RPM Command in LinuxRPM stands for Red Hat Package Manager. It is an open-source package manager (default) and the most famous utility of package management for Red Hat-based systems such as Fedora, CentOS, and RHEL. The tool permits system users and administrators for installing, updating, uninstalling, querying, verifying, and managing system software packages in Linux/UNIX operating systems. Formerly, the RPM is called the .rpm file. It contains compiled software libraries and programs required by the packages. It only implements with those packages that were created in .rpm format. A few facts about RPM
Modes of RPM Command
Where to Search RPM Package The following is the rpm site's list where we can search and download the RPM packages. Note: In Linux, please remember we must be a super user at the time of installing the RPM packages. We can manage the rpm commands using appropriate actions with root privileges.1. Install RPM in LinuxWe can install the RPM package using the following command: 
2. Check the RPM Signature PackageBefore installing the packages on our Linux systems always check a PGP signature of them and ensure their origin and integrity are OK. We can use the below command using an option, i.e., -checksig (stands for check signature) for checking the package's signature which is known as a apacheds-2.0.0.AM26-i386.rpm. 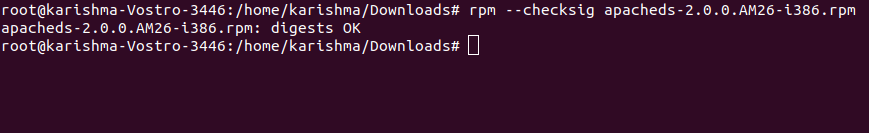
3. Check the RPM Package Dependency before installingLet's assume we wish to check the dependency of the RPM package before upgrading or installing a package. For example, we can use the below command for checking the dependency of a package, i.e., apacheds-2.0.0.AM26-i386.rpm. It will show the package dependencies list: 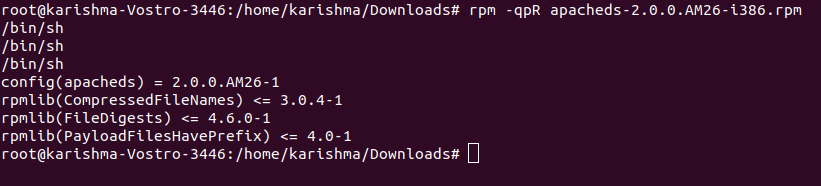
Where,
4. Install the RPM Package without the DependenciesIf we know that every needed package is already installed and the RPM is only being stupid, then we can avoid the dependencies with the help of the -nodeps option (means no dependency check) before installing any package. The command is mentioned as follows: 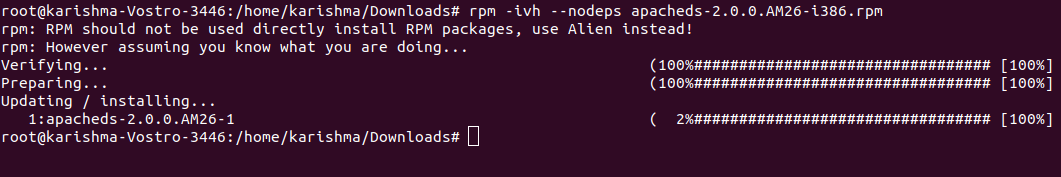
Forcefully, the above command will install the RPM package by avoiding the errors of dependencies. However, when those files of dependency are missing, the program will not implement at all, until we install them. 5. Check the RPM Package (Installed)Using an option -q along with the package name will display whether the RPM package is installed or not. The command is as follows: 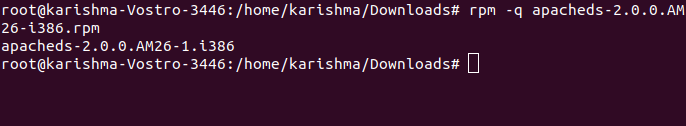
