Difference Between SATA and PATASATA stands for Serial ATA, and PATA stands for Parallel ATA. They both refer to two different methods of encoding and transporting data electronically. The data transfer speed of SATA is higher than that of PATA. Unlike PATA devices, all SATA devices have the 'Hot Swap" feature. They also differ in the physical layout of both connectors and other hardware. Definition of SATASATA stands for serial ATA. It is a computer bus interface that connects the bus adapters to the storage device such as hard disk drives. It has advantages over PATA, such as smaller, and less expensive cables, faster data transfer rates, hot swapping, etc. The SATA devices and host adapters communicate through the high-speed serial cable over the conductors. Because it utilises Primary ATA and the ATAPI command group like legacy ATA devices, it is backwards compatible. SATA brought a major change in computer hardware where it replaced Parallel ATA in customer desktop and laptop computers and in newer embedded applications. The primary STA connector contains seven pins, two twister pairs, and three ground wires. With clock frequencies ranging from 1.5 to 6.0, differential transmission is used. The more recent SATA version additionally offers isochronous transmission capabilities for audio and video devices. An improved technique, known as AHCI, is incorporated in SATA to enable hot plug and (NCQ) Native Command Queuing (Advances Host Controller Interface). Advantages of SATA over PATAThe following are the advantages of SATA over PATA: Increased Data Transfer Rate The faster data transfer speeds offered by SATA are the main reason it is preferred to PATA. PATA can transfer data at speeds of 66, 100, and 133 MB/s while SATA can do so at 150/300/600 MBs/second. The numerous PATA and SATA flavours, with the fastest speeds being the most recent versions of each now offered, are what cause the speed disparities. We will observe that even its at lowest speed, SATA is still faster than PATA, Programs can load more quickly thanks to SATA's increased speed, and larger documents can open more quickly too. Faster data transfer rates can result in improved gaming experiences for fans of video games (i.e., smoother game-play). Support For More Drives Multiple SATA hard drives can be connected together thanks to the four to six SATA connections on a motherboard. On a typical computer motherboard, only two PATA connections can accommodate up to four PATA hard drives. Increased Airflow Because SATA cables are thinner than PATA cables, there is more ventilation inside the computer casing and less heat build-up. A computer's overall life can be extended with better airflow. Easy Cable Management and Cable Length The length of the cable connecting the hard drive to the motherboard of the computer is another benefit of SATA over PATA. The PATA cable can be as long as 18-inches, but a SATA cable can be as long as 3.3 feet (1 metres). This additional length gives us more options for where to attach a hard disc within a computer casing. Disadvantages of SATA over PATAThe following are the disadvantages of SATA of over PATA: One Drive Per Cable Another drawback of SATA is that only one SATA hard drive may be connected at a time using the cable. A PATA cable, however, enables the connection of two PATA hard drives per cable. Drivers and Support Only a few minor drawbacks of SATA over PATA exist; one drawback is that SATA hard drives occasionally need a unique device driver for the computer to detect and use the drive. The specific driver does not have to be loaded because a SATA hard drive can function as a PATA hard drive. However, in order to acquire these mimic capabilities, certain SATA functionality is lost. SATA drives are not supported by the older operating systems like Windows 95 and 98, developed many years before SATA was first offered. Definition of PATAPATA (Parallel ATA) is the latter version of ATA (Advanced Technology Attachment) and the former version of SATA. As was already, the interface standard for connecting storage devices is these AT attachments (hard disks, floppy drives and optical disks). X3/INCITS committee maintains the standard and uses AT attachment (ATA) and AT Attachment Packet Interface (ATAP) standards. The PATA standard is the result of a gradual evolution that began with the original AT attachment interface used in earlier PC AT devices. The original ATA is now known as PATA with the development of the SATA. In PATA, the cable's maximum length is 18 inches (457.2 mm). Only the internal computer storage interface can use PATA cables because of their limited length. The PATA utilises a 16-bit wide data bus in addition to additional support and control signals. It operates at a low frequency and is connected to the ribbon cable by 40-pin connectors. Every cable contains two or three connectors, one of which is connected to the interface adapter, and the other two are plugged into drives. Difference Between SATA and PATA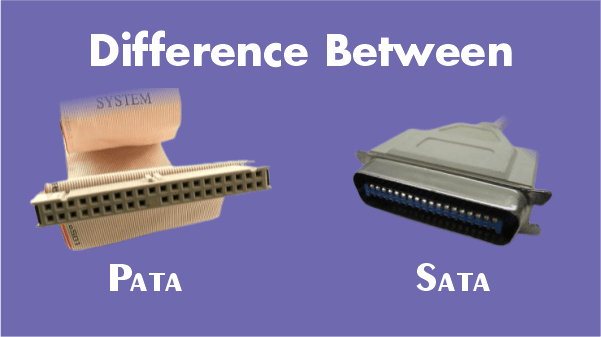
Key Differences Between SATA and PATA
ConclusionAmong SATA and PATA, Serial-ATA has a number of advantages over Parallel-ATA, including quick data transfer and a cable and connector that is smaller than the enormous 40-pin connector.
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










