What is the full form of SMTPSMTP: Simple Mail Transfer ProtocolSMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. It is a standard protocol on a TCP/IP network for sending emails through servers from one computer to another computer. It is a part of the application layer of the TCP/IP protocol, which makes possible to send email messages over the internet to one or more recipients. So, it is used when an email is sent from an email client, such as Outlook Express or Gmail, to the recipient using email servers. 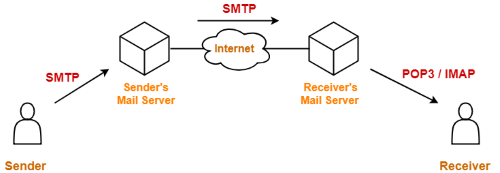
SMTP moves your email across networks through a process called "store and forward." It works in coordination with Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) to send you mail to the right computer and email inbox. It decides how an email will move from one computer's MTA to another computer's MTA. The message moves in steps from its origin to its destination, and at each step, SMTP does its job. SMTP is developed and maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). It is also known as RFC 821 and RFC 2821. It uses port 25 and sets up communication rules between servers and works by starting a session between the user and server, whereas Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) and Mail Delivery Agent (MDA) provide domain searching and local delivery services, respectively. It functions when computers are connected with Internet Service Providers (ISP). The ISP servers then deliver the mail to the recipients having internet service. Components of SMTP:
How SMTP Works:The working of SMTP is a three-step process and is based on the client/server model. In the first step, an email server sends the email (message) from an email client such as Gmail, Outlook, etc., to an email server using SMTP; in the second step, the email server using SMTP sends the email to the receiving email server. In the third step, the receiver server uses an email client to download incoming mail via IMAP and place it in the inbox of the recipient. Let's understand in an easy way:
Benefits or Advantages of SMTP:
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










