Tableau Data JoiningData joining is a common requirement in any data analysis. You may need to join data from different tables in a single source or join data from multiple sources. Tableau provides the feature to join the tables by using the data pane that is available in the Data menu. A join means combining columns from one or more tables in a relational database. It also creates a set that can be saved as a table, or it can be used as it is. Joins are specifies into five types:
Overview of Types of JoinsA join section is used to combine rows from two or more tables, based on a related column between them. 1. Cross Join: Cross join produces rows which combine each row from the first table with each row from the second table. 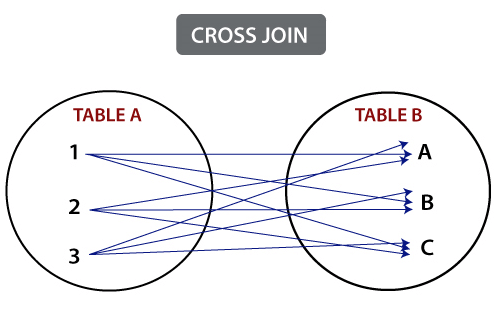
2. Inner Join: An inner join returns the matching rows from the tables that are being joined. 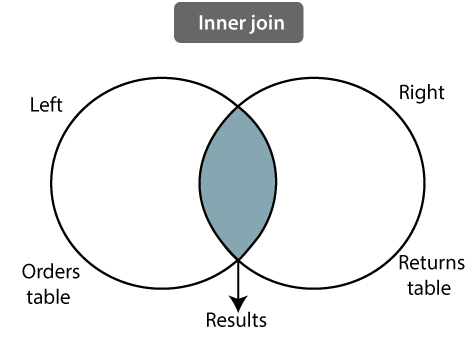
