Stock DefinitionThe ownership of a portion of the issuing company is represented by a stock, sometimes referred to as equity, which is a type of security. Shares, which are fractional units of stock, entitle its holders to a share of the company's assets and income, according to the number of shares they own. Stocks, which are often purchased and sold on stock exchanges, make up the majority of individual investors' portfolios. During stock trading, regulations put in place by the government are required to protect investors from deceptive practices. 
Stocks A Basic OverviewCompanies issue stock to obtain money to run their operations, and a shareholder who owns stock may be entitled to a portion of the company's revenues and assets. A shareholder is recognized as the owner of the issuing company based on the percentage of shares they possess compared to the total number of shares outstanding. One individual would hold and be entitled to 10% of the firm's assets and earnings if the company had 1,000 outstanding shares of stock and that person owned 100 of them. Despite the fact that stockholders are not truly own corporations, the law treats them as legal entities, making them a special type of organization. Businesses file their tax returns. is capable of being sued, borrowing money, and owning property. According to this idea, if a firm is seen as a "person," then it owns its assets. Owner of a corporate office with several chairs and tables is the corporation, not the shareholders. Stock, often referred to as capital stock, is the term used to describe all of the shares that make up a corporation's or company's ownership in the financial industry. 
Shares are also referred to as "stocks" in American English. Depending on the total number of shares, one share of stock corresponds to a small portion of ownership in the business. Upon the satisfaction of all senior claims, such as secured as well as unsecured debt, the shareholder (stockholder) is typically entitled to that portion of the company's earnings, profits from the sale of assets, or voting power, with these portions frequently being distributed in proportion to the amount of money each stockholder has invested. 
Stocks are not all created equal. For instance, some classes of stock may well be issued with enhanced voting rights, without voting rights, or with a particular priority to receive profits or proceeds from liquidation either before or after other classes of stockholders. Types Of StocksThe majority of people usually associate stocks with publicly traded shares that are exchanged on stock exchanges. Yet it's crucial for investors to be aware of the many stock kinds that are out there, to comprehend their special qualities, and to be able to judge the circumstances under which they can be a good investment. To help investors understand the numerous stock classes that are available, we have listed the different stock classifications below. Common And Preferred StockA company's ownership stake is represented by common stock, commonly referred to as ordinary shares. Holders of this type of stock are eligible to receive created earnings, which are normally paid out as dividends. The common investors of a corporation elect the board of directors and set corporate guidelines. Holders of this type of stock are entitled to receive the company's assets in the event of a liquidation, but only after preferred shareholders and other debt holders have been compensated. Common stock is frequently distributed to business founders and staff. 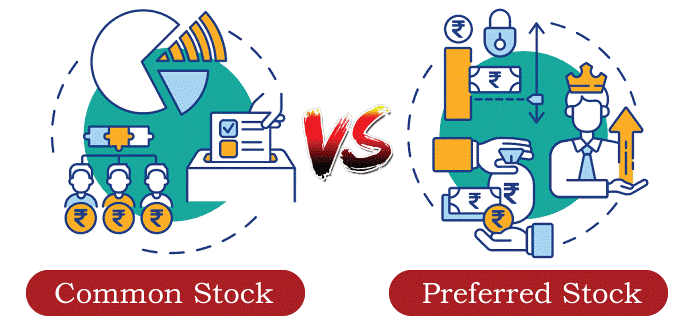
Preferred stock, commonly referred to as preference shares, holders are entitled to periodic dividend payments before dividends are distributed to common shareholders. As was already indicated, preferred shareholders are also paid back first in the event that a firm dissolves or declares bankruptcy. Preferred stock is suitable for investors looking for steady passive income because it has no voting rights. Both ordinary and preferred shares are provided by many businesses. Alphabet Inc., the parent company of Google, offers its preferred Class C stock Alphabet Inc. (GOOG), as well as its Class A ordinary stock Alphabet Inc. (GOOGL). Growth And Value StockGrowth stocks, as their name indicates, are securities that are anticipated to increase in value more quickly than the overall market. In general, economic prosperity and low interest rates are favorable conditions for growth stocks to thrive. For instance, recent years have seen significant gains in technology equities due to a healthy economy and easy access to cash. Investors may track growth equities by following the SPDR Portfolio S&P 500 Growth ETF, an ETF with a specific focus (SPYG). Value stocks, on the other hand, frequently trade at a discount compared to what a company's performance would normally suggest and have more attractive values than the broader market. 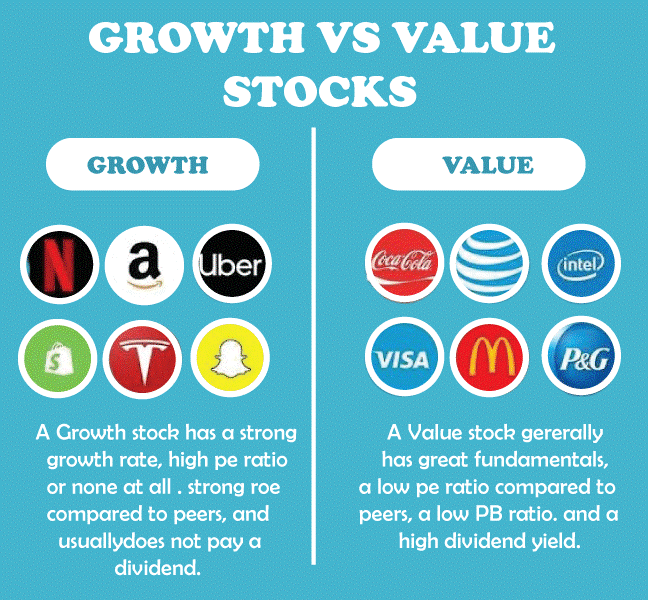
