Prokaryotes Vs. EukaryotesWhat is Prokaryote?The term "Prokaryote" is derived from the Greek word "pro," which means before, and karyon, which means kernel. Thus, it translates to before "nuclei." The Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms with no membrane-bound structures, the nucleus being the most notable. Prokaryotes cells are typically simple, small cells with a diameter of 0.1-5μm. Despite the lack of membrane-bound structures in prokaryotic cells, they do have different cellular areas. A nucleoid is a place in prokaryotic cells where DNA bundles together. Examples of Prokaryotes; Bacteria and Archaea. 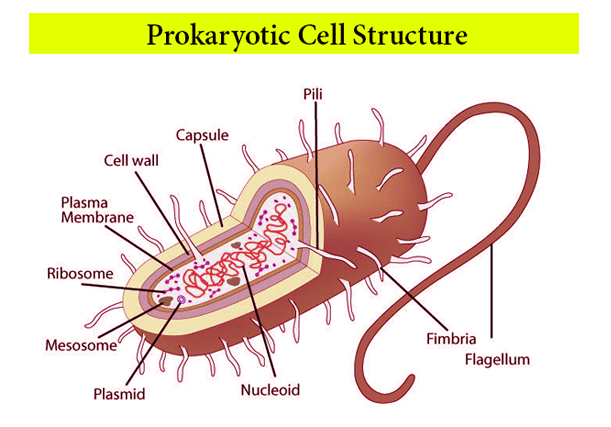
Prokaryotes are one of the oldest living organisms' groupings globally, with fossil records extending back nearly 3.5 billion years. These prokaryotes flourished in the earth's prehistoric environments, with few relying on chemical energy and others on sunlight. For millions of years, the extremophiles are living, evolving and adapting. These organisms may have given rise to eukaryotes, according to scientists. Eukaryotes cells are larger and more complex, whereas prokaryotic cells are tiny and less complex. Another distinguishing feature of prokaryotic cells is that they lack membrane-bound cell organelles like the nucleus. In this, Reproduction occurs via the process of binary fission. Fundamentally, prokaryotes have a case encompassing its whole body and the ability to act as a protective coat. This is significant in terms of phagocytosis prevention (where the bacteria get engulfed by other eukaryotic cells, like macrophages). The pilus is a hair-like appendage present on the outer surface of most of the prokaryotes that aid the organism in adapting to various surroundings. The pilus basically opposes being flushed; hence, it is also known as attachment pili. It is ordinarily seen in bacteria. The cell wall, which provides the cell strength and rigidity, is found directly under the protective coating. The cytoplasm, which aids in cell formation, is found farther down inside the plasma membrane, which divides the cell's internal substance from the external climate. The cytoplasm contains ribosomes, which play a key role in protein synthesis. It's also one of the tiniest components of the cell. In some prokaryotic cells, there is a special structure called mesosomes that help in cellular respiration. Plasmids, which are tiny, circular pieces of DNA, are found in most prokaryotes. In order to help with locomotion, flagella are present; pilus can also be used as a locomotion aid. Features of ProkaryotesThe following are the features of prokaryotes:
What is Eukaryote?The term "Eukaryotes" is derived from the Greek words "eu," which means "good," and "karyon," which means "kernel," therefore, translating to "good or true nuclei." Eukaryotes differ from prokaryotes in that they more complex and much extensive. Except for the kingdom Monera, they include practically all of the primary kingdoms. The plasma membrane is supported and protected by a cell wall in eukaryotes. The plasma membrane surrounds the cell and regulates the inflow and outflow of specific substances. 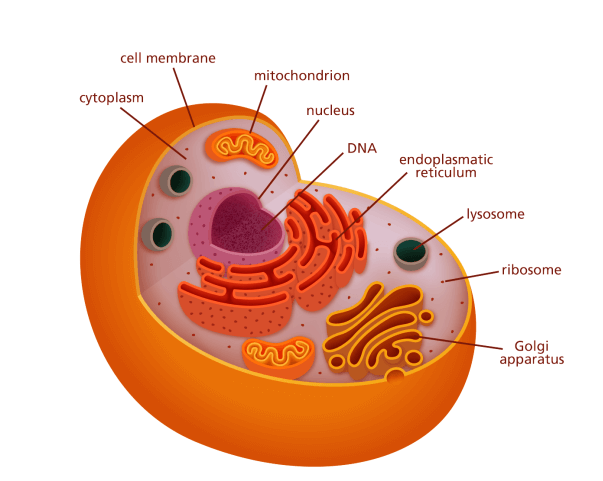
The nucleus comprises DNA, which is responsible for storing all genetic information. The nucleus is surrounding the nucleus. The nucleus is a component of the nucleus that plays an essential function in synthesizing proteins. Eukaryotic cells also have mitochondria, which produce energy that is then used by the cell. There is a nucleus in eukaryotes and other organelles enclosed by a plasma membrane in their cells. Organelles are the internal structures that perform a variety of tasks, such as protein synthesis and energy production. Its only exists in plant cells; chloroplasts are the subcellular sites of photosynthesis. The endoplasmic reticulum aids in the movement of materials. In addition to that they are also other cell organelles which perform several other functions including ribosome, Lysosomes, chromosomes. centrosomes, Golgi, cytoplasm, and Golgi. Eukaryotic cells are large (between 10 and 100 µm) and complex. While the majority of eukaryotes are multicellular organisms, few are single-cell eukaryotes. For Example; Animals, plants, protozoans, algae, and fungi. Eukaryotic Cell FeaturesEvery membrane-bound structure in a eukaryotic cell performs a distinct cellular function. Here are many of the fundamental components of eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryote vs. Eukaryotes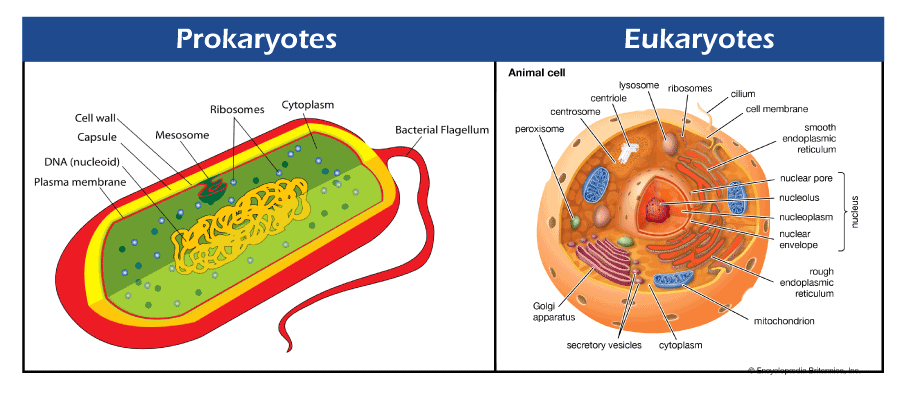
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










