Install Redis on UbuntuIntroduction to RedisRedis can be defined as an in-memory store of data structure, used as an in-memory key-value database, distributed, message and cache broker using optional durability. It stands for Remote Dictionary Server and supports many types of abstract data structures, including spatial indices, streams, bitmaps, HyperLogLogs, sorted sets, sets, maps, lists, and strings. The project was created and handled by Salvatore Sanfilippo, initiated in 2009. From 2015 until 2020, he led a core team of the project approved by Redis Labs. Redis is an open-source application published upon a BSD 3-clause license. Not long after the actual author and primary maintainer left, in 2021, Redis Labs abandoned the Labs from the name and now is called simply "Redis". History of RedisThe Redis project started when Salvatore Sanfilippo, the actual maintainer of Redis, was attempting to develop his Italian startup scalability, improving a real-time analyzer of web log. After encountering serious issues in scaling a few kinds of workloads with traditional database systems, Salvatore Sanfilippo started in 2009 to prototype the first proof of the Redis concept version in Tcl. Later he converted that prototype into the C language and developed the first "list" data type. After some weeks of internally utilizing the project with success, Sanfilippo determined to open-source it, introducing the project on the Hacker News website. The project started gaining traction, specifically in the Ruby community, with Instagram and GitHub being among the initial organizations adopting it.
Difference between Redis and other database systemsRedis affected a system idea that can be treated as a cache and a store simultaneously. It was developed so that the data is always changed and accessed from the primary computer memory, although also saved on disk in a way that's not compatible with irregular data access. This changed data is just restored into memory when the system reboots. Also, Redis offers a data model that's very curious than an RDBMS. The commands of the user don't define a query to be run via the database engine but instead, special tasks that are implemented on provided abstract data types. Hence, data has to be saved in a format that is compatible later with fast recovery. The recovery is implemented without support from the database system in aggregations, secondary indexes, or other basic aspects of traditional RDBMS. The implementation of Redis uses the fork system call to copy the data holding process, so the parent process can continue to manage clients, and the child process makes an in-memory data copy on disk. Supported languages of RedisSince the 2.6 version, Redis has offered a server-client scripting aspect in the Lua language. On the client side, several programming languages include Redis language bindings, including Tcl, Swift, Smalltalk, Scala, Rust, Ruby, Racket, R, Python, Pure Data, PHP, Perl, OCaml, Objective-C, Lua, Julia, JavaScript (Node.js), Nim, Java, Io, Haxe, Haskell, Go, Erlang, Elixir, Delphi[30], Dart, D, Crystal, Common Lisp, Clojure Chicken, C#, C++, C, and ActionScript. Various client software programs are available in these languages. Data types of RedisRedis outlines keys to value types. An essential difference between many structured storage systems and Redis is that Redis not only supports strings but abstract data types as well:
A value type decides what operations (known as commands) are present for the value. Redis provides its support for server-side, atomic, and high-level operations, such as difference, union, and the intersection between sets of a list sorted, sorted sets and sets. Other data types are also supported that are Redis Modules API-based:
More detailed overview of Redis data types:
How can we secure Redis?Redis binds to every interface, and it doesn't include authentication at all. If we use Redis in a highly controller environment, isolated from the outside internet and attackers, that is fine. However, it's a great security concern if any unhardened Redis is disclosed to the internet. If we are not 100% sure that our environment is properly secured, we can follow the below steps to get a more secure Redis. To enhance security, some steps are mentioned below:
Remember that any Redis instance disclosed to the Internet is very easy to exploit without security, so ensure that we follow the above and use a firewall layer. We can try to link to redis-cli from any outside host to prove ourselves the instance is not reachable after the firewall is set. User interfaces of RedisThe redis-cli (Command line interface) is a terminal function used for sending commands to and seeing replies through the Redis server. It contains two primary modes: the first one is an interactive REPL (Read Eval Print Loop) mode in which the user enters Redis commands and gets replies, and the second one is the command mode in which redis-cli runs with extra arguments and the response is displayed on the standard output. To let us work with the Redis deployment, RedisInsight merges the graphical user interface with Redis CLI. Visually, we can browse and collaborate with data, understand by example, take benefits of diagnostic tools, and others.
