Research Problem DefinitionPeople involved in a study can successfully perform testing due to several steps in the research procedure. Defining a research issue is crucial because it can assist you in describing your study's technique. There are various kinds of research problems you might run into, and knowing how they vary can help you to choose the best strategy. 
A research problem places a study's subject and significance in perspective and aids in defining the research question that will be investigated. Additionally, it offers a format for summarizing study findings that emphasize the knowledge gained. This writing covers the definition of a research problem, a list of the various kinds. Definition of Research Problem
The issue or topic that a researcher wants to explore through research is known as a research problem. Any research work must begin here because it establishes the investigation's path, parameters, and goals. The research problem is a thesis that examines a knowledge gap, a problem, or a discrepancy in a specific area. The purpose of a scientist's study or analysis is identified and defined using research problems. If you're interested in advancing societal or scientific knowledge or adding to an existing subject, you might choose to perform a study based on a challenge. A research problem may also assist in defining important terms, broad queries, and other study-related variables. Types of Research Problems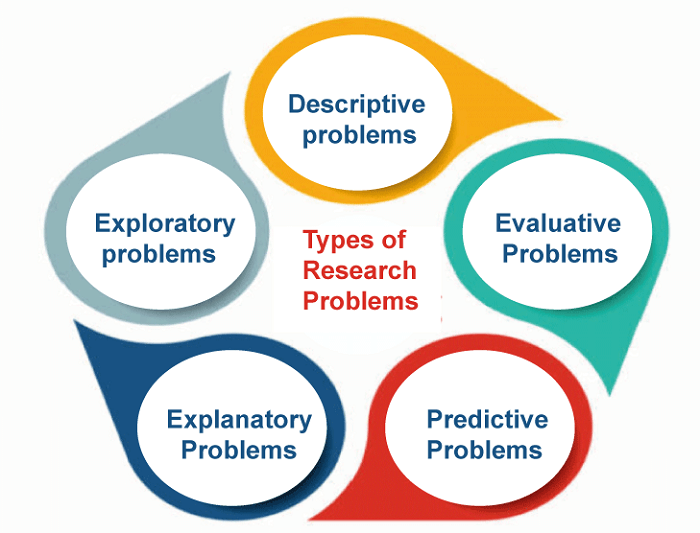
The following are the various types of research problems. 1. Descriptive Problems These issues revolve around describing or recording a specific occurrence, incident, or circumstance. For instance, a researcher might look into the age, gender, salary, and schooling of a particular community. 2. Exploratory Problems These problems are made to look deeply into a specific subject or issue, frequently to develop new theories or ideas. For instance, a scholar might look into the elements that affect workers in a particular industry's level of employee satisfaction. 3. Explanatory Problems These issues usually involve testing ideas or hypotheses to understand why a certain phenomenon or event happens. A scholar might examine the connection between exercise and mental health to determine whether activity directly impacts mental health. 4. Predictive Problems Making predictions or estimates about potential occurrences or patterns is required for these issues. For instance, a researcher may examine the variables influencing possible success in a specific area or business. 5. Evaluative Problems These issues entail determining how well a specific intervention, program, or strategy works. For instance, a researcher might assess the effect of a novel instructional method on the results of pupil learning. How to Define a Research Problem
The research problem is a particular query or problem a researcher tries to answer through a research project. The following stages should be taken when determining a study problem.
Research Problem's Components
A research issue usually consists of the following components
Some Examples of Research Problems1. Research Problem in Psychology
Following are a few examples from psychology.
2. Research Problem in Economics
Here are some examples from economics.
3. Research Problem in Sociology
Here are some sociological examples.
4. Research Problem in Environmental Science
Here are some examples from environmental science.
5. Research Problem in Political Science
Here are some political science examples.
6. Research Problem in History
Here are some history examples.
7. Research Problem in Education
Here are some examples of education research problems.
