SAP ABAP Tutorial
ABAP is the fourth-generation programming language and technical module of SAP, which is used to develop the applications related to SAP. With the help of ABAP, one can customize SAP according to the requirement. It is now used along with Java as the main programming language for the SAP application server. Our ABAP tutorial explains the key concepts of ABAP, such as ABAP workbench, ABAP Dictionary, ABAP Editor, Internal Tables, Objects, Classes, Operators, Variables, etc. It is designed for beginners who want to familiarize themselves with the SAP ABAP technology as it begins with basics and moves to the complex topics. It is also suitable for professionals who want to enhance their skills in ABAP programming and development. What is ABAP?
Why learn ABAP?Below are some reasons that explain the reason to learn ABAP:
Process of ABAP in SAP kernelWe can understand the process of ABAP in SAP by using 3 tier architecture of SAP. Consider the below image: 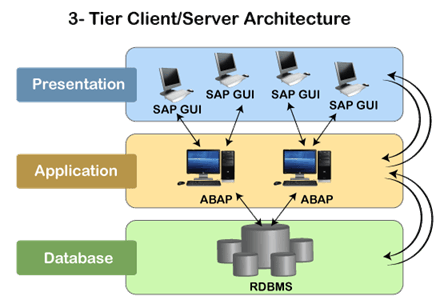
The ABAP application server is present on the Application layer of the SAP architecture. The application layer is the most important component of the SAP architecture as ABAP programs execute in this layer, and it communicates with both layers. The application server is responsible for interpreting the ABAP/4 programs. An ABAP program can start on the presentation server, but it can only execute at the application server. Each ABAP program is stored in the SAP database tables of the database layer, unlike the other C or Java, where programs are stored in other large files. The SAP database stores program in two forms, which are source code and generated code. The source code can be viewed and edited by the Workbench editing tools such as ABAP Editor, and the generated code is the binary representation of the source code. ABAP Runtime EnvironmentABAP Runtime Environment is a part of SAP kernel, and all the ABAP codes are processed under the control of the runtime environment. Since it is responsible for executing the ABAP Statements, controlling the flow logic, and responding to an event, so we can compare it with the Java virtual machine or JVM. Consider the below image to understand the processing of different processing blocks of an ABAP program: 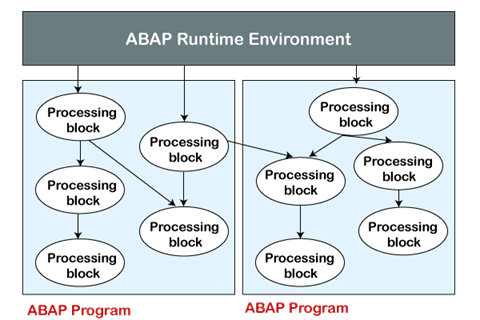
Database Interface is one of the important components of the ABAP runtime systems. It is responsible for converting the database-independent ABAP statements (Open SQL) to the underlying DBMS (Native SQL).All the communication of ABAP programs with RDBMS is handled by the database interface. ABAP ProgramsThe ABAP programs are executable unit or library that provides reusable code to other programs. These programs are executed on the SAP NetWeaver Application Server.An ABAP program contains several processing blocks that can be occurred in any order within source code. Each program in ABAP has its type that specifies how that program will run. There are mainly two types of ABAP programs, which are:
Note: The ABAP programs are explained in later chapters.Transactions/Transaction code in ABAPThe execution of a program in SAP is known as the transaction. The SAP system provides a specific four-character code for all the transactions that take place in SAP, and these codes are known as the transaction codes or TCode. Any ABAP program can be directly executed by entering the transaction code in the command field of the SAP screen. In ABAP programming, the transaction can be invoked programmatically by using statements CALL TRANSACTION and LEAVE TO TRANSACTION. Below is a list of few important TCodes used in ABAP:
Note: All the transaction codes are available in the TSTCT table in the SAP system.ABAP Development EnvironmentThe development environment is where we can develop ABAP based applications, and there are two ways to develop any application in ABAP. These ways are:
ABAP WorkbenchIt is part of the SAP ABAP system that contains various tools for editing in ABAP programs. It can be accessed using the SAP GUI. Some important tools of ABAP Workbench are given below:
ABAP Development Tool:ABAP development tools or ADT are used to run ABAP on the Eclipse platform, hence also known as "ABAP in Eclipse." ADT provides various plug-ins to develop ABAP applications on eclipse. History of ABAPThe ABAP is the core programming language of SAP System, which was first developed in the year 1980 by the SAP AG company in Germany. This language was first designed to develop the reports in the SAP R/2 system that made large corporations capable of building mainframe business applications for MM(Material Management) and FI(Financial Accounting). Over the years, SAP has added various new features to ABAP, such as ABAP Objects, ADT, etc. Below are some milestones in the development of ABAP:
PrerequisiteBefore learning ABAP, you must have the basic knowledge of any Object-oriented programming language such as C++, Java, etc., so that you can easily understand the ABAP programming. You should also have a basic idea about the database related concepts such as PL/SQL. AudienceOur ABAP tutorial is designed to help beginners and professionals. ProblemsWe assure you that you will not find any difficulty while learning our ABAP tutorial. But if there is any mistake in this tutorial, kindly post the problem or error in the contact form so that we can improve it.
Next TopicIntroduction to SAP ABAP Workbench
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share