Rainy SeasonAs the scorching heat of summer fades away, the rainy season arrives, bringing with it a sense of relief and renewal. The sound of raindrops tapping against the roof, the earthy smell of wet soil, and the vibrant greenery that springs up all around are just a few of the things that make the rainy season a beloved time of year. 
But the rainy season is more than just a welcome break from the heat; it plays a crucial role in the environment, agriculture, and the lives of people around the world. In this article, we'll explore the many facets of the rainy season, from its impact on water resources to its effects on biodiversity and infrastructure. When does the Rainy Season occur?The timing of the rainy season varies depending on the location and climate of the region. In some places, the rainy season occurs during the summer months, while in others, it may occur during the winter or spring. For example, in tropical regions, the rainy season typically occurs during the summer months, when the sun is overhead, and the warm, moist air rises, leading to convectional rainfall. In other areas, such as parts of Africa, the rainy season may occur during the spring or fall when the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) shifts north or south, bringing moist air and rainfall. In general, the rainy season is characterized by increased precipitation and humidity and decreased temperatures, and it can last for several weeks or even months. It is important to note that climate change can also affect the timing and intensity of the rainy season, making it more unpredictable in some regions. Causes of the Rainy SeasonThe rainy season is caused by a combination of factors, including changes in atmospheric pressure, temperature, and humidity. 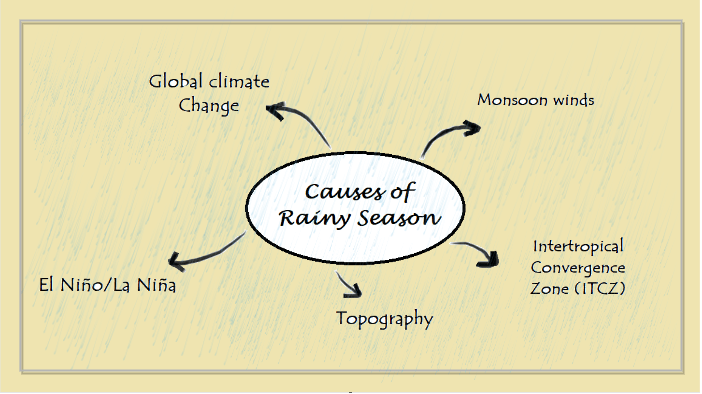
Here are some of the main causes of the rainy season: Monsoon WindsMonsoon winds are a major cause of the rainy season in many parts of the world, including Asia, Africa, and the Americas. These winds are caused by the differential heating of land and sea, which creates a low-pressure zone over the land and a high-pressure zone over the ocean. As a result, moist air from the ocean is drawn towards the land, leading to heavy rainfall. Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)The ITCZ is a belt of low pressure that circles the Earth near the equator. During the rainy season, the ITCZ shifts north or south, bringing with it moist air and heavy rainfall. TopographyThe topography of a region can also play a role in the onset and duration of the rainy season. For example, mountain ranges can create orographic uplift, which leads to increased rainfall on the windward side of the mountains. El Niño/La NiñaEl Niño and La Niña are climate phenomena that can affect the onset and duration of the rainy season in some regions. During El Niño, sea surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean rise, leading to drought conditions in some regions and increased rainfall in others. During La Niña, the opposite occurs, with cooler sea surface temperatures leading to increased rainfall in some regions. Global Climate ChangeThe Earth's climate is changing, and global warming is causing changes in weather patterns, leading to more extreme weather events such as floods, droughts, and storms. These changes can affect the timing, intensity, and duration of the rainy season in some regions. Impact of the Rainy Season on the EnvironmentThe rainy season can have both positive and negative impacts on the environment, depending on various factors such as the intensity and duration of rainfall, the topography of the area, and the state of the ecosystem. Here are some of the impacts of the rainy season on the environment: Positive Impact on BiodiversityThe rainy season can lead to an increase in biodiversity by providing a conducive environment for various flora and fauna. The increased rainfall leads to an increase in plant growth, which provides food and habitat for animals. Wetlands, lakes, and rivers also get replenished, leading to the revival of aquatic ecosystems. Negative Impact on Soil ErosionThe intensity of rainfall during the rainy season can lead to soil erosion, which can have severe impacts on the environment. Soil erosion can lead to the loss of topsoil, which is rich in nutrients and supports plant growth. It can also lead to the degradation of land, resulting in desertification and loss of biodiversity. Negative Impact on Water QualityHeavy rainfall can cause water pollution by washing away pollutants from the soil and carrying them into rivers and lakes. The pollutants can come from agricultural runoff, industrial activities, and urbanization and can severely impact aquatic ecosystems, including fish kills and algal blooms. Positive Impact on Carbon SequestrationRainforests and other forested areas play an important role in carbon sequestration by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The rainy season helps to replenish soil moisture, which is essential for plant growth, leading to an increase in carbon sequestration. Negative Impact on InfrastructureHeavy rainfall can lead to damage to infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings. The damage to infrastructure can have severe impacts on the environment, including the loss of habitats for animals and the degradation of land. In summary, the rainy season can have both positive and negative impacts on the environment, and the magnitude of the impacts depends on various factors. Effective environmental management strategies are necessary to mitigate the negative impacts of the rainy season and ensure that the positive impacts are maximized. Importance of the Rainy Season in AgricultureThe rainy season plays a critical role in agriculture, as it provides the necessary moisture and nutrients for crops to grow and thrive. The availability of water during the rainy season is particularly important in areas that rely heavily on rain-fed agriculture, where