Redemption of Preference SharesThe process or requirement of repaying the capital of preference shares to the shareholders is referred to as redemption of preference shares. A firm can only redeem its preference shares according to the terms that were stated at the time of issuance or as amended once the shareholders of those preference shares have given their assent. The terms of the issue of these shares provide that the firm would refund the amount invested by the shareholders in the company at a later period, as well as pay a set amount in the form of interest on a regular basis over the contract's term. The date of redemption is the maturity date that is given in the preference share certificate. Redemption of preference shares helps the company in adjusting the financial structure. The redemption of these shares takes place:

Why Do Companies Issue Redeemable Preference Shares?There are certain reasons because of why a company may issue redeemable preference shares. They include the followings:
In our country, Section 55 of the Companies Act, 2013 governs the issue and redemption of preference shares. Conditions for Redemption of Preference Shares
Procedure for Redemption of Preference Shares1. Prior Notice of the Meeting of the Board of DirectorsCompanies with non-convertible preference shares listed on an exchange must notify the Board of Directors in advance of the meeting. This information should be given at least 11 working days prior to the day when the company will begin paying the redemption amount. 2. Call and Convene a Board MeetingThere are several sub-steps included in this step:
3. Payment of Redemption AmountThe corporation will pay the redemption amount and the premium amount (if any) to the redeemable preference shares after the second stage is completed. 4. Relevant Entries in the Register of MembersNow, the company will make the relevant entries in the Register of Members in Form MGT-1. This work should be done within 7 days from the date on which the BoD's meeting was conducted to get approval for the redemption of preference shares. 5. Corporate ActionsAfter making the entries, the company is required to file the necessary corporate action so that the preference shares can be debited from the account of the shareholders. The company can do this work after allotting the redeemable preference shares in Demat format. 6. File NoticeThe corporation will file a notice of redemption of preference shares with the ROC in Form SG-7 at this point. This notice must be submitted within 30 days of the redemption date. The paperwork should be accompanied by a copy of the Board Resolution allowing the redemption of such shares. 7. Transfer of Amount to Capital Redemption Reserve AccountFinally, the corporation will send to the Capital Redemption Reserve Account an amount equivalent to the nominal value of redeemed preference shares. This step can be completed if the corporation has redeemed preference shares with profits from the business. Methods of Redemption1. For Fully Paid-up Preference SharesAs per the Companies Act 2013, the company must redeem the preference shares within the maximum period, i.e., 20 years allowed under the Act. Thus, a company does not have the right to issue irredeemable preference shares. Sector 55 of the Companies Act, 2013, deals with the issue related to the redemption of preference shares. It makes sure the redemption does not cause any reduction in the shareholders' funds and thus the interest of the external parties remains unaffected. For this, it is needed that the redemption is done by the fresh issue of shares and/or undistributed profits which are transferred to the 'Capital Redemption Reserve Account'. To protect the interest of the outsiders, Section 55 provides for the redemption of only fully paid-up preference shares. The 'gap' generated in the capital of the company due to redemption much be filled in in the following ways: 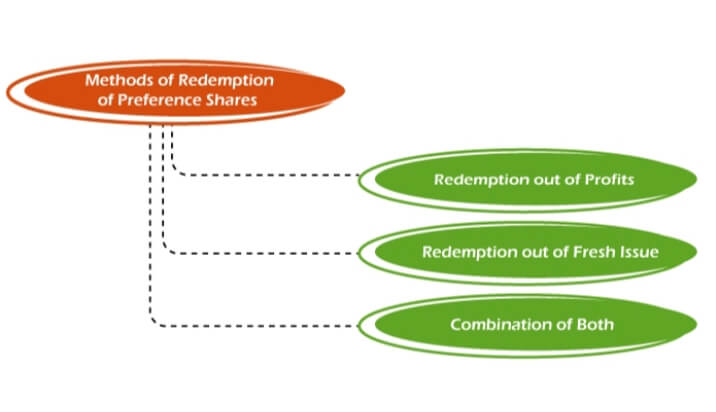
1.1. Redemption by Fresh Issue of SharesThe proceeds of a new share offering are one of the most typical mechanisms for the redemption of preference shares. A company is free to use new equity or preference shares and the proceeds from them can be used for redemption purposes. The company can prefer this method under the following conditions:
Advantages
Disadvantages
1.2. Redemption by Capitalization of Undistributed ProfitsA corporation can also use its undistributed earnings to redeem preference shares, according to the Companies Act of 2013. When utilizing this technique, the corporation must debit the amount of distributable profit and transfer an amount equivalent to the face value of the shares to the Capital Redemption Reserve Account. In other terms, the company keeps some part of the distributable profit to make sure that the amount will not be distributed as a dividend. This newly formed account's balance can be used for fully paid bonus shares, which ultimately convert the retained profits into share capital. Advantages
Disadvantages
1.3. Redemption by Combination of Fresh Issue and Capitalization of Undistributed ProfitsA company can also use the combination of both, i.e., partly from fresh issues and partly from capitalization of undistributed profits for the redemption of preference shares. In order to fill the 'gap' between the face value of redeemed shares and the revenues from the new issue, the firm must make a transfer from distributed profits to Capital Redemption Reserve. This approach employs the following formulae:
Sale of InvestmentsThe companies can also sell their investments in the market to arrange sufficient funds for the redemption of preference shares. 2. For Partly Called-up Preference SharesIn such a case it is assumed that the final call on the redeemable preference shares is demanded and received before proceeding with redemption. This is done because of a condition of redemption which is that the company can redeem only fully paid-up preference shares. If the company has the information about both partly and fully paid-up preference shares then it will redeem only fully paid shares. 3. For Fully Called but Partly Paid-up Preference SharesIn this case, the redemption of shares can be divided into the following two categories: 3.1. When the company has received Calls-in-ArrearsIf the company has collected the number of unpaid calls before redemption then the following entry is passed: Bank A/c Dr. To Calls-in-Arrears A/c Once the company receives call-in-arrears the shares got converted into fully paid-up and then the procedure of redemption can be continued in the normal course. 3.2. When the Shares are ForfeitedIf shareholders fail to pay for unpaid calls despite receiving adequate notice from the corporation, the Board of Directors may forfeit the shares and cancel them rather than reissuing them. This is due to the fact that these shares are due to be redeemed immediately or in the near future. In this situation, the corporation will proceed with the forfeiture entries as usual.
Next TopicAccounting Period Concept
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