3. Natural Join: Natural join is not used any comparison operator. It does not concatenate the way. Only we can perform a Natural Join if there is at least one common attribute that exists between two relations. Also, the attributes must have the same name and domain. Natural join works on those matching attributes where the values of attributes in both the relation are same. 4. Outer Join: An outer join is an extended form of the inner join. It returns both matching and non-matching rows for the tables that are being joined. Types of outer joins are as follows: i) Left Outer Join: The left outer join returns matching rows from the tables being joined, and also non-matching rows from the left table in the result and places NULL values in the attributes that come from the right table. 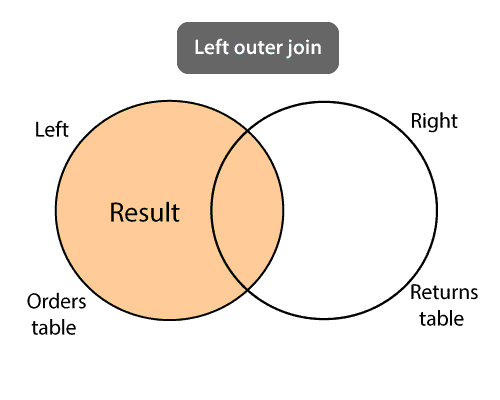
ii. Right Outer Join: The right outer join operation returns matching rows from the tables being joined, and also non-matching rows from the right table in the result and places NULL values in the attributes that come from the left table. 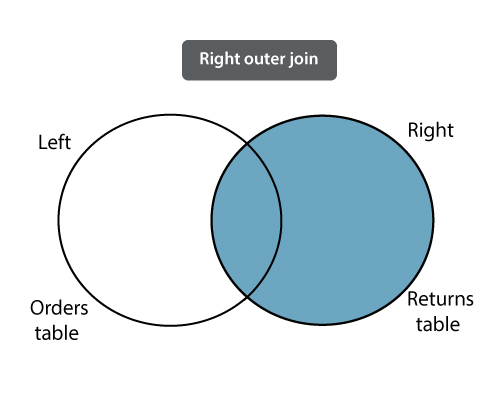