8. Research Problem in BusinessHere are some business examples.
Research Problem's Benefits
The following are some benefits of a specified research problem. 1. Focus A research problem gives the investigation a specific and concentrated direction. It ensures that the research problem is not a deviation and that the study continues on course. 2. Clarity A research problem gives the research topic context and focus. It ensures that the study is not overly wide or focused and that the goals are properly described. 3. Relevance A research problem guarantees that the study is relevant to the topic of study and adds to the body of current knowledge. It deals with areas needing more information, concerns requiring more research, or theoretical or practical challenges. 4. Feasibility A research problem assures that the study is feasible due to the availability of information, resources, and research techniques. Given the available time, funds, and assets, it guarantees that the study can be carried out accurately and practically. 5. Novelty A research problem guarantees the study's originality and creativity. It gives an updated or original viewpoint on an ongoing issue, investigates a brand-new field of research, or adapts an existing theory to a novel situation. 6. Importance The existence of a research problem assures that the study's importance and significance because of its potential influence on a certain area of research or society are both significant. It can provide new information, develop established theories, or resolve a crucial societal problem. 7. Rigidity A research problem guarantees that the study is rigid and conforms to accepted research procedures. It ensures the analysis is carried out methodically, objectively, and impartially. The Objective of Research Problems
Research challenges serve the objectives of identifying a field of study that needs more examination and developing a clear research question. The clear issue or problem that has to be addressed is defined by a research problem, which also acts as the project's starting point. Discovering a research problem is crucial because it establishes the scope of the investigation and provides a structure for the design and interpretation of the study. Additionally, it guarantees that the study is pertinent and adds to the knowledge already accumulated in the field of study. A clearly stated research problem should have the following elements
Uses for the Research Problem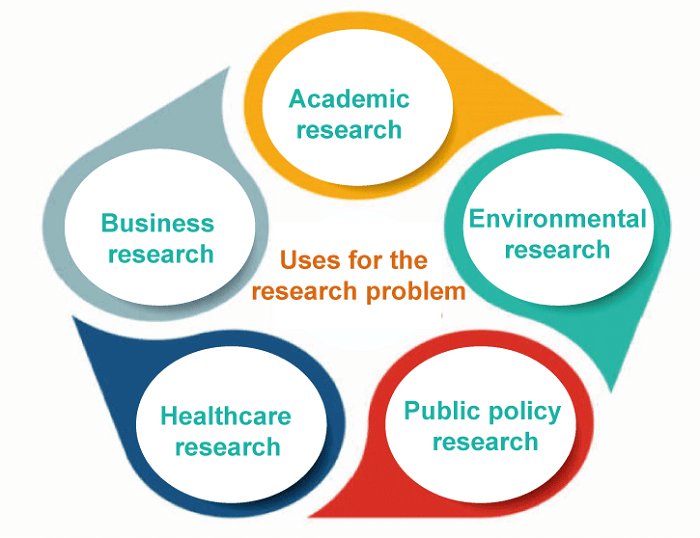
The following are ways to utilize the research problem. 1. Academic Research Academic research is performed in various subjects, including the social sciences, humanities, and engineering. Researchers employ research challenges to fill in knowledge gaps, solve theoretical or practical problems, and discover new fields of study. 2. Business Research Organizational, market, and consumer behavior studies and other types of business research are all guided by research problems. Researchers employ research problems to determine company difficulties, look at potential solutions, and create plans for achieving business development and success. 3. Healthcare Research Medical, clinical, and health services research, as well as other types of this field's study, are all guided by Healthcare research problems. Academics use research problems to determine issues in healthcare, create new therapies and interventions, and enhance the quality of care and its results. 4. Public Policy Research Policy analysis, program assessment, and policy formation are all examples of public policy research. To solve societal concerns, researchers employ research questions to determine social problems, evaluate the efficacy of current policies and programs, and create brand-new policies and programs. 5. Environmental Research Environmental science, ecological research, and environmental management are all influenced by problems with the study. When identifying environmental issues, evaluating the effects of human activity on the environment, and creating long-term solutions to safeguard the environment, researchers employ research problems.
Next TopicReverse Osmosis Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










