way to learn them. Examples will help you understand a noun phrase and how it is utilized in a sentence. Examples of Noun PhrasesNoun phrases are just nouns that have been modified. Noun phrases, like nouns, can function as subjects, objects, and prepositional objects. Similarly, noun phrases can function as adjectives, participle, infinitive, and prepositional or absolute phrases in a statement. Noun phrases are useful for providing more information about a noun. A noun or a pronoun must always appear in a noun phrase. A noun phrase is often made up of simply one word. It will either be a noun or a pronoun. Below are few examples of simple noun phrases:
You may have observed that these are not whole sentences. Instead, noun phrases are used to support lengthier sentences, such as:
Each phrase contains a noun as well as words that change it. Sentences can also contain multiple noun phrases, and noun phrases can be embedded within other noun phrases. You might also make the noun phrase longer. In fact, this is rather common, and children may be unaware that they utilize it on a regular basis. 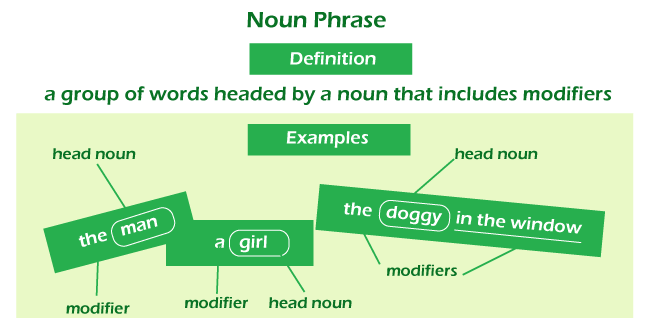
Noun Phrase and ModifiersA noun is defined as an individual, location, object, or idea. A noun phrase will include a noun as well as words that describe or alter the noun. Even a basic modifier, such as a numerical or an article such as "the" or "a," transforms the group of words that includes the noun into a noun phrase. Tip: It is crucial to remember that modifiers do not necessarily have to occur before the noun in order for the collection of words to be considered a noun phrase. They can follow a noun, such as an adjective clause or infinitives. Note: A modifier is always present in a noun phrase.Noun vs Modifier ExamplesThe noun is bolded, and the modifier is underlined in the below-mentioned sentences;
It's most likely be articles, possessive nouns, possessive pronouns, adjectives, or participles if they appear just before a noun. Modifiers have been highlighted for ease of recognition
Prepositional phrase, adjective clause, participle phrase, and infinitive are examples of modifiers that follow after the noun.
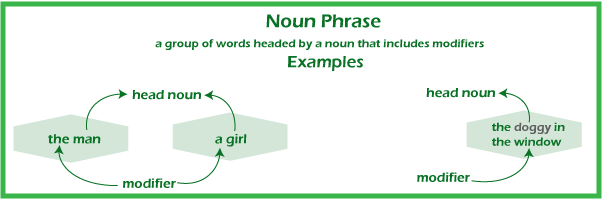
The Purpose and Usage of Noun Phrases in SentencesA noun phrase's function is to add extra detail to a sentence. As a result, a noun phrase can serve multiple functions inside a sentence. Explore a few examples of sentences that use noun phrases in various ways. Noun Phrase as a SubjectA subject is essential for a sentence to be whole or complete. Noun phrases are simple to use as sentence subjects. And they usually give the reader a better idea about the subject. Below are some of the examples of the same ;
Noun Phrase as an ObjectWithin a sentence, you must have both a subject and an object. The objects in the statement work with the verb, as seen by these noun phrases. Below are some of the examples of the same ;
Noun Phrase as the Prepositional ObjectWhen a noun phrase is transformed into a prepositional object, it will begin with a preposition such as "in" or "to." Below are some of the examples of the same;
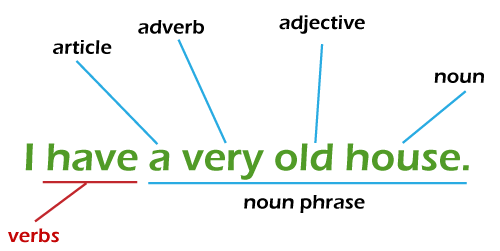
Noun Phrase With AdjectiveWe often also come across sentences in which the noun phrase incorporates adjectives. In "the bike wash," for example, the word "bike" serves as an adjective for the noun "wash."
Participle Noun PhraseYou've most likely come across a participle in a statement like "planting." A noun phrase, on the other hand, can become a participle within a statement. Examine a few samples to see how this works ;
Noun Phrase Plus to-InfinitiveA noun phrase can be utilised as a to-infinitive to indicate something that is either a requirement or a possibility. Examine how this works with a few samples.
Noun Phrases as Prepositional PhrasesThe noun phrase functions as a prepositional phrase in this form of the statement. The preposition is underlined in the instance, whereas the noun phrase is bold.
Noun Phrase as an Absolute Phrase to a SubjectThe noun phrase can also be used as an absolute term for a certain subject. Examine the examples below with the noun phrases highlighted in bold and the subject italicized to see how this works.