Installation of Redis on UbuntuFollow the steps given below to install Redis on Ubuntu: First setup a non-root user using sudo and then install build and test dependencies: 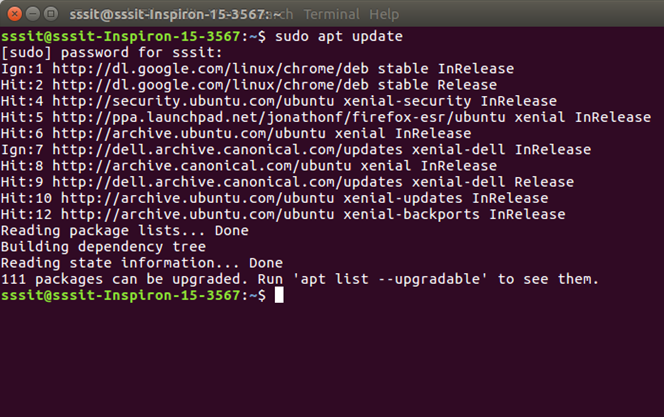
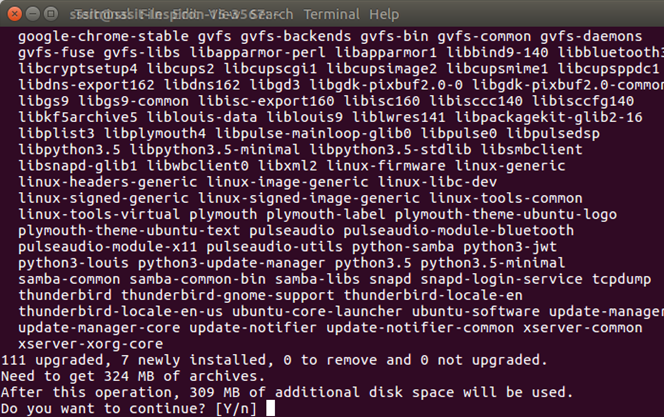
To continue press Y 
Install Redis ServerUse the following command to install Redis server: 
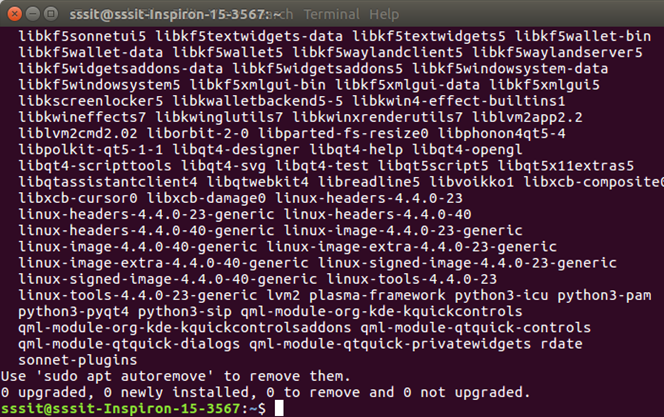
Now Redis Server is installed. You can start the Redis server: Start Redis ServerYou the following command to start redis server: 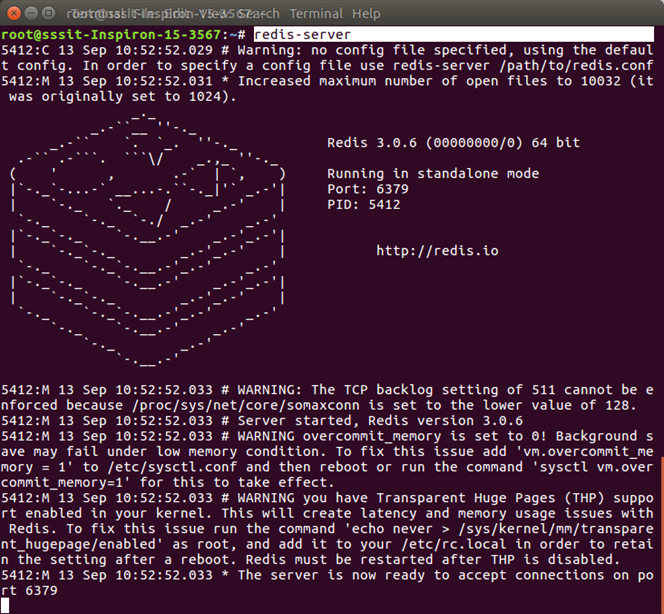
Start Redis ClientRedis server is started so you can start redis client to make communication between them. 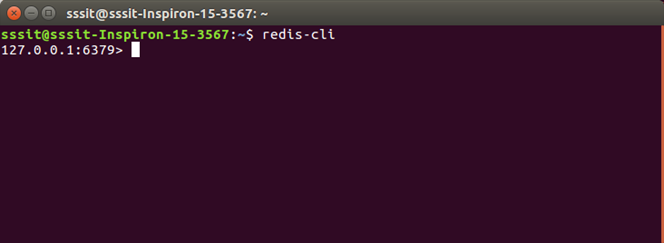
Verify if Redis is workingExecute the following command: This will open a redis prompt. redis 127.0.0.1:6379> In the above prompt, 127.0.0.1 is machine's IP address and 6379 is the port on which Redis server is running. Now type the following PING command. It specifies that Redis is successfully installed on your system. 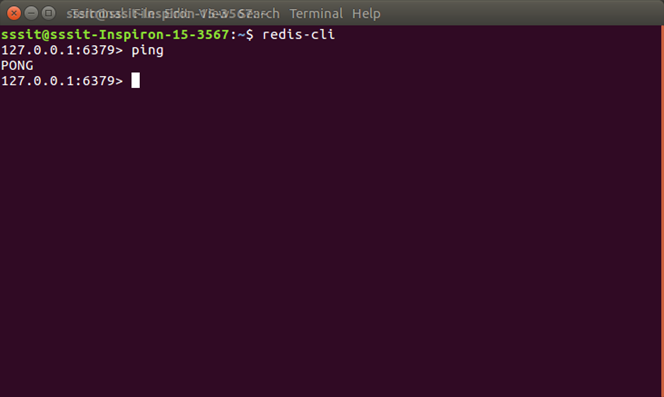
Next TopicRedis Configuration
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










