Table Per Concrete class using xml file
In case of Table Per Concrete class, there will be three tables in the database having no relations to each other.
There are two ways to map the table with table per concrete class strategy.
- By union-subclass element
- By self creating the table for each class
Let's understand what hierarchy we are going to map.
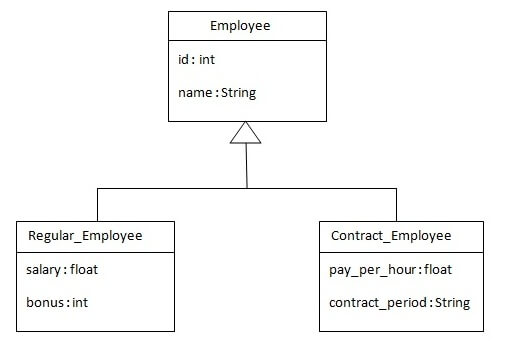
Let's see how can we map this hierarchy by union-subclass element:
| In case of table per concrete class, there will be three tables in the database, each representing a particular class. |
| The union-subclass subelement of class, specifies the subclass. It adds the columns of parent table into this table. In other words, it is working as a union. |
| The table structure for each table will be as follows: |
Table structure for Employee class
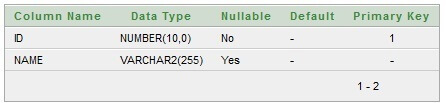
Table structure for Regular_Employee class
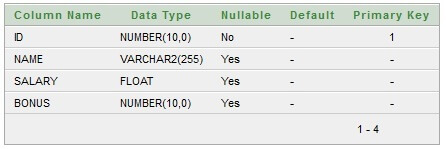
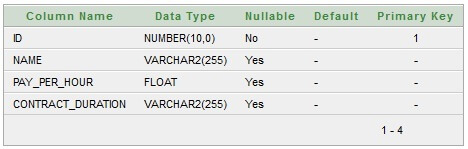
Table structure for Contract_Employee class
Example of Table per concrete class
In this example we are creating the three classes and provide mapping of these classes in the employee.hbm.xml file.
1) Create the Persistent classes
You need to create the persistent classes representing the inheritance. Let's create the three classes for the above hierarchy:
File: Employee.java
File: Regular_Employee.java
File: Contract_Employee.java
2) Create the mapping file for Persistent class
The mapping has been discussed above for the hierarchy.
File: employee.hbm.xml
3) Add mapping of hbm file in configuration file
Open the hibernate.cgf.xml file, and add an entry of mapping resource like this:
Now the configuration file will look like this:
File: hibernate.cfg.xml
The hbm2ddl.auto property is defined for creating automatic table in the database.
4) Create the class that stores the persistent object
In this class, we are simply storing the employee objects in the database.
File: StoreData.java
|  For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now