What exactly are expanded noun phrases?You may come across the phrase enlarged noun phrase on occasion. An expanded noun phrase provides more information about the noun found in a plain noun phrase. Look for the following to identify an expanded noun phrase: an article an adjective or adjectives an article Let's look at an example of how to make a simple noun phrase into an expanded noun phrase: She swam in the lake. The noun phrase in the preceding statement is "the lake." We can add an adjective to change the noun "lake" to make it an expanded noun phrase. As an example: She swam in the salty lake. "The salty lake" is now an enlarged or expanded noun phrase. "the" is the article, whereas the adjective is salty, and the lake is the noun. The expansion might also come after the noun. In addition to the adjective, one can provide extra information that is still relevant to the noun phrase as a whole. As an example: The spooky mansion with its large, shattered windows was terrifying. The adjective "spooky" describes the mansion in the above instance, and the extension "with large, shattered windows" modifies the noun "mansion." As a result, the expanded noun phrase includes both. 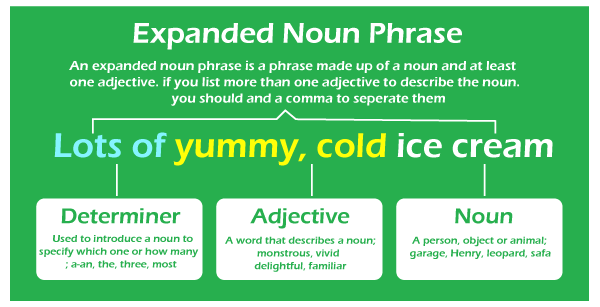
Why is it essential to understand enlarged noun phrases?Learning about enlarged noun phrases enhances writing creativity. Incorporating additional info into nouns makes writing more fascinating and builds vivid images in the mind of the reader. Expanded noun phrases stimulate and inspire creativity, immersing both the readers and the writers in the scene. This is vital and significant that youngsters will benefit from this for all their life. Whether writing essays, tales, or application forms, they're more likely to make a positive impact if they can catch their reader's interest. Tip: When dealing with noun phrases, make sure to check the subject-verb agreement. When dealing with noun phrases, always check the verbs when the noun phrase is the subject. The verb does not necessarily relate to the closest noun. As an example: The eerie mansion with damaged walls are for auction. (incorrect) While "walls" is a plural noun, it is a component of the noun phrase's modifier. The head noun to which the verb must refer is "mansion." As a result, the right statement is: The eerie mansion with the damaged windows is for auction. To double-check subject-verb agreement, substitute a pronoun for the noun phrase. Pronouns and Noun Phrase FunctionsAs previously stated, the role of a noun phrase is similar to that of a noun. In a statement, the noun phrase might serve as a compliment, a subject, or an object. A compliment is a term that describes the subjects or the objects of a phrase. A statement's subject is the noun (person, location, object, or idea) that is doing or being anything in the statement. The nouns on the receiving side of the verbs are the statement's object. Since noun phrase functions as a noun, replacing it with a pronoun is a straightforward approach to determine whether it is a noun phrase or not. A pronoun is a term that can stand in for a noun. Consider the following noun phrases that have been converted into pronouns: Noun Phrase The cat was starving. Noun Phrase Pronoun has been replaced. She was starving. "The cat" is the statement's basic noun phrase or subject. The pronoun "she" can be utilised in place of the noun phrase. Consider another example: Noun Phrase The eerie mansion with large smashed glass was terrifying. Noun Phrase Altered with Pronoun It was terrifying. In this statement, the noun phrase is "the eerie house with large smashed glass." We use the pronoun "it" rather than the noun phrase. Here's another illustration: Noun Phrase I devoured the delectable cheesecake. Noun Phrase Replaced with Pronoun I ate it. The statement's object, and so the noun phrase, is "the delectable cheesecake." If we substitute the phrase with a pronoun, we get the sentence "I ate it. " Finally, consider a statement in which two noun phrases have been converted into pronouns. Noun Phrase The beautiful girl is an excellent performer. A pronoun replaces a noun phrase She is one of them. The subject in the above sentence is "the beautiful girl," and the subject's complement is "a excellent performer." They are both noun phrases. When the words are replaced with pronouns, the new statement reads: "She is one." Tip: Possessive pronouns can also be used to express ownership instead of noun phrases. They are frequently used to return to a noun phrase from the previous statement. For instance, "You recognize that turquoise novel on the tabletop? It's all mine." The noun phrase is "that turquoise book," while the possessive pronoun that relates to the novel is "mine." Nouns and Their PurposesNouns are words that describe individuals, locations, things, or concepts. As there are so many of them, they can be categorised into a wide range of categories. The following are some examples of nouns :
The Function Of Nouns In SentencesNouns are commonly used as subjects and objects in statements. They can, however, change other terms by being possessive or appositive. The "manager's motor" is an instance of a possessive noun, referring to the motor of the manager. "My sister, the honest helper ," for instance, is an appositive noun. Nouns can also function as adjectives, as in "hot milk," where "hot" alters "milk." They can also be used as an adverb, such as "he went to work," where "work" specifies where she is headed. Forming Fuller ConceptsNoun phrases, regardless of their form or purpose, help to construct more complete thoughts. Instead of simply discussing a cat, you can use an adjective to describe a speckled cat. You can describe the situation with his joy booming through the air rather than simply saying they strolled into the dawn. Many writers enjoy using noun phrases. It enables them to create images, such as "a crimson hair woman was in an unpleasant situation". Given the complexity of the English language, you may be shocked to hear that there are more sorts of phrases, such as verb phrases and gerund phrases. Look at phrase instances to discover more about creating illustrative statements that will stick in the minds of your readers.
Next TopicPhrases Examples
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










