Simple Present Tense DefinitionIn English grammar, the simple present tense is a fundamental tense that's utilized to describe acts, events, and circumstances that are presently taking place or that are largely true. It is the most often used tense in English and is utilised in everyday communication. In this blog post, we will look more closely at the definition and applications of the simple present tense. 
What Exactly Is Simple Present Tense?The simple present tense is a grammar tense used to describe activities or events that are now taking place or that take place on a regular or habitual basis. In this tense, the verb adopts the base or root form, which stays unchanged regardless of the subject or number of subjects. "I play tennis," for example, and "He plays tennis" are both examples of the simple present tense. With both singular and multiple subjects, the verb "play" remains unchanged. Use Of the Simple Present Tense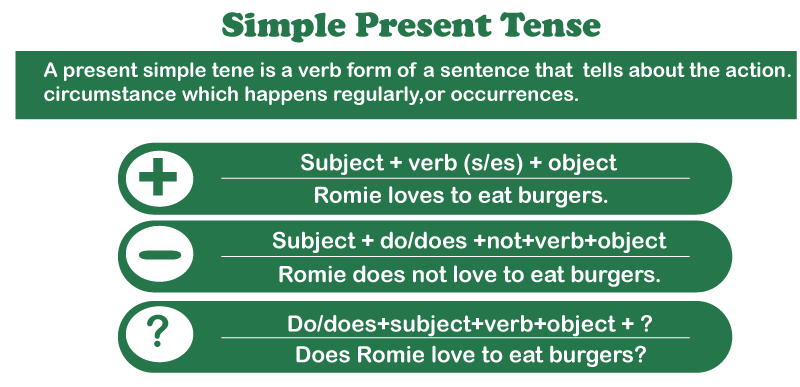
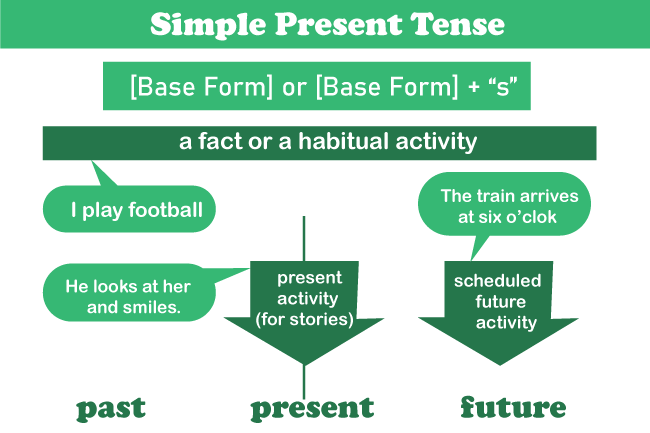
In English grammar, the simple present tense has various applications. Among the most common applications are: Defining Routines and BehavioursRoutines, habits, and generic facts are frequently described in the simple present tense. "I eat fruits every evening," for example, and "The sun revolves around the earth are both instances of the simple present tense . Opinions and Broad GeneralisationsThe simple present tense is additionally utilized to communicate generalisations and ideas. "I think dogs are terrific pets," for instance, and "The city is usually crowded" are both instances of the simple present tense used to express thoughts and generalisations . Describe the Current EventsAnother popular application of the simple present tense is to describe acts that are taking place at the time of speaking. for example "She engages in phone conversations with her boss, " In Reference to Scheduled EventsThe simple present tense may also be employed to allude to scheduled or organised future occurrences, as in "My plane leaves tomorrow night" and "The performance begins at 8 p.m. tomorrow. " It is crucial to note that, whereas the Simple Present Tense may be utilized to describe actions that happen on a regular or routine basis, it cannot express actions that happen in the present. "I eat a meal every day," for instance, indicates a habitual action, whereas "I am eating cereal right now" describes a current action Forming the Simple Present TenseThere are a few guidelines to follow based on the verb used to construct the Simple Present Tense. The root form of the verb is used to create the Simple Present Tense. Regular Verbs: The basic form of a regular verb is the same as the present participle, which finishes in -ing. Simply remove the -ing ending to form the Simple Present Tense. For example, travel (base form) becomes "I travel to work each day. " Speak (base form) becomes "Every evening, she speaks on the phone with her colleagues. " Irregular Verbs: The root form of an irregular verb may vary from the present participle. The basic form is used to create the Simple Present Tense in this situation. For instance, dine (base form) becomes "I dine ever weekend with my friends." Go (root form) becomes "He goes to the workout after office . Singular Third Person: The verb form in the third person singular (he, she, it) is frequently modified by introducing -s or -es to the base form. For instance , Visit (base form) becomes "He visits to park every day. " Research (base form) becomes "She researches for course work every night. " When trying to add -s or -es to the root word, there are some exceptions to this rule. Verbs that finish in -s, -sh, -ch, -x, or -o, for example, add -es rather than -s. As an example : 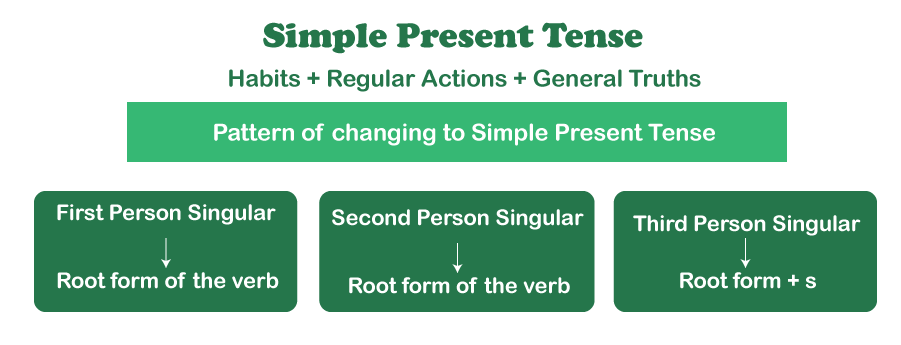
Carry (base form) becomes "She carries the board perfectly. " Rinse (base form) becomes "He rinses the clothes every night. " Finally, the Simple Present Tense is constructed by employing the verb's base form. The base form of a regular verb is the same as the present participle, whereas the base form of an irregular verb may be different. With a few exceptions, -s or -es is frequently attached to the basic form of the verb in the third person singular. Importance and Significance of Simple Present Tense
Finally, the simple present tense is an important aspect of English grammar. It is used to communicate information about what is now happening, whatever we do on a regular basis, and what we think to be true. Communication in English would be less accurate and efficient without the simple present tense. Tips To Use Simple Present Tense CorrectlySimple present tense is the basic fundamental tense that is used by all. Here are some common mistakes that learners often make while using Simple Present Tense; Students frequently forget to add -s to the third person singular in the present simple:
