Skip list in Data structureWhat is a skip list?A skip list is a probabilistic data structure. The skip list is used to store a sorted list of elements or data with a linked list. It allows the process of the elements or data to view efficiently. In one single step, it skips several elements of the entire list, which is why it is known as a skip list. The skip list is an extended version of the linked list. It allows the user to search, remove, and insert the element very quickly. It consists of a base list that includes a set of elements which maintains the link hierarchy of the subsequent elements. Skip list structureIt is built in two layers: The lowest layer and Top layer. The lowest layer of the skip list is a common sorted linked list, and the top layers of the skip list are like an "express line" where the elements are skipped. Complexity table of the Skip list
Working of the Skip listLet's take an example to understand the working of the skip list. In this example, we have 14 nodes, such that these nodes are divided into two layers, as shown in the diagram. The lower layer is a common line that links all nodes, and the top layer is an express line that links only the main nodes, as you can see in the diagram. Suppose you want to find 47 in this example. You will start the search from the first node of the express line and continue running on the express line until you find a node that is equal a 47 or more than 47. You can see in the example that 47 does not exist in the express line, so you search for a node of less than 47, which is 40. Now, you go to the normal line with the help of 40, and search the 47, as shown in the diagram. 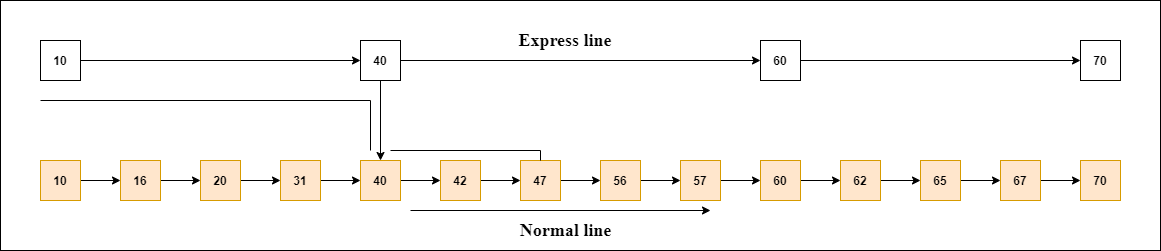
Note: Once you find a node like this on the "express line", you go from this node to a "normal lane" using a pointer, and when you search for the node in the normal line.Skip List Basic OperationsThere are the following types of operations in the skip list.
Algorithm of the insertion operation Algorithm of deletion operation Algorithm of searching operation Example 1: Create a skip list, we want to insert these following keys in the empty skip list.
Ans: Step 1: Insert 6 with level 1 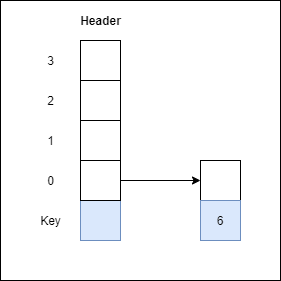
Step 2: Insert 29 with level 1 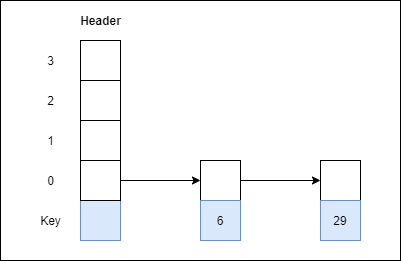
Step 3: Insert 22 with level 4 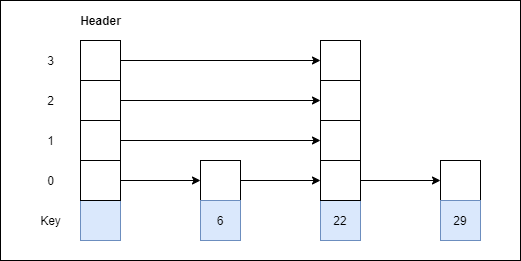
Step 4: Insert 9 with level 3 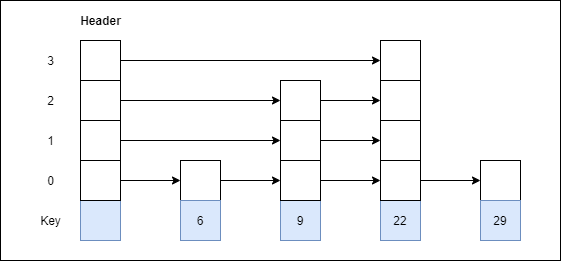
Step 5: Insert 17 with level 1 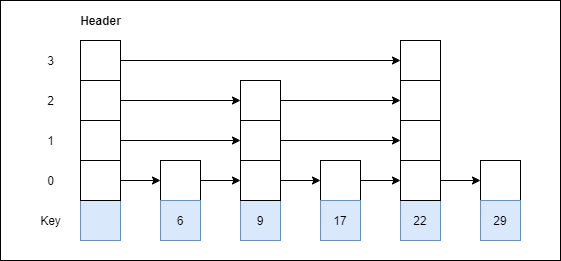
Step 6: Insert 4 with level 2 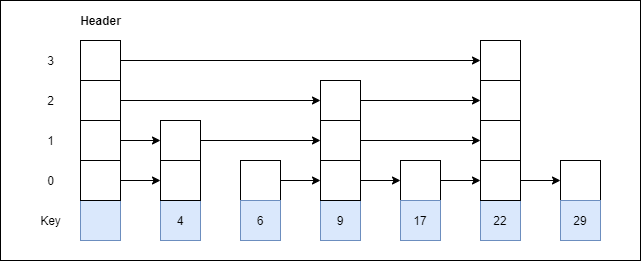
Example 2: Consider this example where we want to search for key 17. 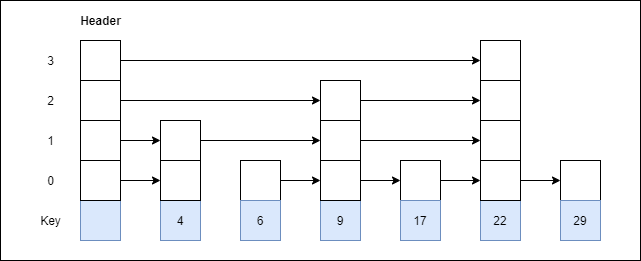
Ans: 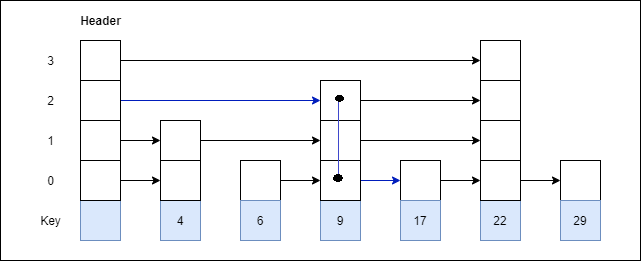
Advantages of the Skip list
Disadvantages of the Skip list
Applications of the Skip list
Next TopicData Structure stack
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










