Purification of ColloidsIt refers to reducing the amount of impurities especially electrolytes present in the colloidal sol. The electrolytes are added to the sols to provide them stability. In small concentration, they stabilize the sol, but, when present in a large amount they may destabilize the colloidal sols, so their amount must be reduced to make the sols stable. There are various methods that are used to purify the colloids. Some of the commonly used methods for the purification of colloids are described below; i) DialysisAs the name suggests, in this methods, the impurities are removed from the sol through dialysis. In this method, diffusion occurs through a semi-permeable or any other suitable membrane. In diffusion, solute particles move from a region of high concentration to low concentration. The impurities are separated from the colloidal particles by diffusion through a suitable membrane. The colloidal particles cannot pass through this membrane, only the impurities' particles can pass. 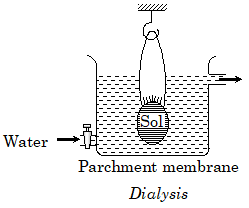
Let us see how it works; A bag made of a suitable membrane (animal membrane or parchment paper or cellophane sheet) is filled with the impure colloidal solution. This bag is dipped in a container filled with freshwater which keeps flowing or entering and leaving the container continuously. The concentration of impurities like crystalloids and electrolytes is high in the sol contained in the bag than in the fresh water. So, diffusion occurs in which the impurities start moving out of the bag by passing through the membrane. The dispersed phase (colloidal particles) remains in the sol as they cannot pass through the membrane due to their large size. The water keeps changing due to its continuous flow so the concentration of impurities does not increase and always remains low in the water than in the sol and thus diffusion continues until pure colloidal sol is left in the bag. For example, blood, which is a negatively charged colloidal sol, is also purified by dialysis when the kidneys are not working. ii) Electro-dialysisThis method is also based on dialysis. It uses the same apparatus and sol in the bag that were used in the dialysis. The only difference is that it makes use of electricity. The bag filled with impure sol is suspended in the water. Electrodes are present in the container that produce an electric field across the bag. 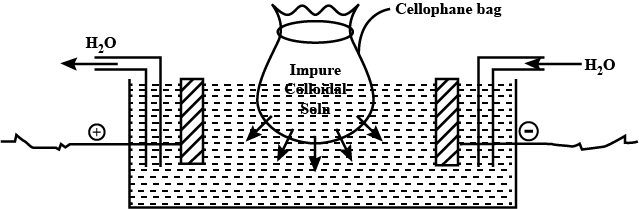
Electro-dialysis is used for the sols that contain only one type of electrolyte as an impurity. One electrode is positively charged and another is negatively charged. The negative ions present in the colloid contained in the bag will come out by passing through the membrane and move to the positively charged electrode. Similarly, the positive ions from the bag move towards the negatively charged electrode. Electro-dialysis is widely used in blood purification as it is a fast process. The impure blood is passed to artificial kidney apparatus. The impurities from the blood diffuse out through the dialysis membrane, whereas, the colloidal particles of blood remain in the blood. The purified blood is obtained and is passed back into the body of the patient. iii) UltrafiltrationIn this method, the colloidal particles are separated from the sol through filtration. The colloidal sol is passed through an ultra-filter paper that filters only the dispersed phase (colloidal particles). The dispersion medium along with impurities passes through the filter paper. A fresh dispersion medium is added to the separated or filtered colloidal particles to make a pure colloid. 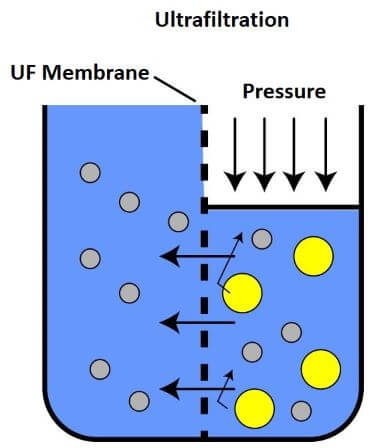
A normal filter paper cannot be used for this method as its pores are large that cannot filter the colloidal particles. The sol along with all of its components will pass through it. Due to this reason, an ultra-filter paper is used, which is prepared by soaking the filter paper in a collodion solution. This solution is a 4% solution of nitrocellulose in a mixture of alcohol and ether and is hardened by formaldehyde. A normal filter paper can be converted to ultra-filter paper. The pore size of an ordinary filter paper is 0.7-25 micrometre, whereas, the pore size of an ultra-filter paper is 0.0015 micrometer. Besides this, ultra-filtration is a slow process, so its speed is increased by applying pressure or suction. iv) Ultra-centrifugationThe method involves the use of an ultracentrifuge machine. The impure sol is poured in a tube, which is placed in the machine. When the tube is rotated at high speed, the colloidal particles settle down at the bottom of the tube, whereas, the impurities stay in the solution (centrifugate). The particles settled at the bottom are separated and a suitable dispersion medium is added to them to regenerate a pure sol.
Next TopicChemical Reaction
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