6. List each file of the installed RPM packageWe can use the -ql option (query list) with the RPM command for viewing each file of the installed RPM package. The command is as follows: 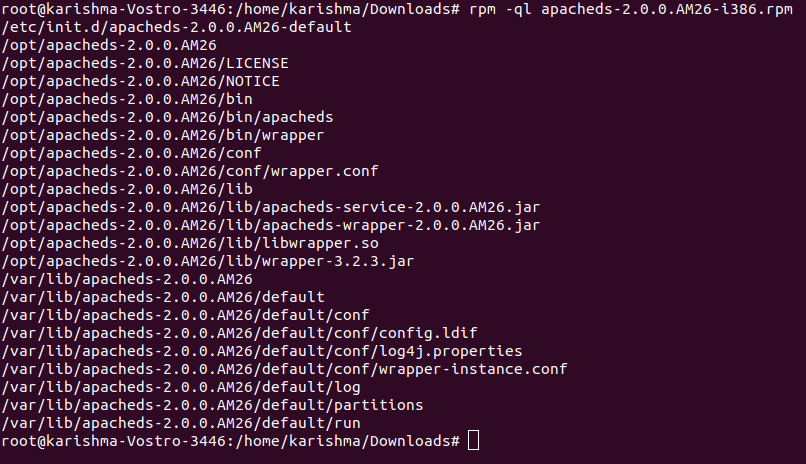
7. List RPM Packages (Recently Installed)We can apply the below command of RPM with an option, i.e., -qa (query all). This option will list every RPM package that is recently installed. The output will be as follows: 
8. List Each RPM Package (Installed)We can use the below command for printing each name of the package (installed) on our Linux system. the output is as follows: 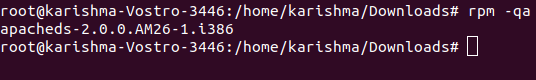
9. Remove the RPM PackageFor uninstalling or removing the RPM package, for instance, we can use the name of the package apacheds-2.0.0.AM26-i386.rpm, not the real name of the package apacheds-2.0.0.AM26-i386.rpm. In the following command, we are using an option, i.e., -e (erase) for removing the package. The output will be as follows: 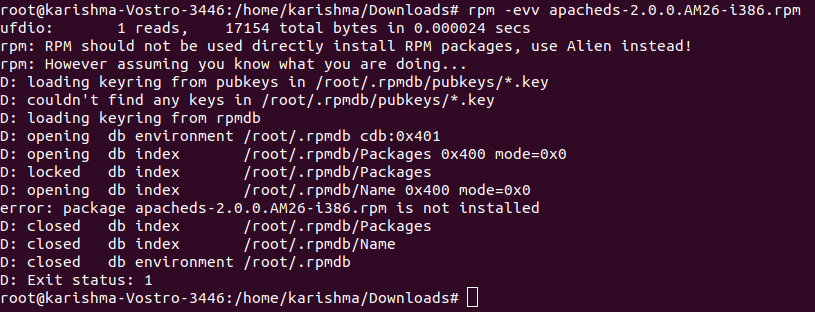
10. Query the Details of RPM Package (Installed)Let's say we have installed any RPM package and we wish to know the details of the package. The below option, i.e., -qi (query info) will print the details of an installed package that are available. The output is as follows: 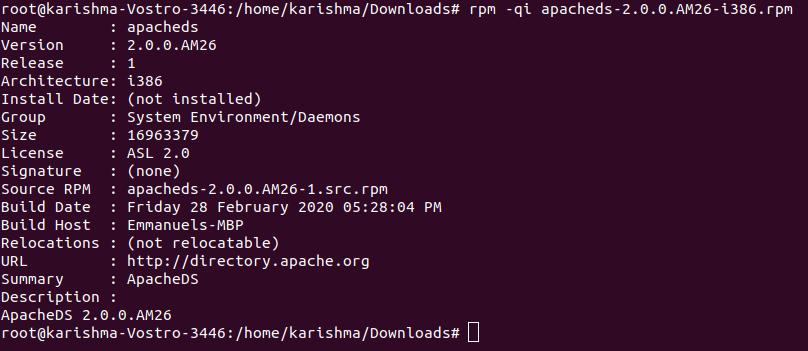
11. Details of the RPM Package Before InstallingWe have downloaded any package using the Internet and we wish to know the details of this package before installing. The below -qip (query info package) option will print the details about the package. The output is as follows: 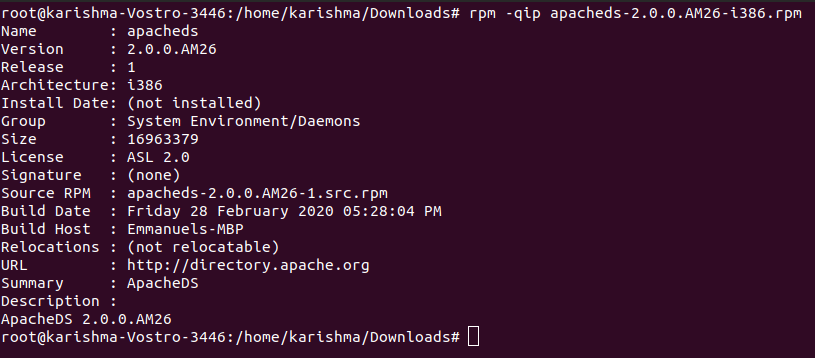
12. Verify the RPM PackageVerify any package will compare the installed file's information of the package for the data of the RPM. The -Vp (verify package) option is used for verifying the packages. The output will be as follows: 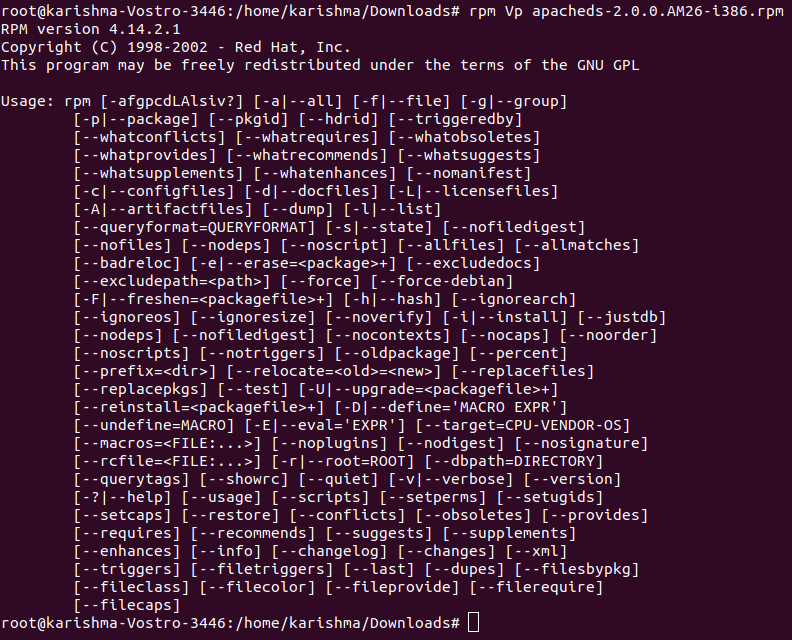
13. List Each imported GPG Key of RPMWe can use the below command for priting each imported GPG key in our system. The output is as follows: 
Next TopicCron Command
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