Students frequently employ the present simple for actions occurring at the time of speaking rather than the present continuous:
Students can substitute will for the present simple to signify a future action after phrases like if, as soon as, before, when, and whether :
Students can utilize the present continuous rather than the present simple when discussing well-known facts and persistent situations:
Pupils forget that the present continuous shouldn't be employed after phrases that indicate feelings, senses, or emotions :
When pupils speak about something that was not completed at the time they spoke, they forget to utilise the present perfect. They must not employ the simple present or the continuous present:
Examples of Simple Present TenseHere are some examples of Simple Present Tense
How To Make Simple Present Tense NegativeWe use the phrase do not accompanied by the root of the verb to make the simple present tense negative, excluding the third person singular, when we use does not accompanied by the root of the verb. The contractions don't and doesn't are also acceptable. Following are some negative examples of the simple present tense:
Our good friend the verb be is a classic exception to this rule. When we use the verb be, we modify it normally and add the word not after it. Here are several examples:
Contractions can also be used :
A less typical case involves assisting verbs. While assisting verbs are rarely employed by themselves, they do occur before the word not when used in the negative. Consider the following examples:
Present Simple QuestionsWe employ 'Do' or 'Does' to form queries in the Present Simple. When we pose inquiries in The word order in English is distinctive : Do/Does + subject + verb
When should we use do vs does ?
Questions with a yes/no answer Use 'Do'/'Does' (or 'Don't'/'Doesn't' for a negative inquiry) + the base form of the primary verb to construct a question that will be replied with a 'yes' or 'no' .
When using 'Does,' do not include '-s' to the primary verb . - Does he write stories ? NOT: Does he writes stories ? Specific Inquiries Special questions (also known as wh-questions) demand extra information in their responses. They are composed of wh-words such as what, where, when, why, which, who, how, how many, and how much. To create a special question, employ the exact same wording as for yes-no questions, but place a whword in front of the verb 'do' or 'does'. The format is as follows: wh- word do or does subject primary verb.
'Be' is a verb. We refrain from conjugating 'do' or 'does' with the verb 'to be'. We use the words 'am,' 'is,' or 'are'. The word order is identical .
Final NotesIf you wish to talk about an action that is happening right now, you will use the present simple tense. This is a prevalent tense in the English language that has its own set of grammar rules. It is critical to understand and apply these standards so that your communication is concise and comprehensive. The simple present tense of English verbs is more difficult than its name implies. The simple present tense is among the many verb forms linked with the present tense in English grammar. The simple present tense is commonly employed in the four general instances listed below:
Most of the time, the first, second, and third person plural regular verbs are uncomplicated and look exactly like the infinitive verb form . The third person singular contains a couple grammatical principles that may require some learning at first but will become second nature with practice .
Examples : Infinitive: To Read ; First Person: I read/We read ; Second Person: You read ; Third Person- He goes/ reads/They go/read ; First Person: I study/We study ; Second Person: You study ; Third Person: She studies/They study Infinitive: To fix ; First Person: I fix/We fix ; Second Person: You fix ; Third Person: he fixes/they fix The simple present tense can be coupled with numerous expressions to indicate that an action occurs on a regular basis, such as "every Wednesday," "always," "generally," "once a week," and so on. Furthermore, this form can be rendered negative or utilised in the interrogative form. This so-called simple tense allows us a great deal of versatility in expressing complex ideas.
Next TopicSupply Chain Management Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










