Russell 2000 Index Definition and Key MetricsWhat exactly is the Russell 2000 Index?It is a stock market index that gauges the performance of the Russell 3000 Index's 2000 smaller businesses. The FTSE Russell Group of London handles the Russell 2000. Because it concentrates on smaller firms focusing on the US market, it is frequently seen as a barometer of the US economy. It monitors the performance of around 2000 of the smallest publicly listed firms in the United States. It is a component of the Russell 3000 Index, which is much larger and accounts for around 98% of the investable US stock market. 
Investors compare the performance of small-cap mutual funds to the movement of the index because it is thought to be a better representation of possible options in that entire sub-section of the market than broader indexes, which may have preconceived ideas or more stock-specific hazards that could skew outcomes. The Russell 2000 Index: An OverviewThe Frank Russell Company established the Russell 2000 Index in 1984. It is a US index managed by FTSE Russell, a London Stock Exchange affiliate. The index includes 2,000 small-cap firms. The index is the most often quoted gauge of small-cap to mid-cap stock performance. It makes up around 10% of Russell 3000's total market capitalization. It comprises the lower two-thirds of the Russell 3000 index's firm size. However, the more comprehensive index may also cover almost 98% of all publicly listed equities in the United States. Mutual fund investors like the Russell 2000 Index because it reflects the investment opportunity given by the whole market, as opposed to the possibility afforded by smaller indexes, which may contain bias or higher stock-specific risk, skewing a fund manager's performance. Many mutual and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are related to or based on the Russell 2000. What are prominent companies represented in the Russell 2000?The Russell 2000 index is composed of small-capitalization companies, which implies that their market capitalizations, or the total value of all outstanding shares, are smaller than those of companies in larger-capitalization indexes such as the S&P 500 or the Dow. According to FTSE Russell, which oversees the Russell 2000 index, the median market size of a firm in the Russell 2000 was around $1.03 billion in February 2022. It also claimed that the Russell 3000 Index has a median market size of $2.28 billion. Below are some of the top companies that make up the Russell 2000:
What does the Russell 2000 measure?It is a market-capitalization-weighted index, which means that the index's value is determined by the company's market capitalization or the total value of its outstanding shares. The weighting of a firm in the index changes in response to the performance of its shares. The index is commonly used as a performance benchmark by active small-cap investors. For example, suppose you invest in an actively managed small-cap mutual fund. In that case, the fund's performance will likely be compared to the Russell 2000 to decide if its active approach adds value for its owners. What's the best way to invest in the Russell 2000?One cannot invest directly in the Russell 2000 Index, but one can do so through mutual funds and exchange-traded funds that track the index. Fortunately, these funds are usually accessible for minor expenses. The iShares ETF is a popular ETF that provides investors with small-cap diversity for a 0.19 per cent (%) yearly cost. The Vanguard Russell 2000 Index Fund ETF (VTWO) is another ETF that mimics the index and has an expense ratio of only 0.10 per cent. How can a company become a part of the Russell 2000?To be eligible for inclusion in the Russell 2000, a company must first be eligible for inclusion in the Russell 3000. The Russell 2000 Index comprises the bottom 2,000 firms ranked by market capitalization by FTSE Russell. The top 1,000 firms are represented by the Russell 1000, which tracks large-cap enterprises. As new businesses that qualify for the Russell 2000 go public during the year, they are added to the index, occasionally pushing the total number of component firms past 2000. The index undergoes reconstitution once a year, in which firms are added or eliminated based on their current market cap. How is the Nasdaq Composite Index different from the Russell 2000 Index?NASDAQ is a stock exchange where users may purchase and sell equities electronically. The Nasdaq Composite index covers all the firms that trade on the NASDAQ market, including many technology and internet-related enterprises. The Nasdaq Composite Index is widely used to evaluate the performance of technology-related stocks, much as the Russell 2000 index is used to assess the performance of smaller US enterprises. Other famous indexes that monitor mostly large and profitable firms include the S&P 500 and the Dow Jones Industrial Average. The S&P 500 tracks around 500 companies, whereas the Dow tracks only 30. Is the Russell 2000 Index a component of the Russell US Index?The Russell 2000 Index is a component of the Russell US Index, and it essentially represents small-cap firms trading on the US stock exchange. The Russell 1000 Index reflects significant cap equities combined with the Russell 2000 Index to generate the Russell 3000 Index jointly. It is a significant proportion of the Russell 3000 Index, accounting for over 10% of its total market capitalization. 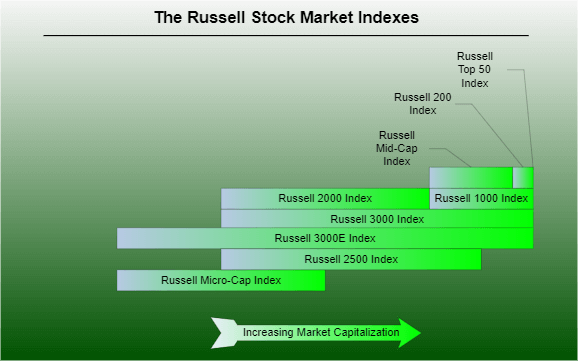
