SISDSISD stands for 'Single Instruction and Single Data Stream'. It represents the organization of a single computer containing a control unit, a processor unit, and a memory unit. Instructions are executed sequentially, and the system may or may not have internal parallel processing capabilities. Most conventional computers have SISD architecture like the traditional Von-Neumann computers. Parallel processing, in this case, may be achieved by means of multiple functional units or by pipeline processing. 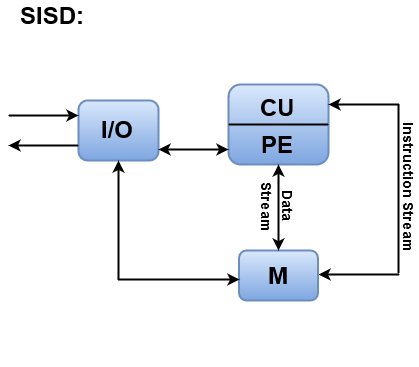
Instructions are decoded by the Control Unit and then the Control Unit sends the instructions to the processing units for execution. Data Stream flows between the processors and memory bi-directionally. Examples: Older generation computers, minicomputers, and workstations
Next TopicSIMD
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