irrigation infrastructure may be limited or non-existent. Here are some of the ways that the rainy season is important in agriculture: Water Supply for CropsRainwater is the primary source of water for crops during the rainy season. Adequate rainfall ensures that crops have enough moisture to grow and develop. Soil FertilityRainwater helps to replenish soil nutrients, which can be lost through leaching, erosion, and plant uptake. This leads to an increase in soil fertility, which is crucial for crop growth. Seed GerminationSeeds require moisture to germinate, and the rainy season provides the ideal conditions for this. Adequate rainfall ensures that seeds are properly hydrated, which leads to good germination rates and strong plant growth. Increased Crop YieldsAdequate rainfall during the rainy season leads to increased crop yields, which is critical for food security and economic development in many countries. Pest and Disease ManagementRainfall helps to control pests and diseases by washing away pests and pathogens from crops and reducing their proliferation. In summary, the rainy season is important for agriculture because it provides the necessary water and nutrients for crops to grow and thrive, leading to increased crop yields, improved soil fertility, and better pest and disease management. Effects of the Rainy Season on Water ResourcesThe rainy season can have both positive and negative effects on water resources, depending on various factors such as the intensity and duration of rainfall, the topography of the area, and the state of the water infrastructure. On the positive side, the rainy season can replenish groundwater, surface water, and reservoirs, thereby increasing water availability for human consumption, irrigation, and industrial use. This can be particularly beneficial in arid and semi-arid regions, where water scarcity is a major challenge. However, if the rainfall is too intense or if the area is prone to floods, the rainy season can also have negative impacts on water resources. Floods can cause erosion, sedimentation, and contamination of water sources, which can lead to water quality issues and damage to infrastructure. In addition, excess rainfall can cause landslides and soil erosion, which can result in the loss of soil fertility and the degradation of aquatic habitats. Furthermore, in areas with insufficient infrastructure for water management, such as inadequate reservoirs or drainage systems, heavy rainfall can lead to the loss of excess water that could otherwise be stored for later use. This can result in the wastage of water and exacerbate water scarcity issues in the dry season. Overall, the effect of the rainy season on water resources depends on various factors, and effective water management strategies are necessary to ensure that the positive impacts of rainfall are maximized while the negative impacts are minimized. Natural Disasters Associated with the Rainy SeasonThe rainy season can bring about various natural disasters, which can have devastating consequences on human lives, property, and infrastructure. Here are some of the natural disasters associated with the rainy season:
In summary, the rainy season can bring about various natural disasters, including floods, landslides, mudslides, lightning strikes, cyclones and hurricanes, and droughts. It is essential to be prepared for these disasters by having early warning systems, emergency supplies, and evacuation plans in place to mitigate the risks and minimize the impact on human lives and the environment. How to prepare for the rainy season?Preparing for the rainy season is crucial to minimize the potential impact of natural disasters, protect your property, and ensure that you and your family stay safe during heavy rainfall. Here are some steps you can take to prepare for the rainy season:
By taking these steps, you can prepare for the rainy season and minimize the potential impact of natural disasters, protect your property, and ensure the safety of yourself and your loved ones. Tips for Staying Safe during the Rainy SeasonStaying safe during the rainy season is essential to avoid the potential dangers associated with heavy rainfall and natural disasters. 
Here are some tips for staying safe during the rainy season:
By following these tips, you can stay safe during the rainy season and avoid potential dangers associated with heavy rainfall and natural disasters. Conclusion and Future Outlook for the Rainy SeasonIn conclusion, the rainy season is a crucial period that brings both benefits and challenges to the environment, people, and economy. While the rains provide much-needed water for agricultural production, they also bring risks of floods, landslides, and other natural disasters. The impact of the rainy season on the environment can be both positive and negative. The rains can rejuvenate the soil, replenish water bodies, and support biodiversity, but they can also cause soil erosion, damage to infrastructure, and loss of property and life. To prepare for the rainy season, it is essential to take necessary precautions such as cleaning gutters and drains, checking roofs, sealing windows and doors, investing in flood protection, and stocking up on emergency supplies. In the future, with climate change, it is expected that the intensity and frequency of rainfall will increase, and this will have significant implications for the environment and people. To adapt to changing weather patterns, there is a need for innovative solutions, such as the development of more resilient crops, the improvement of drainage systems, and the use of early warning systems to alert people of impending natural disasters. Overall, while the rainy season brings benefits and challenges, proper planning and preparation can help mitigate the risks and ensure that people and the environment are better equipped to handle the changing weather patterns in the future.
Next TopicSpring Season
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










