Tax DefinitionA tax is a compulsory payment or charge that local, state, and federal governments levy on citizens and corporations to fund essential public goods, services, and operations. A tax may be levied in a number of different ways, including a tax on gifts, income, imports, property values, and estates. A high tax on cigarettes, for instance, is applied to deter people from purchasing them. Taxes may be intended to affect consumer behavior. In 3000-2800 BC, the first recorded taxes were enacted in ancient Egypt. Non-compliance with the law, including tax evasion or resistance, is punished by a fine or other punishment for late payments. 
A tax demands that a portion of the taxpayer's income or funds be withheld and given to the government. It is required to pay taxes at the rates set by the government, and it is illegal to intentionally underpay taxes, which is known as tax evasion. Tax avoidance, on the other hand-actions designed to reduce your tax burden and increase your after-tax income-is completely lawful. History of TaxAlthough opinions about what constitutes good tax policy have an impact on the selection and design of tax codes, administrative reasons may mainly account for historical patterns of taxation. For instance, import charges were among the first taxes because they were simpler to impose on imported goods than on domestic produce. Similar to how the straightforward turnover tax (assessed on gross sales) predominated before the introduction of the economically better but administratively more onerous VAT (which allows credit for tax paid on purchases). Real estate can be more easily identified, valued, and taxed than other types of assets. A head tax is even simpler to enact. So, it is not surprising that land and head taxes were the first direct levies. Despite the lengthy history of taxes, it had a very limited impact on ancient society. Consumption taxes were imposed in ancient Greece and Rome. When it came to the generation of revenue, tariffs, which are taxes on imported commodities, were frequently far more significant than internal excises. Property taxes would be levied briefly during times of war as a way to raise more revenue. These taxes were initially only applicable to real estate, but they were eventually expanded to cover other assets. Transactions involving real estate were also taxed. In Greece, free citizens and slaves were subject to various tax duties, while under the Roman Empire, nationals and inhabitants of conquered lands were treated differently under the tax code. Types of TaxIndividuals, businesses, and organizations of all kinds are all required to pay the appropriate taxes in a variety of ways. Depending on how they are paid to the taxing authorities, these taxes are further divided into direct and indirect taxes. These taxes are implemented in different ways. Certain taxes, such as the dreaded income tax, corporation tax, wealth tax, etc., are paid directly by the taxpayer, while others are paid in another way, such as sales tax, service tax, value-added tax, etc. Some of the key taxes the government imposes on Indian nationals are listed here: 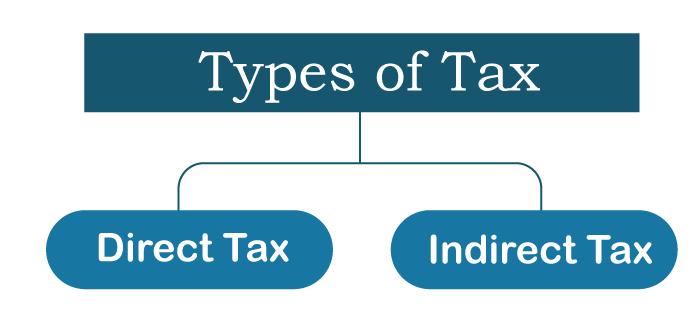
Direct TaxAs mentioned earlier, Direct Tax are those types of tax which are paid directly by the citizens to the government. Such taxes are imposed by the government directly on a person or an organization, and they cannot be transferred to another person or organization. The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), which is overseen by the Department of Revenue, is the only such federation that just that looks after direct taxes. The CBDT has the support of multiple statutes that oversee various parts of direct taxes to help it with its feeling of responsibility. The following taxes are subdivided further into direct taxes. 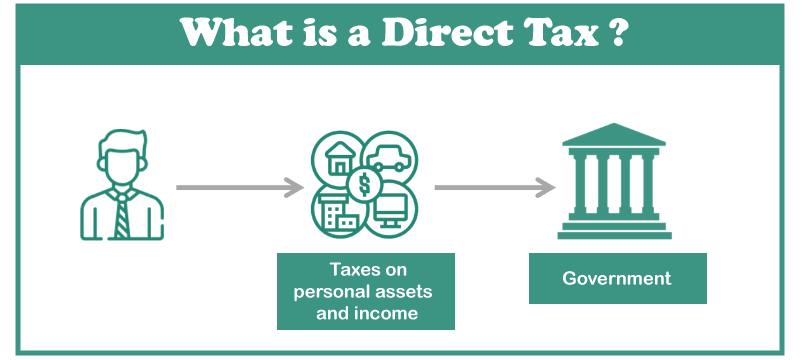