iii. Full Outer Join: The full outer join is used to combine tables. As a result, it contains all values from both tables. When a value from a table doesn't have a match with the other table, then it returns a NULL value in the data grid. 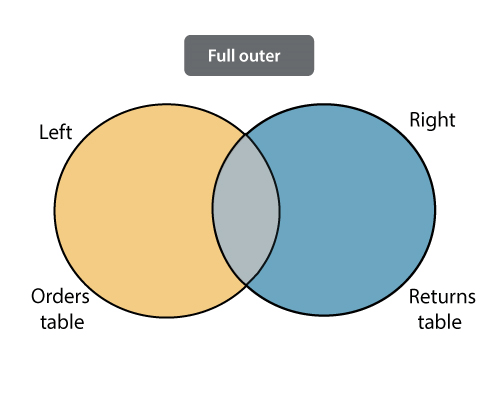
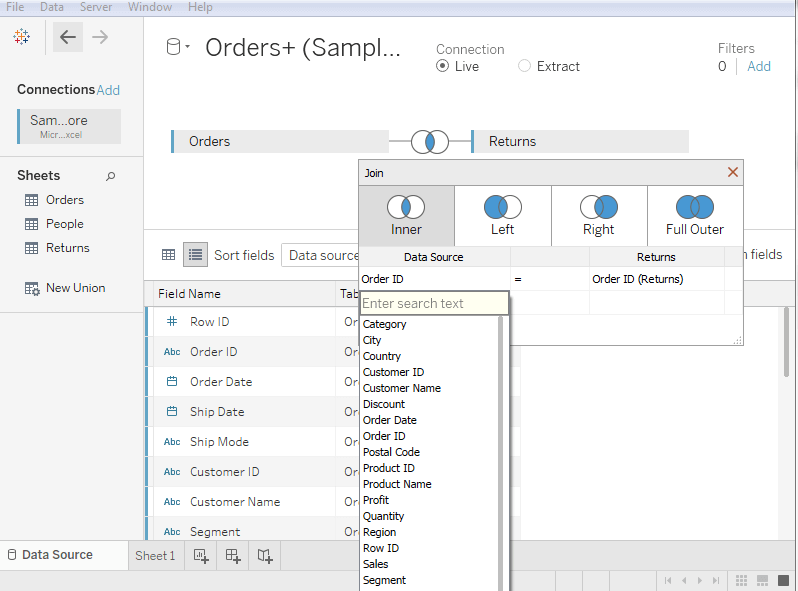
5. Self-Join: The self-join is used to join a table with itself. It means that each row of the table is combined with itself as well as with every other row of the table. Creating a Join in TableauLet's assume a data source Sample-superstore to create a join between two tables such as Orders and Returns.
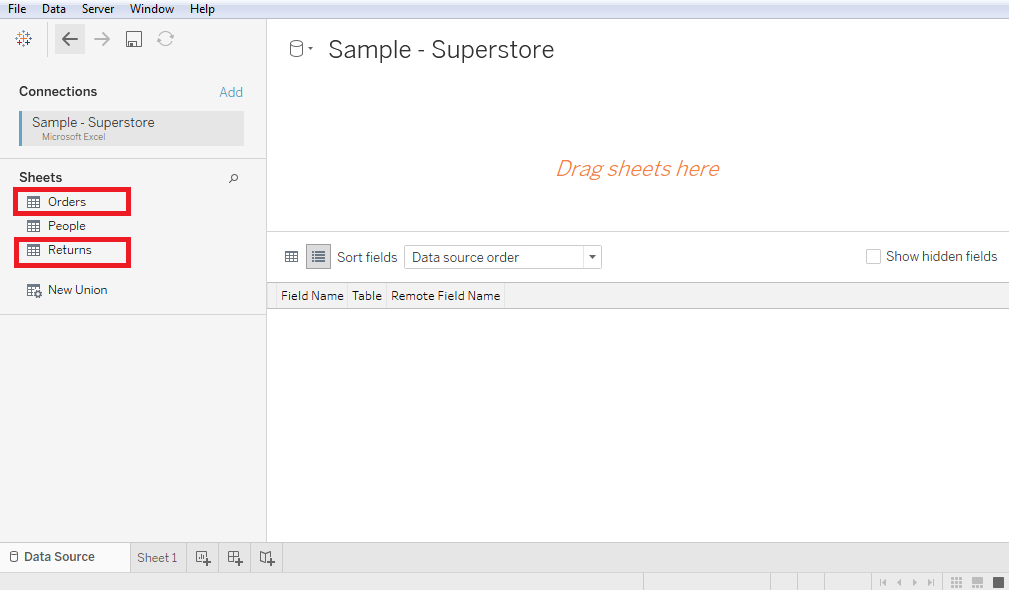
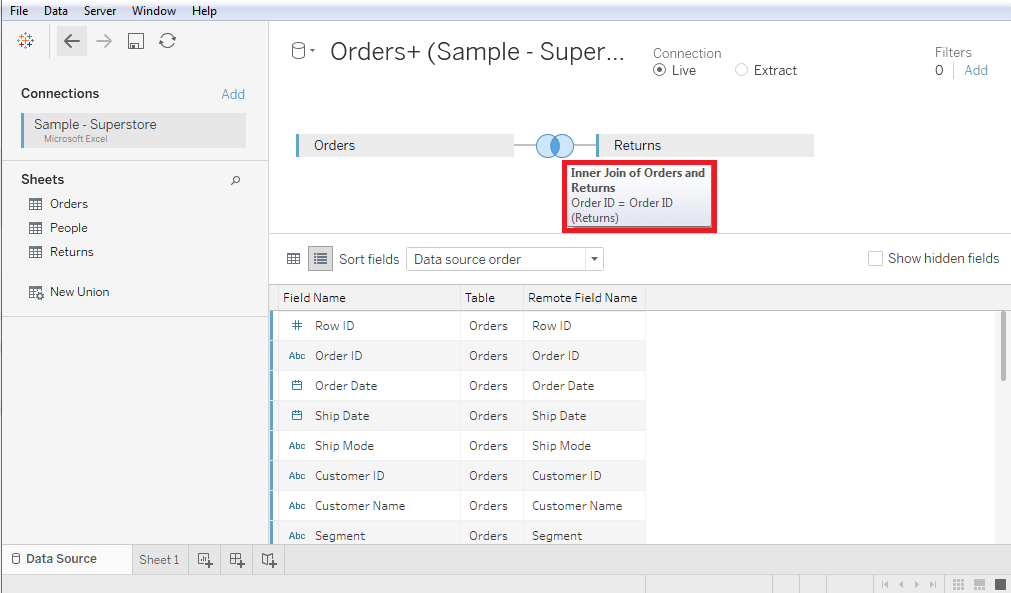
Edit a Join Type in TableauTableau automatically creates a type of join between two tables, but it can be changed as per need.
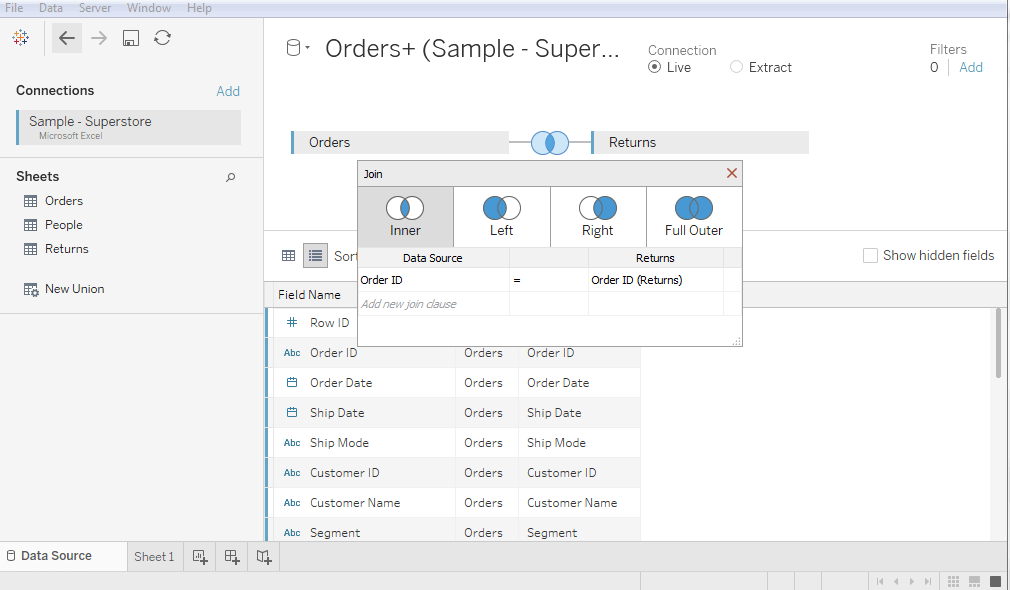
How to Edit Join Fields in Tableau
Next TopicData Blending in Tableau
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