Value equities, such as those in the banking, healthcare, and energy sectors, frequently beat growth stocks during economic recovery because they typically have consistent income streams. By adding the SPDR Portfolio S&P 500 Value ETF (SPYV) to their watchlist, investors may monitor value equities. During the previous ten years, growth stocks have outpaced value equities by around 5.93%. Income StocksThe term "income stocks" refers to securities that offer investors a regular stream of income by paying out dividends that are greater than the industry average from a company's profits or excess cash. These securities?think utilities?generally have lower volatility and fewer capital gains than growth securities, which makes them suited for risk-averse investors looking for a steady income stream. Via the Amplify High Income ETF, investors get access to income equities (YYY). Blue-Chip StocksKnown for their huge market capitalizations, blue-chip stocks belong to well-established businesses. Businesses have a long history of reliably dominating their market or industry and generating constant, dependable income. Blue-chip stocks may make up the majority of a conservative investor's portfolio, especially during uncertain times. The leading fast-food company McDonald's Corporation (MCD), the technology behemoth Microsoft Corporation (MSFT), and the petroleum juggernaut Exxon Mobil Corporation are a few examples of blue-chip stocks (XOM). 
Cyclical and Non-Cyclical StocksThe status of the economy has a significant influence on cyclical stocks since they frequently track economic cycles of expansion, peak, recession, and recovery. During strong economic periods when customers have more disposable income, they typically exhibit greater volatility and outperform other equities. Apple Inc. (AAPL), a manufacturer of iPhones, and Nike, Inc., a major brand in sporting goods, are two examples of cyclical equities (NKE). Investors can purchase the Vanguard Consumer Discretionary ETF to include cyclical stocks in their portfolios (VCR). Non-cyclical stocks, on the other hand, operate in "recession-proof" sectors of the economy that typically do rather well at all times. As long as demand for essential goods and services remains stable, non-cyclical equities often outperform cyclical companies during economic slowdowns or downturns. The Procter & Gamble Company, one of the world's largest personal care companies, as well as beverage producers PepsiCo, Inc. (PEP) and The Coca-Cola Company are among the large-cap defensive equities that are exposed through the Vanguard Consumer Staples ETF (VDC) (KO). Defensive StocksIn most economic and market environments, defensive stocks typically offer stable returns. These businesses often offer necessities like food, medicine, and utilities along with other goods and services. Defensive stocks may be useful in protecting a portfolio from significant losses during a sell-off or bear market. Defensive stocks may be featured in addition to blue-chip, non-cyclical, value, income, and value equities. Cardinal Health, Inc., a global leader in healthcare, is one of the defensive businesses that make up the Invesco Defensive Stock ETF's core holdings. 
IPO StockWhen a business goes public, it offers shares of stock in an IPO (IPO). Before the company's equity listings on the stock exchange, IPO stock is often distributed at a discount. In order to prevent shareholders from selling the whole of their shares as soon as the stock starts trading, it could also include a vesting timetable. When referring to freshly listed stocks, market analysts also use the phrase "IPO stocks." On the Nasdaq website, investors may keep an eye out for forthcoming IPOs. 
How Stocks Are TradedThe majority of equities are listed on a stock exchange, which are gathering areas for buyers and sellers to negotiate prices. A trading floor is present in some exchanges, which are actual places where transactions are made. You've probably seen images of trading floors where people are shouting, waving, and signaling to one another while violently flinging their arms up. The other kind of exchange is virtual, consisting of a computer network where transactions are carried out electronically. A stock market's main function is to make it easier for buyers and sellers to trade assets, which lowers the risks associated with investing. Just consider how challenging it would be to sell stock if you had to make cold calls to potential buyers in your neighborhood. A stock market is really just a highly advanced farmers market that connects buyers and sellers. 