Income Tax One of the most common and least implicit taxes is the income tax. This type of tax is levied on your income once a year. Income tax has many different aspects, including taxable income, income reduction, tax slabs, tax deducted at source (TDS), and more. This tax affects both businesses and people. According to the tax bracket a person falls into, they must pay a certain amount toward taxes. This tax slab, which ranges from no tax for lower income groups to 30 percent for higher income groups, determines how much tax an individual must pay based on their yearly income. For distinct groups of individuals, including very senior citizens (those over 80 years old), senior citizens (those between 60 and 80 years old), and regular taxpayers, the Indian government has established numerous tax slabs. Capital Gain Tax One must pay capital gains tax anytime he/she get a significant amount of money. It could come through an investment or the sales of any type of property. Generally speaking, there are two categories of capital gains:
Long-term capital gains from investments held for more than 36 months and short-term capital gains from investments held for less than 36 months. While the long-term capital gains tax is 20% and the short-term capital gains tax is based on the income category someone fall into, the taxes that apply to each of them are also different. The intriguing aspect about capital gains tax is that profits are not necessarily have to be in monetary form. Another possibility is barter in kind, in which case the value of the deal would be taken into account for tax purposes. Securities Transaction Tax Knowing how to trade stocks properly, exchange securities, and remain still while making a sizable profit is not a difficult task. Although having its own tax known as the Securities Transaction Tax, this source of revenue is also abundant. How is that tax collected? This tax is imposed by adding the tax to the share price. This implies that you pay this tax each time you buy or sell a share. This is attached to each and every security traded on the Indian Stock Exchange. 
Perquisite Tax The term "perquisites" refers to all the benefits and privileges that employers may bestow onto their staff. Individuals may be granted a car or a house by the firm as part of these civic privileges. These benefits can also include reimbursement for items like phone bills or petrol, so they are not only limited to large rewards like houses or automobiles. The method through which the employer receives the benefit and the employee utilizes it is used to determine how much perquisite tax is due. When it comes to vehicles, it's possible that the employee receives a car from the company, and that car is used for both work and personal purposes, making the employee eligible for the tax, while the car used just for work is not. Corporate Tax A corporation tax is the amount of income tax that a business pays from the revenue it generates. In order to determine how much tax must be paid, the corporation tax also has its own slab. According to the corporation tax, which is imposed on both local and international enterprises, the company's revenue is considered differently from the shareholder's dividend. Indirect TaxIndirect taxes are those imposed on products and services. They vary from direct taxes in that they are levied on things instead of people, who then pay the intermediary, who is the person selling the commodity, to collect them. Direct taxes are levied on people, who pay the Indian government directly for the services rendered. Sales taxes, taxes on imported goods, value-added taxes (VAT), and other such levies are the most insignificant forms of indirect taxes. These taxes are enforced by adding them to the value of the good or service that will probably increase the cost of the good. Indirect taxes are separated into a number of additional taxes, some of which are included here. 