Is the Russell 2000 overvalued?In theory, businesses are worth the current value of their future revenues or profits. However, stock prices might differ significantly from their actual or intrinsic values at any time. There are various methods for computing the value of an index. Still, looking at multiple price earnings is one of the most used metrics. According to some associates, the Russell 2000 traded at a price-earnings ratio of about 23 as of March 2022, based on earnings expectations for the following 12 months. It is crucial to realize that this ratio is based on estimated earnings; therefore, actual revenues may differ. Following the initial fear over the worldwide epidemic (COVID-19), the Russell 2000, like other stock indices, did remarkably well. Nonetheless, it has recently retreated as investors became concerned about increasing interest rates and the Russia-Ukraine crisis. As of February 28, 2022, the index has declined by 6% in the previous year. Some Considerations before Investing in the Russell 2000 IndexThe Russell 2000 has several applications for investors. Individual investors can gain experience with the Russell 2000 through mutual funds and exchange-traded funds that attempt to replicate the index's performance, but investing directly in an index is not feasible. ETFs are more frequent than mutual funds that follow the Russell 2000. Here are a few of the biggest:
The advantage of utilizing the Russell 2000 as a balanced asset allocation process is that having stocks with both small and high capitalizations would help diversify a portfolio. This is especially true at different points of the economic cycle, with small-cap businesses frequently guaranteeing better-than-average returns during upswings, owing to their domestic revenue concentration. The Bottom LineThe Russell 2000 Index measures the performance of around 2,000 of the smallest publicly traded companies in the United States. Because it focuses on small enterprises that do business primarily in the United States, the Russell 2000 is sometimes viewed as an important economic indicator. It is a common approach to monitoring the universe of small-cap investment. Investors who want to profit from the index's success can purchase low-cost mutual funds and ETFs that follow it. It might be a benchmark or reference for investors who wish to emphasize more specialized sectors. The index is available to both institutional and individual participants. Because it is one of the most often utilized in the world, almost everyone who invests in small-cap stocks may use or come across it. FAQsQ. What is the Russell 2000 index? It is a component of the Russell US Indexes that primarily reflects small-cap equities traded on the US stock exchange. The Russell 2000 index covers around 2000 minor firms based on market capitalization and current index membership. It basically measures the performance of US small-cap equities. Q. How does the Russell 2000 Index tend to perform? The Russell 2000 was up roughly 14.40% a year to date in 2021, compared to 8.46% for the S&P 500 and 5.36% for the Nasdaq 100. The Russell 2000 stocks that have gained in value by more than 1000% in the previous year include Gamestop Corp, Digital Turbine, Silvergate Capital Corp Cl A, Five Prime Thera, At Home Group Inc, Sm Energy Company, Overstock.com Inc, Pacific Biosciences, Exp Realty International, and Novavax Inc. Q. Is the S&P 500 part of the Russell 2000? No, these two sets of stocks are in distinct categories. The Russell list only measures small-cap stocks, whereas the S&P 500 index tracks large-cap stock performance. Despite being market capitalization-weighted lists, the Russell 2000 and S&P 500 are vastly different. The Russell 2000 index is made up of 2000 small-cap businesses from the Russell 3000 index. The S&P 500, on the other hand, has no sequence; it combines 500 distinct shares from the most outstanding large-cap firms. The Russell 2000 index is a small-cap benchmark, whereas the S&P 500 is a large-cap benchmark. Russell has made significant investments in the health sector, whereas the S&P 500 focuses on information technology and financial businesses more. Q. How to buy the Russell 2000 Index Fund? Investing in Russell 2000 Index fund does not mean investing in all 2,000 stocks of it. A person can invest in the Russell 2000 Index by buying a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) that is designed to passively track the index. The Vanguard Russell 2000 ETF is an excellent example because it invests in all of the firms in the index based on their relative weights. The ETF's costs are minimal, with a tiny expense ratio.
Next TopicTop 3D Printing Stocks for Q4 2022
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










