Difference between Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmission
Before starting the topic difference between synchronous and asynchronous transmission, you must know about the transmission. The action of transferring data or anything from one place to other is referred to as transmission. It is a method of sharing data between two devices linked by a network, also known as communication mode. Synchronous and asynchronous transmissions are the two main types of transmission used in computer networking.
In both synchronous and asynchronous transmission, data is sent between the transmitter and the receiver based on a clock pulse utilized for synchronization. These serial data transmission techniques are both known as synchronous transmission.
In this article, you will learn about the difference between Synchronous and Asynchronous transmission. But before discussing the differences, you must know about Synchronous and Asynchronous transmission with their advantages and disadvantages.
What is Synchronous Transmission?
Synchronous transmission is an effective and dependable method of sending huge amounts of data. The data travels in a full-duplex method in the type of frames or blocks in Synchronous Transmission. The transmitter and receiver must be synced so that the sender knows where to start the new byte. As a result, every data block is marked with synchronization characters, and the receiving device obtains the data until a certain ending character is found.
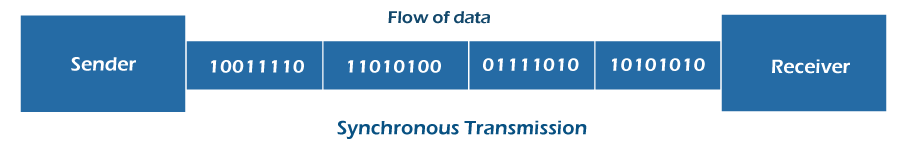
It also allows connected devices to interact in real time. Synchronous transmission can be seen in chat rooms, video conferencing, telephonic talks, and face-to-face interactions. It utilizes the broad-band and voice band channels because they enable quicker speeds of up to 1200 bps and meet the objective of high data transfer speed.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Synchronous Transmission
There are various advantages and disadvantages of synchronous transmission. Some advantages and disadvantages of synchronous transmission are as follows:
Advantages
- It aids the user in transferring a huge amount of data.
- Every byte is sent without a pause before the next.
- It also helps to reduce timing errors.
- It allows connected devices to communicate in real-time.
Disadvantages
- The sender and receiver must operate at the same clock frequency simultaneously.
- The accuracy of the received data is determined by the receiver's capacity to count the received bits precisely.
What is Asynchronous Transmission?
Asynchronous transmission is also referred to as start and stop transmission. It sends data from the transmitter to the receiver using the flow control approach and synchronizes data between the source and destination without utilizing a clock.
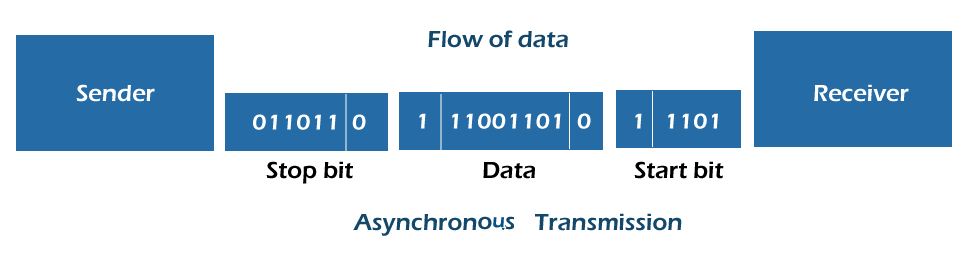
This transmission technique sends 8 bits or one letter at a time. In this system, each character transmits the start bit before the transmission process begins, and it also transmits the stop bit when the character is sent. The total number of bits is 10, including the character, start, and stop bits.
It employs character-based synchronization for the receiving terminal to synchronize with receiving data on a character. It is easy, quick, and inexpensive and doesn't need two-way communication. Asynchronous transmission is demonstrated via letters, televisions, emails, forums, and radios.
Asynchronous transmission makes use of voice-band channels that are narrow and operate at a slower speed. In this case, the transmitting device operates manually or intermittently.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Asynchronous Transmission
There are various advantages and disadvantages of Asynchronous transmission. Some advantages and disadvantages of Asynchronous transmission are as follows:
Advantages
- It doesn't require synchronizing the receiver and transmitter.