Sales Tax Sales tax refers to any tax levied on the purchase of any good. Any item made in India or imported from outside can be considered a "product," and services can also be included. Sales taxes are collected on the person who sells the goods, who then passes them on to the person who purchases it, with the price of the product being adjusted to include the tax. The limitation of this tax is that it is only applicable to a certain product, therefore if that thing is resold, the seller cannot charge sales tax on it. Basically, a sales tax that is exclusive to each state in India is levied according to its own Sales Tax Legislation. In certain states, there are also extra fees like as purchase taxes, turnover taxes, works transaction taxes, and similar taxes. This is also one of the factors that made sales tax one of the major sources of income for many state governments. Also, the state and federal governments each charge a sales tax. Service Tax Similar to sales tax, service tax is added to the cost of goods supplied in the nation. It is not assessed on commodities but rather on the businesses that provide services, and it is gathered either once every three months or once a month depending on how services are delivered. If the business is a sole proprietorship, service tax is only paid once the client has settled the invoices. For businesses, the service tax must be paid regardless of whether the client pays the amount at the time the invoice is produced. It's important to keep in mind that determining who is liable for service tax can be challenging because the service provided at restaurants combines the use of the restaurant's facilities, the wait staff, and the food. There was a pronouncement made that restaurants will collect service tax on 40% of the entire cost in order to eliminate haziness in this respect. GST (Goods and Services Tax) Since the market started opening up 25 years ago, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) has undergone the largest revision to India's indirect tax system. Because it is based on consumption and is imposed where the consumption occurs, the goods and services tax is indeed a consumption-based tax. Every step of the supply chain's consumption of value-added services and commodities is subject to the GST. The GST charged on the purchase of the goods and services can be offset against the GST chargeable on the delivery of the goods and services. The seller must pay the GST at the appropriate rate in order to redeem the GST, however he may do so using the tax credit method. Value Added Tax Value Added Tax (VAT), often known as commercial tax, is not applicable to goods that are zero-rated for food and essential medicines or those that are exported. Manufacturers, dealers, distributors, and end users are all subject to VAT at every stage of the supply chain. The VAT was a levy levied on the country's state governments' discretion. When it was announced, not all states implemented it. A variety of commodities sold inside the state are subject to the VAT, and the tax's level was set by the state. Customs Duty and Octroi One must pay a fee termed as the customs tax when they purchase anything that must be imported from another country. It is applicable to all goods that arrive by air, sea, or land. Despite the fact it is possible to purchase goods in India that have been imported from other nations, a customs tax will be applied. In order to ensure that imported items are taxed and paid for, customs duties are imposed. Similar to how customs duty ensures that commodities bound for other nations are taxed, Octroi is tasked with ensuring that items bound for Indian state boundaries are duly taxed. The state government imposes this tax and conducts business in a manner that is very similar. Excise Duty All manufactured or produced commodities in India are subject to a tax known as the excise duty. This tax, which is also known as the Central Value Added Tax or CENVAT, differs from customs duty in that it is solely applicable to goods manufactured in India. The government collects this tax from businesses that produce items as well as from organizations that buy manufactured commodities and hire individuals to carry them between businesses and recipients. According to the Central Excise Regulation created by the Central Government of India, anybody who creates "excisable goods or products" or stockpiles such items in a depot would be required to pay the duty that is applicable to those products. No excisable products, on which some duty is payable, shall be allowed to travel from any location where they are made or produced without paying the necessary duty payments under this plan. Tax IncomplianceThere is a distinct deadline or filing requirement for each sort of tax. Certain taxes, such as sales taxes or tariffs, are instantly collected at the moment of a transaction or in the days before one. Others have a predefined repeating calendar where the due date repeats on a certain day or day/month combination (i.e., property taxes being due the first day of April). For the same types of taxes, various governmental entities will have different deadlines (i.e., different counties will have different property tax due dates). There are several penalties that might be charged for failing to pay the correct amount of tax to the taxation authorities. These are some examples of possible tax penalties for the different taxes stated above:
In a NutshellFor the majority of governments, taxes are their main source of income. This money is used to support public services like education, emergency services, and social programs, as well as to maintain and enhance public infrastructure like the roads we use every day. The government levies taxes on its citizens in order to boost the national economy, enhance living conditions for citizens, and generate funds for economic development programs. Our government is able to raise taxes since the Indian Constitution only provides the central and state governments the authority to do so. An authorizing law that has been adopted by the State Legislature or the Parliament must support all domestic taxes.
Next TopicTaxonomy Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










