Puppet ModulesPuppet Module is a collection of files, classes, templates, and resources. Each module handles a specific task in your infrastructure, such as installing and configuring a piece of software. Since modules allow you to divide your code into multiple manifests, it is very helpful in organizing your puppet code. Modules are the reusable and shareable units in the puppet. Modules must be installed in the puppet modulepath. And the modulepath is /etc/puppet/modules directory. Module ConfigurationWe have two partitions in any Puppet module, which allows us to define the structure of code and control the denominations.
Modules SourcePuppet allows a different location to store the modules. We can store the module in a different file system in our machine. There is only one condition that all paths of the modules must be defined in the configuration variable called modulepath. modulepath is a path variable where puppet searches for all module directories and in the boot time loads all the module directories. The default path is: Module Internal OrganizationWhen creating a new module in Puppet, it uses the same structure and adds distributed files, manifests, templates, and plugins organized in a specific directory structure, as given in the code below. Once you create the module, it adds init.pp manifest file at a particular fix location in the manifest directory. init.pp is a default file that runs first in any module and includes a list of all classes related to that module. ExampleLet's see an example to create an autofs module that installs a fixed auto.homes map and generates the auto.master from templates: The file system will have the following files: Installation of Puppet ModuleThe open-source puppet has many pre-existing modules. These modules are written and developed by the puppet communities. Anyone can update pre-existing modules. These are the in-built, public modules that anyone can download, install, and use it. There are over 6,000+ pre-existing modules available in the Puppet Forge. Let's see the steps to download and install these pre-existing puppet modules. Here, we are going to download the vim module from Puppet Forge. Vim is available in a package that is a free and open-source text editor in Linux operating system. Step 1: Click here to open the official Puppet Forge page. When you click on the link, it will display the following page: 
Step 2: In the search bar, enter the name of the module that you want to download. Here, we are going to download vim module: 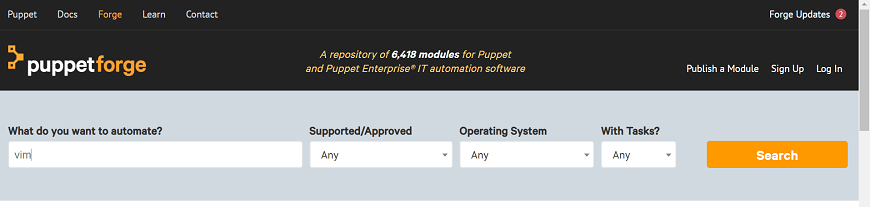
Step 3: When you click on the Search button, it will display multiple results. Choose the appropriate one. To decide your selection, you can click on the individual module to see complete details. In our case, we will use dhoppe vim. 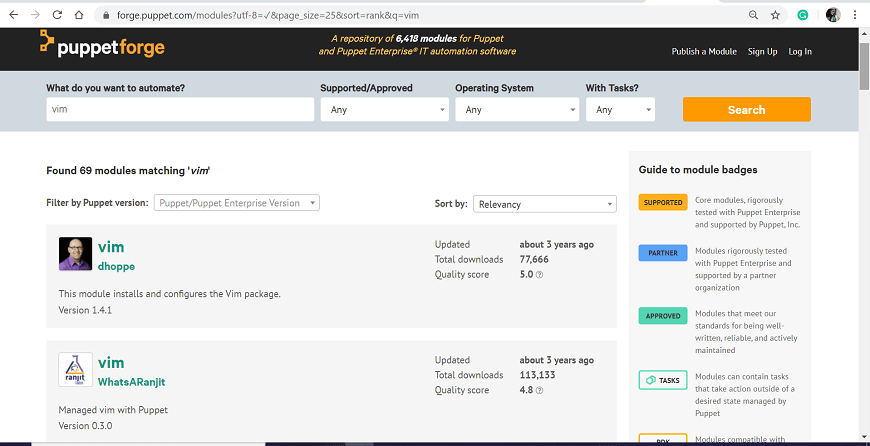
Step 4: To download the module, click on the download button from the right side of the page, and we will get the module in tarball format. 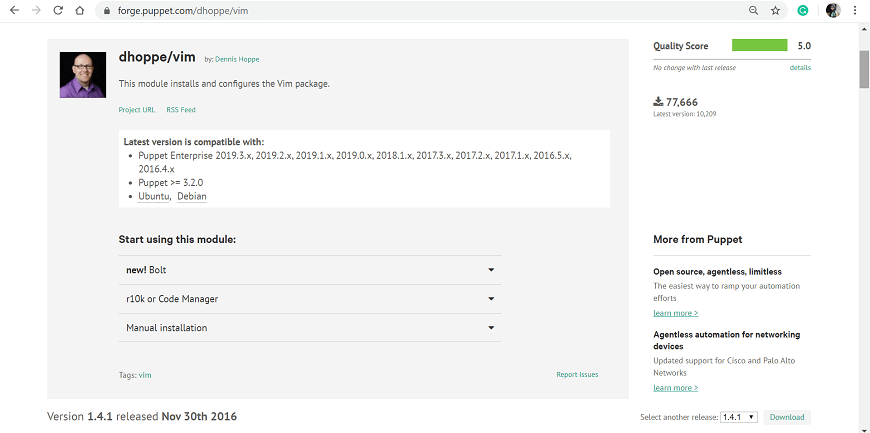
Step 5: Once the download finish, execute the following command to install a module from the tarball: In the above command, 'path' is the path of the directory where your tarball is saved. We can also install the puppet modules online. To download and install the module from the puppet module tool, execute the following command: 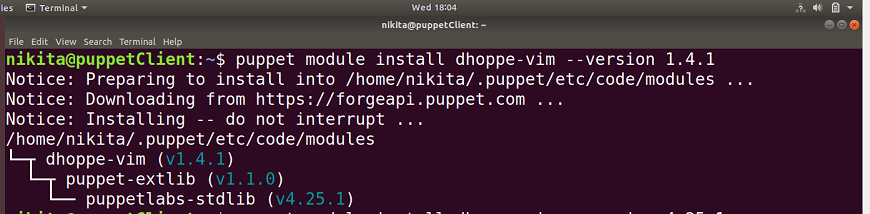
Next TopicPuppet Facter & Facts
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