- It is a very flexible technique of data transmission.
- This kind of transmission is simple to implement.
- It allows users to send signals from sources with varying bit rates.
- When the data byte transmission is complete, the data transmission may be resumed.
Disadvantages
- The timing errors may occur because synchronization is difficult to determine.
- These bits could be mistakenly recognized due to the noise on the channel.
- The start and stop bits are extra bits that must be utilized in asynchronous transmission.
- It transmits information at a slower rate.
Key differences between Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmission
Here, you will learn about the key differences between Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmission. Some of the main differences between Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmission are as follows:
- A synchronous transmission is a form of transmission that enables synchronized communication by sharing a common clock pulse between the sender and the receiver. In contrast, an asynchronous transmission is a form of transmission in which the transmitter and receiver have their internal clocks and hence don't require an external common clock pulse.
- Data is transmitted as frames in synchronous transmission. In contrast, asynchronous transmission transmits data one byte at a time.
- In synchronous transmission, the amount of time between two successive broadcasts remains constant. In contrast, the time gap between two successive transmissions is random in asynchronous transmission.
- The data transfer rate of synchronous transmission is fast. In contrast, the data transfer rate of asynchronous transmission is slow.
- Synchronous transmission is complicated and costly. In contrast, asynchronous transmission is simple and cost-effective.
- Synchronous transmission is simple to design. In contrast, asynchronous transmission is both complex in nature and design.
- There is no gap between data in Synchronous transmission due to the common clock pulse. Whereas there is a gap between the data bytes in asynchronous transmission. It has start and end bits between which actual data is present.
- Local storage is not necessary for synchronous transmission at the terminal end. In contrast, local buffer storages are needed to construct blocks at both ends of the line in asynchronous transmission.
- In Synchronous Transmission, the voice-band and broad-band channels are primarily utilized. In contrast, asynchronous transfer is employed with voice-band channels that have a limited type.
Head-to-head comparison between Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmission
Here, you will learn the head-to-head comparisons between Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmission. The main differences between Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmission are as follows:
| Features |
Synchronous Transmission |
Asynchronous Transmission |
| Definition |
It is a type of transmission that enables synchronized communication by sharing a common clock pulse between the transmitter and the receiver. |
It is a form of transmission in which the transmitter and receiver have their own internal clocks and hence don't require an external common clock pulse. |
| Basic |
The transmission begins with the block header, which contains a bit sequence. |
It employs the start and stops bits to precede and follow a character. |
| Data Unit |
Data is transmitted as frames in synchronous transmission. |
It transmits data one byte at a specific time. |
| Storage |
It doesn't require any storage at the terminal end. |
The local buffer storages are needed to construct blocks at both ends of the line in asynchronous transmission. |
| Transmission speed |
The data transfer rate of synchronous transmission is fast. |
The data transfer rate is slow. |
| Cost |
It is complicated and costly. |
It is simple and cost-effective. |
| Gap between the data |
There is no gap between data in Synchronous transmission due to the common clock pulse. |
There is a gap between the data bytes, and it has start and end bits between which actual data is present. |
| Implementation |
It is implemented by hardware and software. |
It is only implemented by hardware. |
| Time interval |
The time delay between two transmissions is constant. |
The time delay between two transmissions is random. |
| Bits |
The start and stop bits are not utilized in data transmission. |
The start and stop bits are used to transmit data with additional overhead. |
| Synchronized clocks |
It doesn't require any synchronized clocks. |
It needs synchronized clocks at both ends. |
| Complexity |
It is simple and easy to design. |
It is complex to design. |
| Band Channels |
It mainly uses both voice-band and broad-band channels. |
It mainly uses voice-band channels that have a limited type. |
| Examples |
Some examples of synchronous transmission are Video Conferencing, Chat Rooms, and Telephonic Conversations. |
Some examples of asynchronous transmission are emails, letters, forums, etc. |
Conclusion
Both synchronous and asynchronous transmission has some benefits and drawbacks. Asynchronous transmission is easy and inexpensive for sending small amounts of data.
In contrast, synchronous transmission is utilized to transfer most of the data because it is more efficient and has less overhead. As a result, the conclusion is that data transfer requires both synchronous and asynchronous transmission.
|



 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










