Coupling and CohesionModule CouplingIn software engineering, the coupling is the degree of interdependence between software modules. Two modules that are tightly coupled are strongly dependent on each other. However, two modules that are loosely coupled are not dependent on each other. Uncoupled modules have no interdependence at all within them. The various types of coupling techniques are shown in fig: 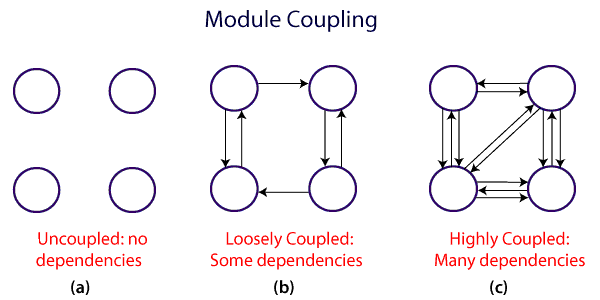
A good design is the one that has low coupling. Coupling is measured by the number of relations between the modules. That is, the coupling increases as the number of calls between modules increase or the amount of shared data is large. Thus, it can be said that a design with high coupling will have more errors. Types of Module Coupling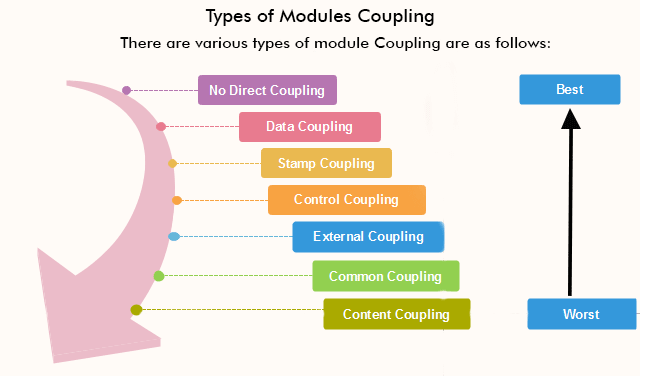
1. No Direct Coupling: There is no direct coupling between M1 and M2. 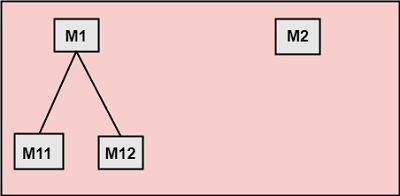
In this case, modules are subordinates to different modules. Therefore, no direct coupling. 2. Data Coupling: When data of one module is passed to another module, this is called data coupling. 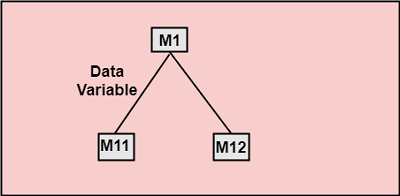
3. Stamp Coupling: Two modules are stamp coupled if they communicate using composite data items such as structure, objects, etc. When the module passes non-global data structure or entire structure to another module, they are said to be stamp coupled. For example, passing structure variable in C or object in C++ language to a module. 4. Control Coupling: Control Coupling exists among two modules if data from one module is used to direct the structure of instruction execution in another. 5. External Coupling: External Coupling arises when two modules share an externally imposed data format, communication protocols, or device interface. This is related to communication to external tools and devices. 6. Common Coupling: Two modules are common coupled if they share information through some global data items. 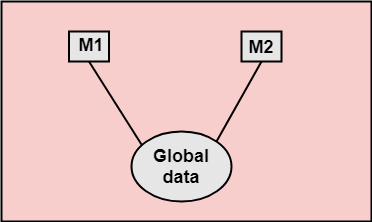
7. Content Coupling: Content Coupling exists among two modules if they share code, e.g., a branch from one module into another module. Module CohesionIn computer programming, cohesion defines to the degree to which the elements of a module belong together. Thus, cohesion measures the strength of relationships between pieces of functionality within a given module. For example, in highly cohesive systems, functionality is strongly related. Cohesion is an ordinal type of measurement and is generally described as "high cohesion" or "low cohesion." 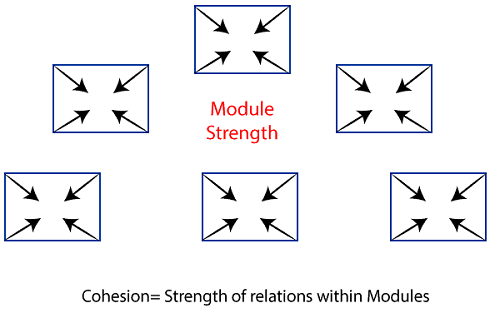
Types of Modules Cohesion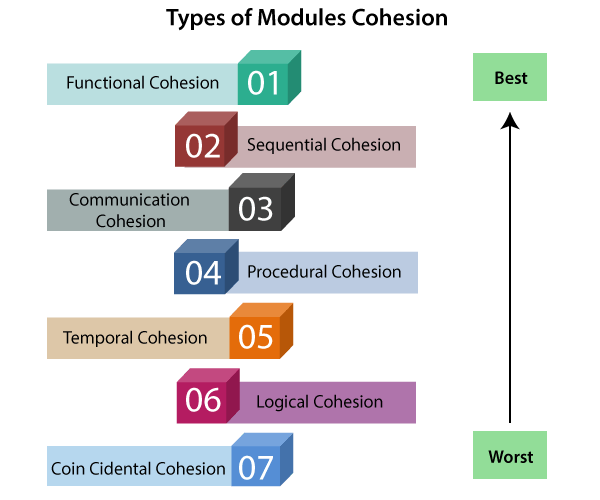
Differentiate between Coupling and Cohesion
Next TopicFunction Oriented Design
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










