What is the full form of PBXPBX: Private Branch ExchangePBX stands for Private Branch Exchange. It refers to a telephone switching system of an enterprise. It is used to switch calls between VoiP (voice over Internet Protocol or IP) users on local lines to facilitate internal communication of a business. Its main function is to allow in-house calling between extensions and to allow routing for outside calls. For example, when an employee makes a call to another employee on the same network, the call is routed through the PBX without requiring an outside line. He can also make a call outside the company network through the same exchange. PBX allows companies save costs and improve efficiency, e.g. If a company doesn?t use a PBX, it might need to install 500 separate lines if it has 500 employees. PBX is owned and managed by the company; the telephone exchange does not control it. Earlier, PBX was based on analogue technology, but today, it uses digital technology. 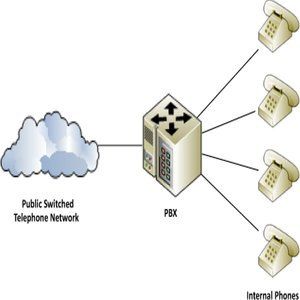
Parts of a PBXPBX mainly comprises lines and stations. The lines are connections to the PSTN and Stations are endpoints like fax machines, desk phones, credit card terminals, etc. The basic parts of a PBX are as follows: Exchange: It is a large switching station that connects and route calls internally or externally. It is the main part of the PBX system. Gateway: It connects the internal network to the outside world. It routes calls from the exchange unit to the local Public Switched Telephone Network (PTSN) lines. For example, when someone dials an outside line, the gateway connects the internal extension to the outside line to complete the call. Handsets: The handsets used with PBX systems are provided with various special functions. They allow users to dial inside extensions, connect to outside calls, and use intercom and other features provided within the given system.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