Separating the "main" market from the "secondary" market is important before moving on. The primary market is where securities are created, as opposed to the secondary market when investors trade previously issued securities without the involvement of the issuing companies (via an IPO). The secondary market is what people mean when they speak to "the stock market." It's crucial to realize that a firm is not involved directly in the trading of its shares. New York Stock ExchangeThe New York Stock Exchange is the world's most prestigious exchange (NYSE). The "Big Board" was established more than 200 years ago in 1792 when 24 stockbrokers and merchants from New York City signed the Buttonwood Accord. The NYSE is currently the preferred exchange for the biggest firms in America, and it offers stocks from companies like McDonald's, General Electric, Citigroup, Coca-Cola, Gillette, and Wal-Mart. The NYSE is the first kind of exchange , where a lot of the trading is done face-to-face on a trading floor. This exchange is also known as one that is "listed." Orders are placed through brokerage companies that are members of the exchange and then are passed down to floor brokers who travel to a specified area on the trading floor where the stock is traded. 
The "expert," who works at this place called the trade post, is responsible for connecting buyers and sellers. The current price is the highest sum that any buyer is willing to pay and the lowest sum that any seller is willing to accept. Prices are established using the auction method. After a trade is completed, the brokerage firm receives the information and notifies the investor who placed the order. Don't assume that the NYSE is still operating in the Stone Age just because there is some human interaction in this process; computers play a significant part. The NasdaqThe Nasdaq is the most well-known over-the-counter (OTC) market, which is the second type of exchange. Over-the-counter markets operate virtually. There are no floor brokers or any kind of central location in these marketplaces. A network of dealers using computers and telecommunications facilitates trading. Historically, all "second tier" equities traded on various exchanges, whereas the biggest corporations were only listed on the NYSE. All of this was altered by the late-90s tech boom; now, the Nasdaq is home to a number of significant tech giants, including Microsoft, Cisco, Intel, Dell, and Oracle. As a result, the Nasdaq is now a significant rival to the NYSE. Brokerages serve as "market makers" for different equities on the Nasdaq. A market maker offers ongoing bid and ask prices for the shares for the shares that are assigned to form a market, within a predetermined percentage spread. They may directly connect buyers and sellers, but often they will keep a stock of shares to suit investor demand. 
Other ExchangesAmerican Stock Exchange is the third-largest exchange in the United States (AMEX). The Nasdaq now serves as the NYSE's replacement for the AMEX, which once served as a substitute. The parent organisation of Nasdaq, the National Association of Securities Dealers (NASD), actually acquired the AMEX in 1998. Small-cap stocks and derivatives currently account for the majority of trading on the AMEX. There are several stock exchanges spread throughout almost every nation in the world. Although the US market is unquestionably the biggest and most significant, global investments still account for a small portion of it. The London Stock Exchange is located in London, while the Hong Kong Stock Exchange is located in Hong Kong. These are the two other major financial centres. 
The bulletin board located outside of the store is the final location worth highlighting (OTCBB). Although the Nasdaq legally qualifies as an over-the-counter market, the phrase is typically used to describe smaller public businesses that don't fulfil the listing requirements of any of the regulated exchanges, including the Nasdaq. Because of the little or non-existent regulation, penny stocks are found on the OTCBB. This makes purchasing OTCBB stock highly appealing and risky as well. BottomlineA stock represents a portion of an organization's equity. It differs from a bond, which functions more like a loan provided to the corporation by creditors in exchange for regular payments. When a firm wants to finance new initiatives or grow its operations, it issues stock to attract funds from investors. The privileges and rights of ownership are determined by the kind of stock, ordinary or preferred, that a shareholder owns. Every investment carries some level of risk. Depending on the state of the market, the value of stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds may decrease. Choosing what to do with their financial resources is a decision they make while investing. Because of market circumstances or corporate choices, including whether to grow into a new industry or combine with another firm, their investment value may increase or decrease. In the past, equities have consistently outperformed the majority of alternative assets over the long term. 
A stock grants a minor ownership stake in a firm to the investor, and the returns on the stock are often depending on the company's success. Stock investing is a popular technique for people to increase their own wealth. There are no promises, though. Investors in a public company's shares are likely to lose money whenever it fails. But, the fewer stocks you buy, the less likely it is that one poor stock choice would cause your portfolio to suffer significantly.
Next TopicStrategy Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










